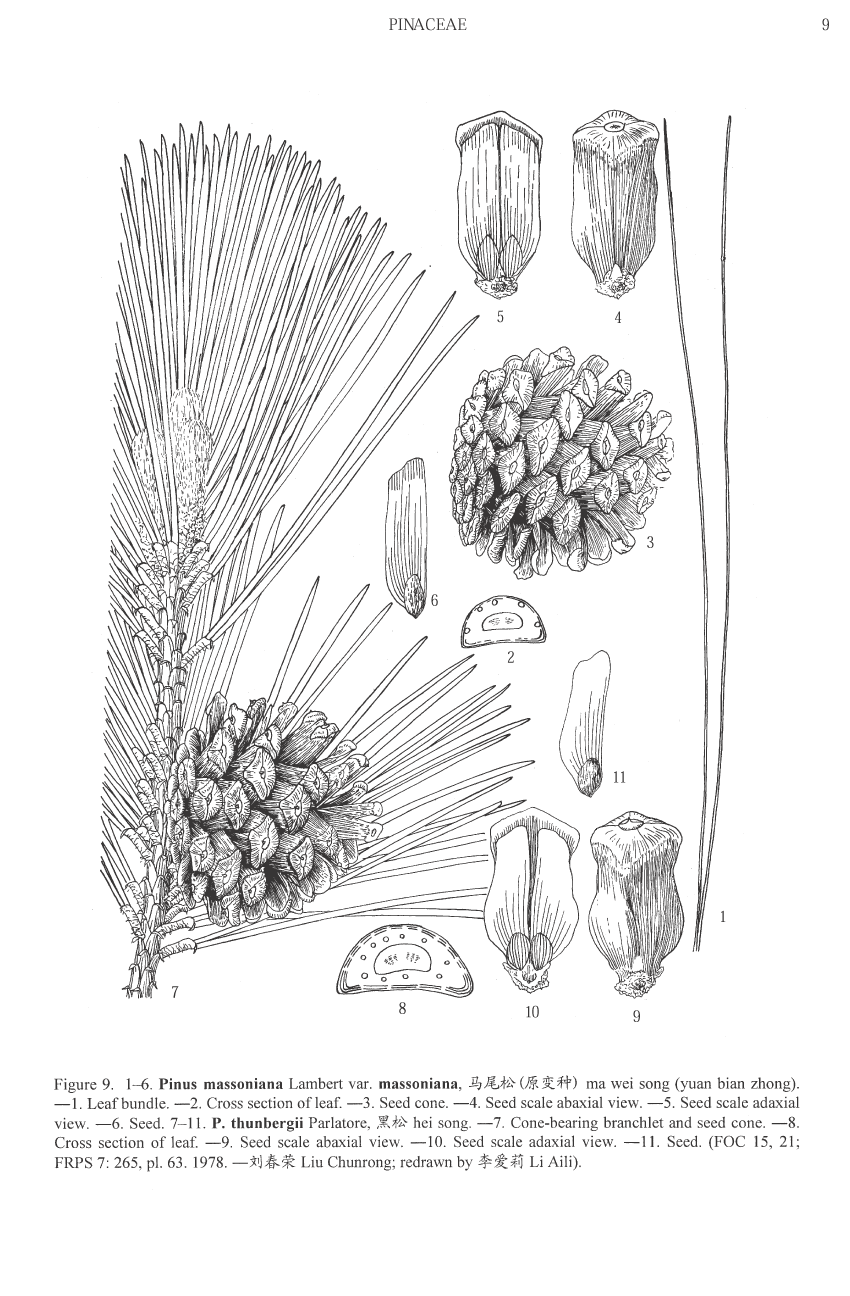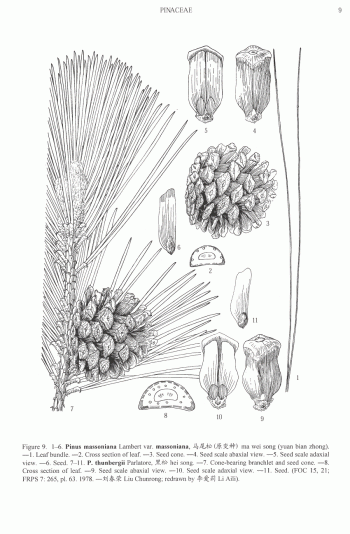
subgenus Pinus, section, Pinus, subsection Pinus. This is one of the 'œclassic' old-world, 2-needled, hard pines.
