subgenus Pinus, section Trifoliae (Duhamel), subsection Sabinianae (Loudon).

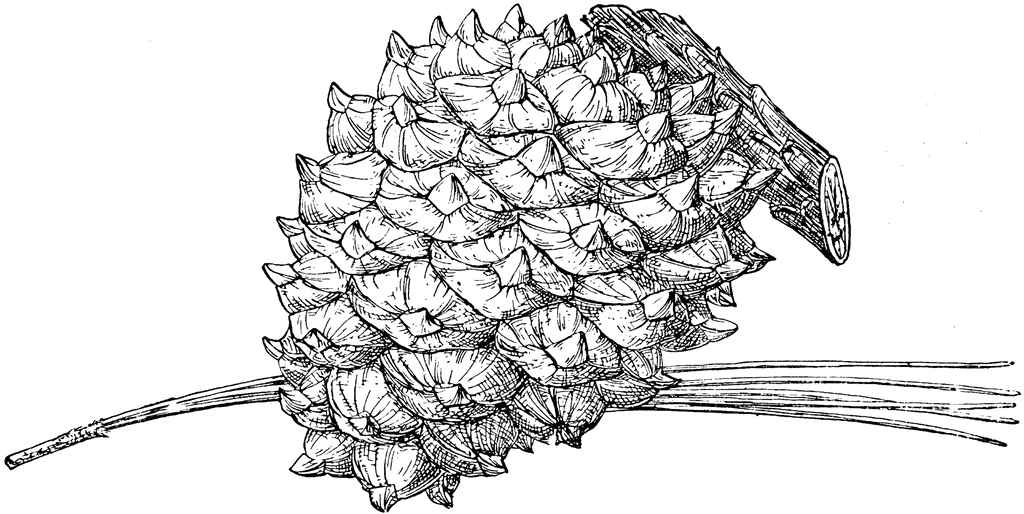
Pinus torreyana, as described in 1855 by Charles Christopher Parry (1823-1890) ex Elie-Abel Carrière (1818-1896), in Traité Général des Conifères, is commonly known as Torrey pine, or Soledad, lone or Del Mar pine. The species name honors John Torrey (1796 - 1873), the American botanist to whom Charles Perry sent the original herbarium specimens with accompanying descriptions for publication.
Ethnobotany. The pine nuts were an important food for the Kumeyaay tribe and the Chumash nations of indigenous American people. Pinus torreyana has been considered as a plantation tree for forestry use in Australia, New Zealand and Kenya. Under cultivation, on richer soils with higher rainfall or supplemental irrigation, the Torrey pine is capable of fast growth to a large size.
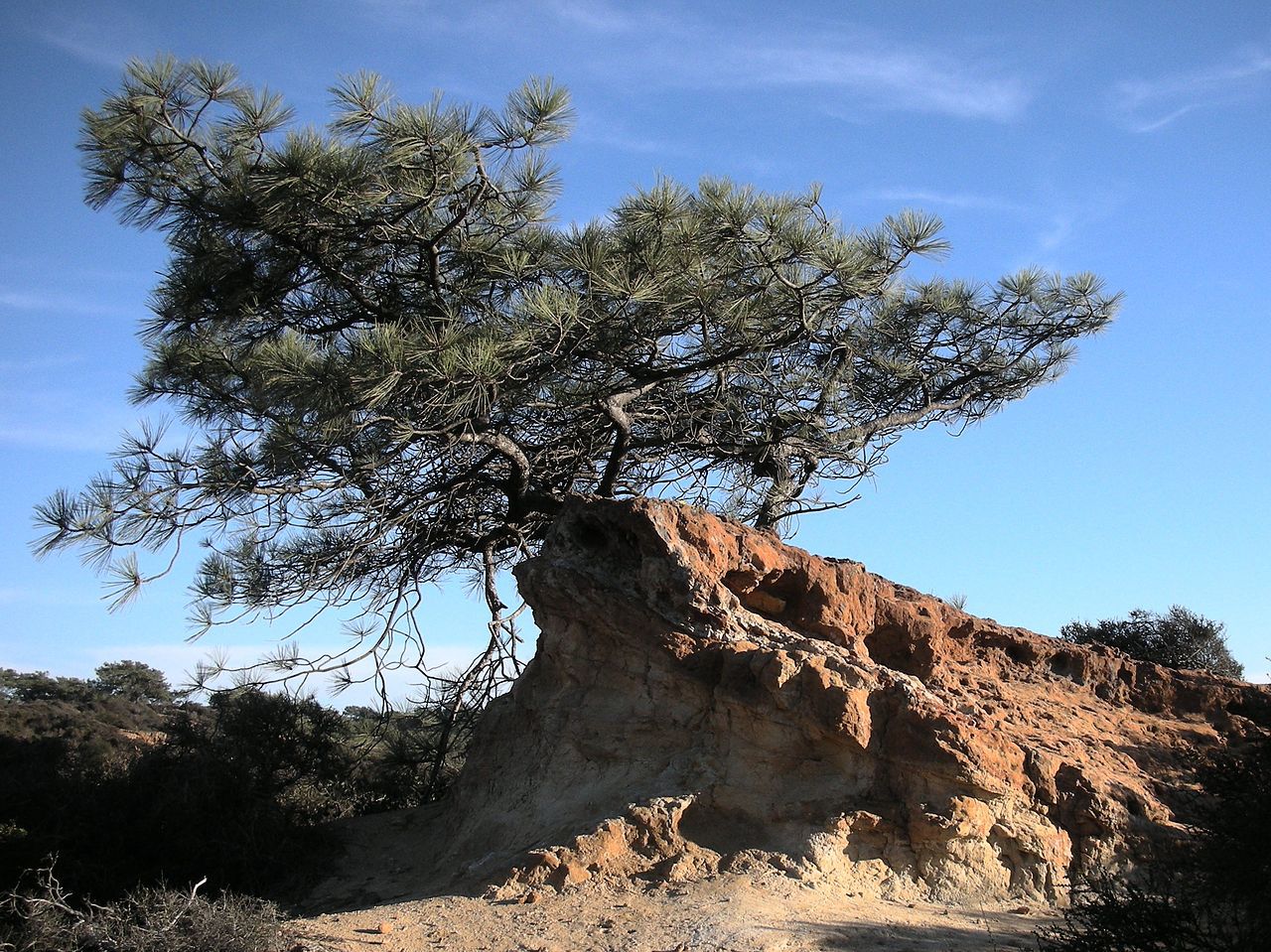
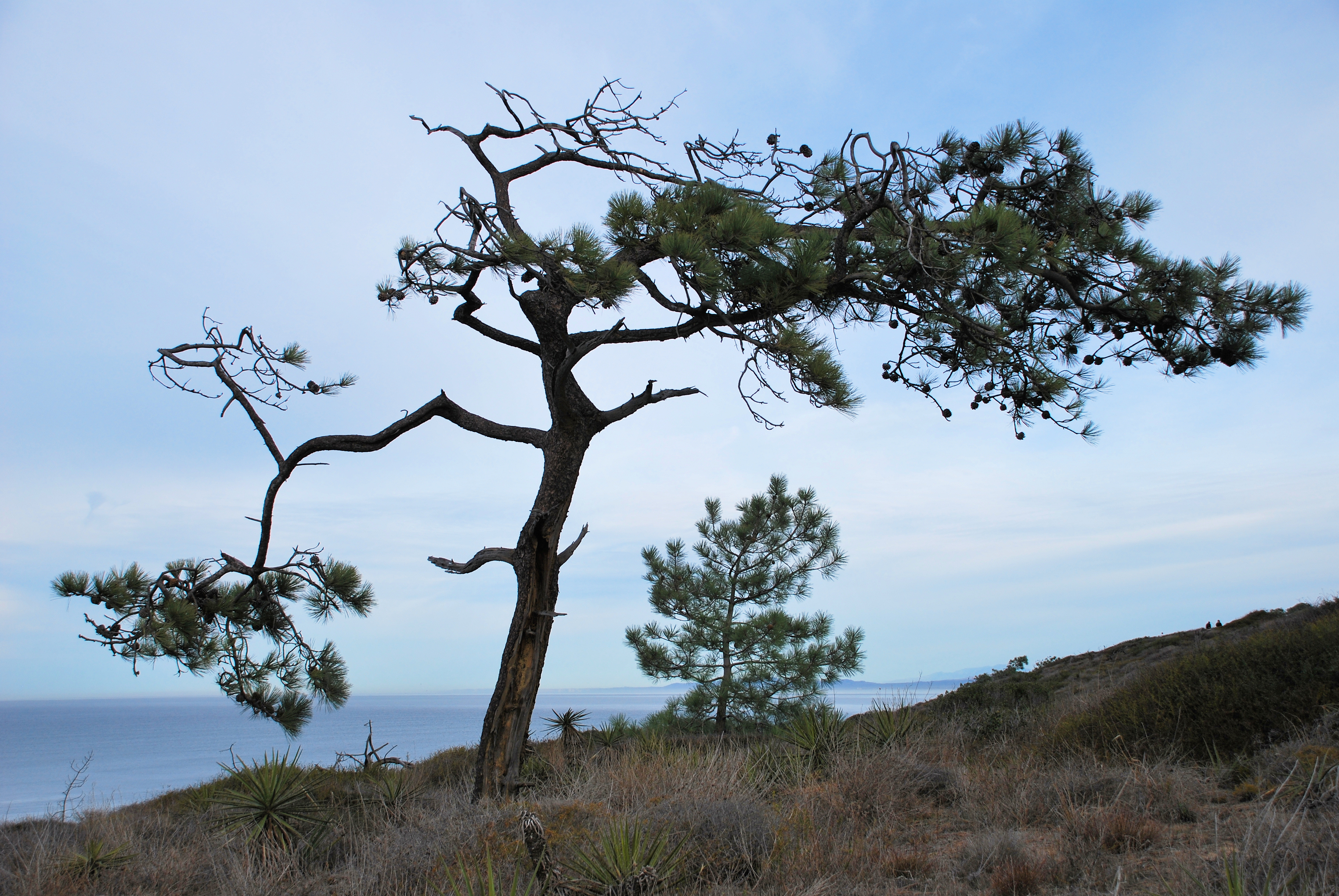
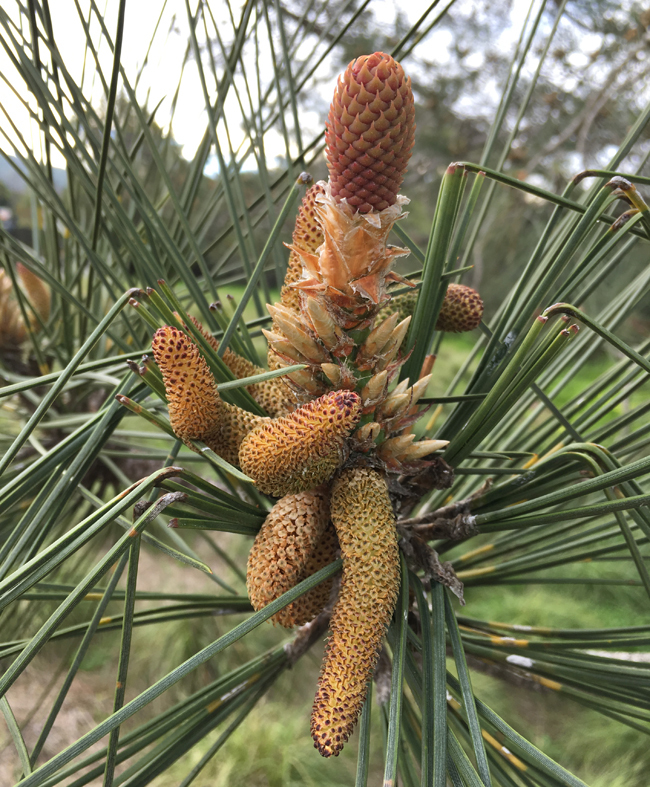
Description. Torrey pine is an evergreen, coniferous species of tree that grows to mature heights of 50 feet (15 m) with a naturally crooked and leaning trunk up to 40 inches (100 cm), in diameter, measured at breast height; but tall and straight in planted stands and ornamentals; crown is rounded to flattened and irregular.