Pinus massoniana, first described in 1803 by Aylmer Bourke Lambert (1761-1842), is commonly known as Masson pine, Horsetail pine, or Chinese red pine; as well as 马Š°¾æ¾ (ma wei song) in the Chinese language and as Thông duôi ngua, or Thông tà u Vietnamese. The species honors Francis Masson (1741 - 1805), the first plant collector sent out by the Royal Botanic Gardens at Kew. Although Masson spent most of his time in South Africa, he is known at times, to have worked in China, and sent plant material to Alymer Lambert.
Ethnobotany. According to Forest Inventory and Planning Institute, this conifer's sapwood and heartwood are distinctive - heartwood is yellow-brown, coarsely veined, straight and light wood light (density 0.39-0.49). Used in construction, for mining poles, matches, ordinary furniture, boxes and underwater construction (on land, it is easily attacked by termites and insects). Wood contains 62% of cellulose and can be used for paper and artificial fibers. The resin is resource for industry and medicine.
Wu and Raven state that this is an important tree for afforestation in southern China. The timber is used for construction, railway sleepers, mine timber, furniture, wood pulp, etc., and the trunk as a source of resin and tannin, and for cultivating fungi.
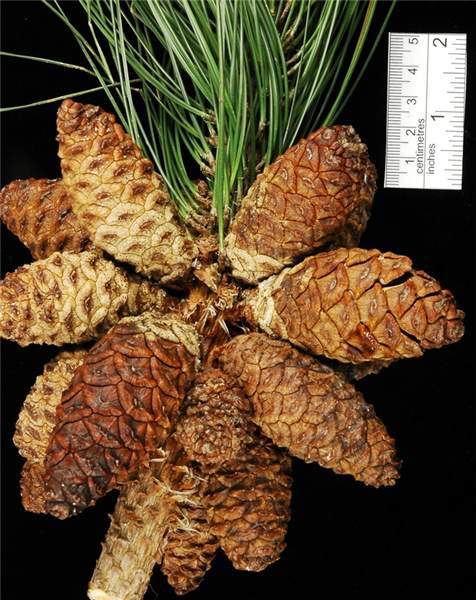