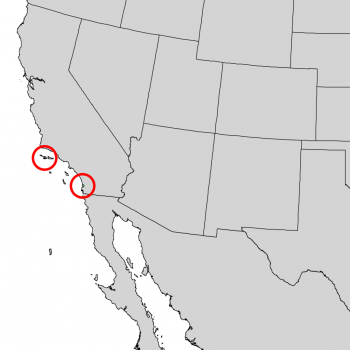
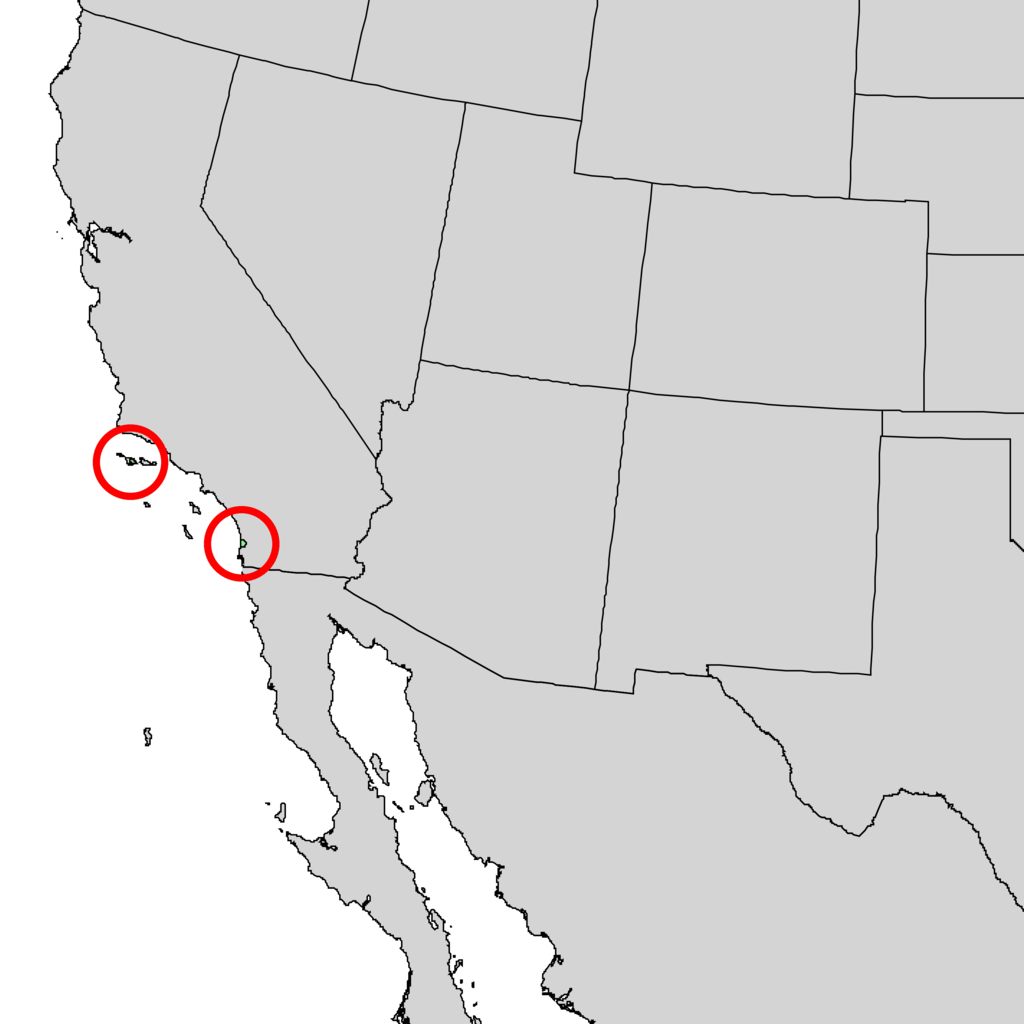
Distribution. This species is native to USA - California - the Pacific coast at Del Mar in San Diego County, and the east end of Santa Rosa Island with Channel Islands National Park, growing from immediately above the high tide mark to about 600 feet (180 m) above sea level on rocky or sandy slopes. On these sites it seems dependent on the daily fog that comes in from the ocean in the afternoon, mitigating the heat of the sun and the resulting excessive evapo-transpiration. It grows with a sparse chaparral and few other trees; in ravines sometimes accompanied by a few oaks (Quercus sp.) and Arbutus menziesii.
Hardy to USDA Zone 8 - cold hardiness limit between 10° and 20°F (-12.1° and -6.7°C).