Description. Masson pine is an evergreen coniferous species of tree that grows to mature heights of 60 to 150 feet (18 - 45 m) with a crooked trunk up to 60 inches (150 cm) in diatmeter, measured at breast height, forming an irregular, usually broad head.
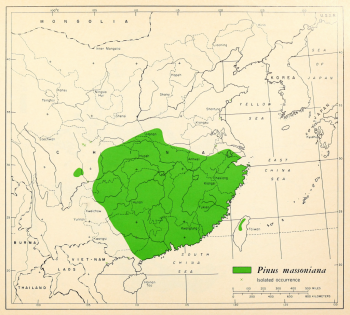
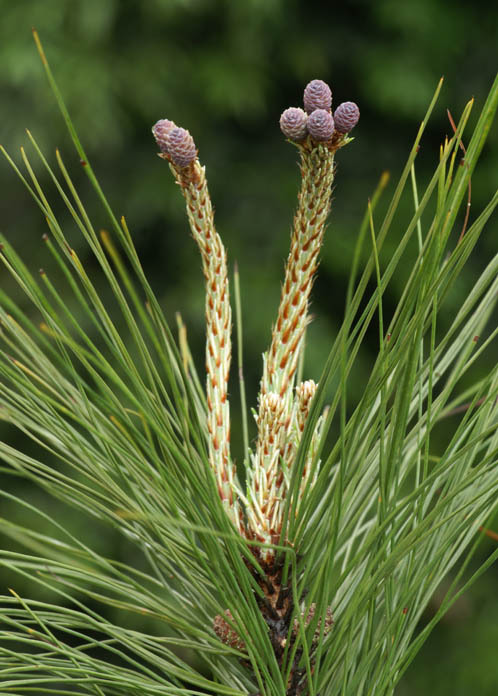
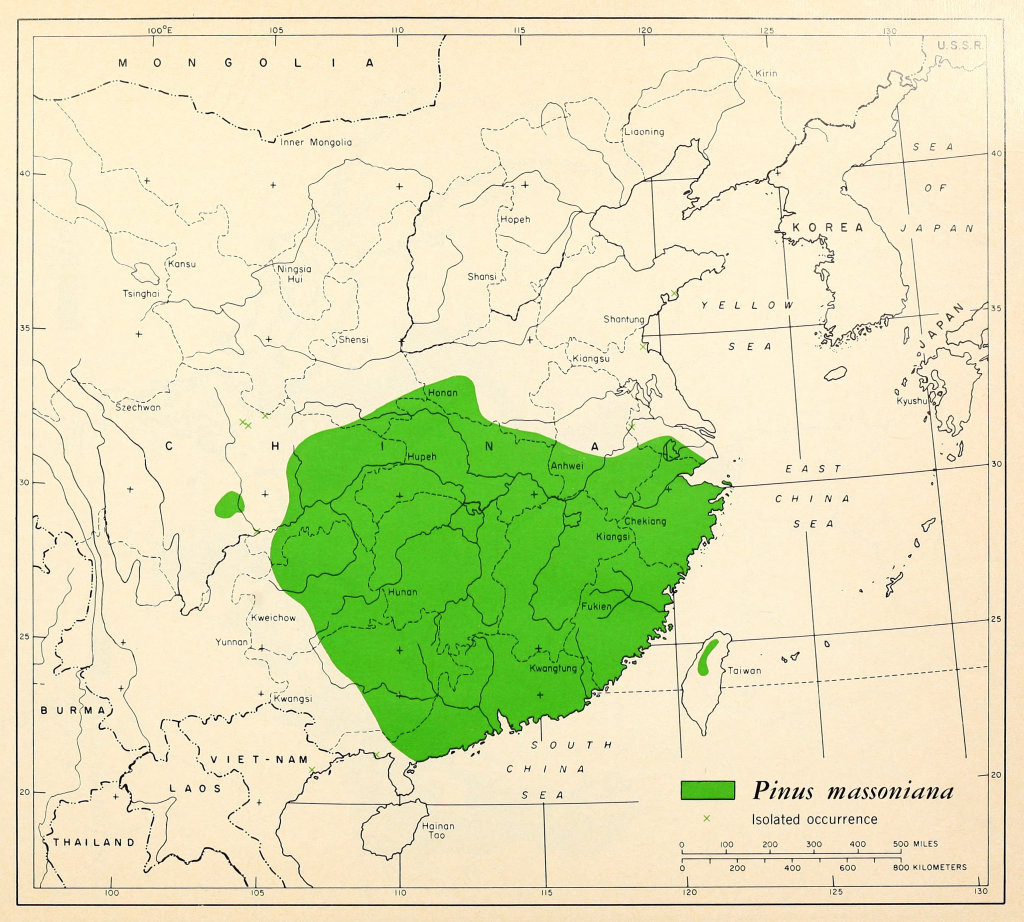
Distribution. This species is native to China - Anhui, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Guizhou, Hainan, western Henan, Hubei, Hunan, southern Jiangsu, Jiangxi, southeastern Shaanxi, Sichuan, Taiwan, eastern Yunnan, Zhejiang; occuring from plains to mountains, from near sea level to 6,000 feet (2,000 m) above sea level. It has been planted in some provinces of Vietnam, such as Ha Tay (Da Chong), Ha Bac (Phan Son), Thanh Hoa (Phu Dien) and Quang Ninh (Yen Lap). It is a light and humid-demanding tree that cannot tolerate shade. The root system is deep; growing on deep and well-drained soil but also met on poor soils and on bushy hills. Fast-growing at the first stage, later gradually slow-growing. Usually forming pure stands, or mix with other light-demanding tree species. Flowering in April, fruits mature in November-December of the following year.
Hardy to USDA Zone 7 - cold hardiness limit between 0° and 10°F (-17.7° and -12.2°C).