subgenus Strobus (Lemmon), section Quinquefoliae (Duhamel), subsection Strobus (Loudon).
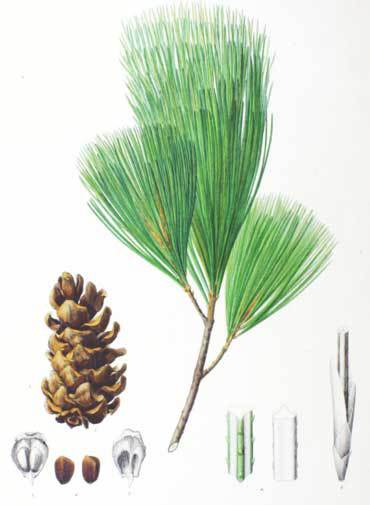
Pinus koraiensis, as described in 1842 by Philipp Franz von Siebold (1796-1866) and Joseph Gerhard Zuccarini (1790-1848) in Flora Japonica, 2nd edition, is commonly known as Korean pine; as well as 잣나무 (jasnamu / pine tree) in the Korean language; as ãƒãƒ§ã‚¦ã‚»ãƒ³ã‚´ãƒ¨ã‚¦ (Chosen goyo, Chosen-matsu) in Japanese; as çº¢æ¾ (Hóng sŠng) in Chinese; and as КоÑ'ейÑкий кедÑ' (Koreyskiy kedr) in Russian. Its seeds are extensively harvested and sold as pine nuts, particularly in northeastern China; it is the most widely traded pine nut in international commerce. The nut oil contains 11.5% of the unusual fatty acid pinolenic acid.
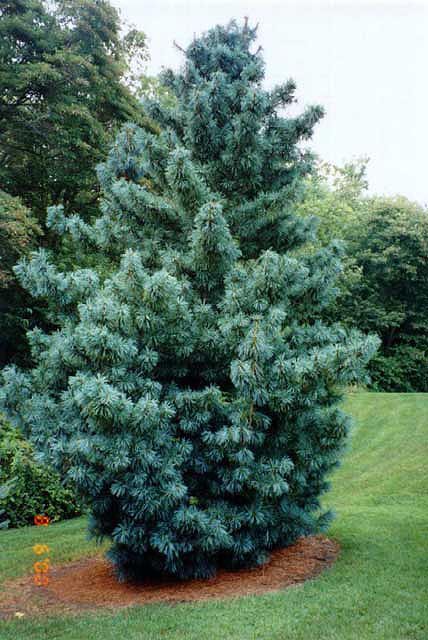
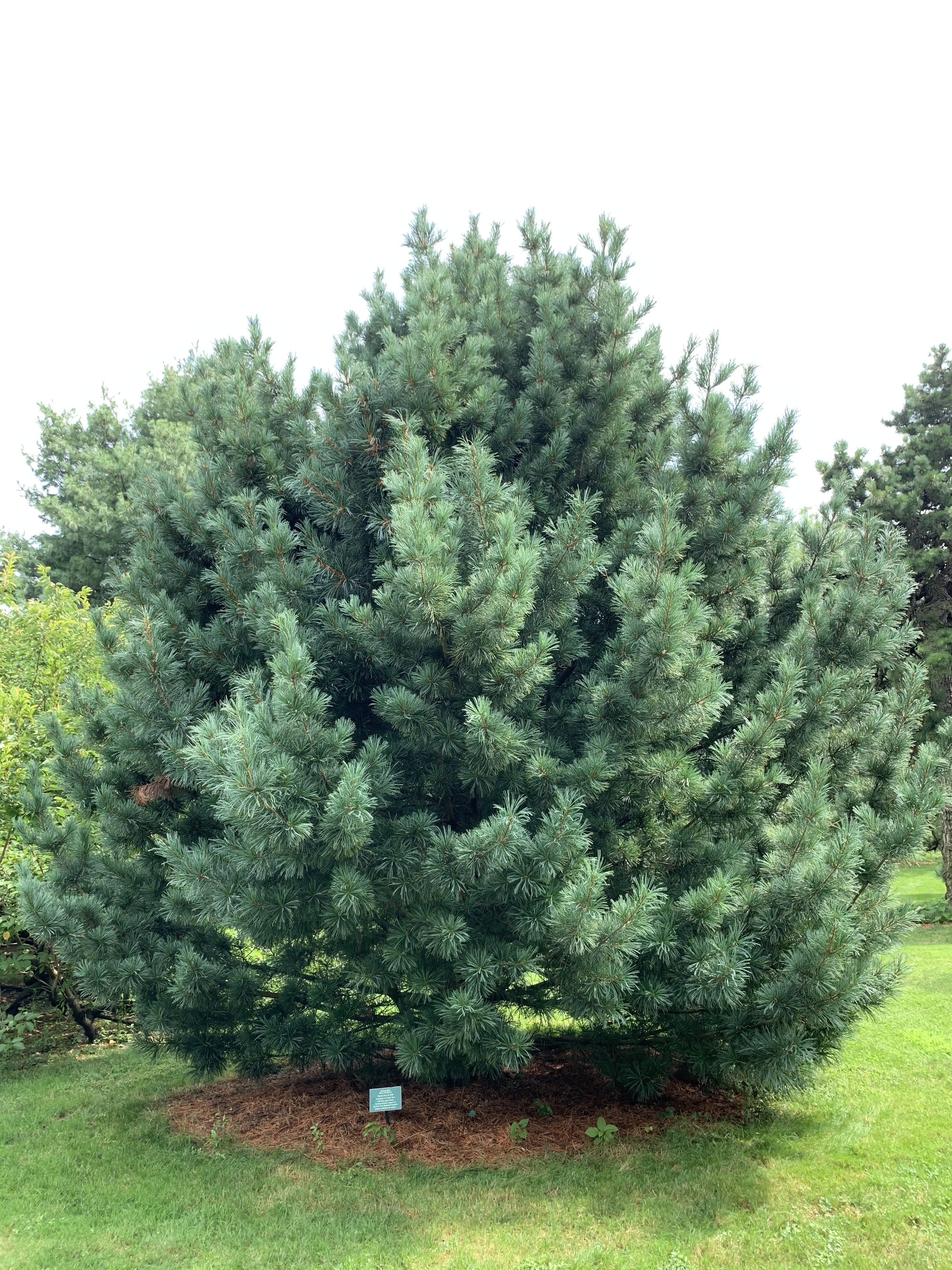
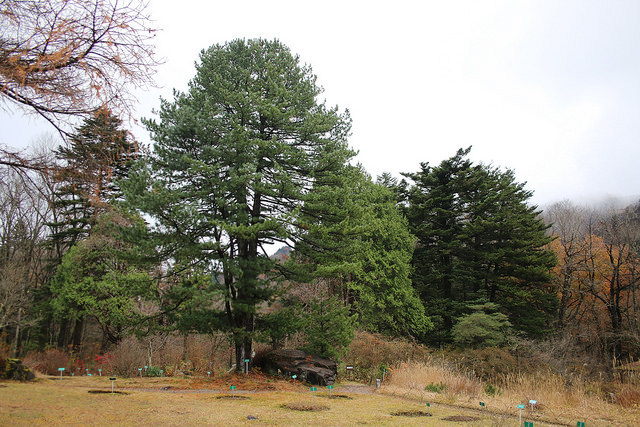
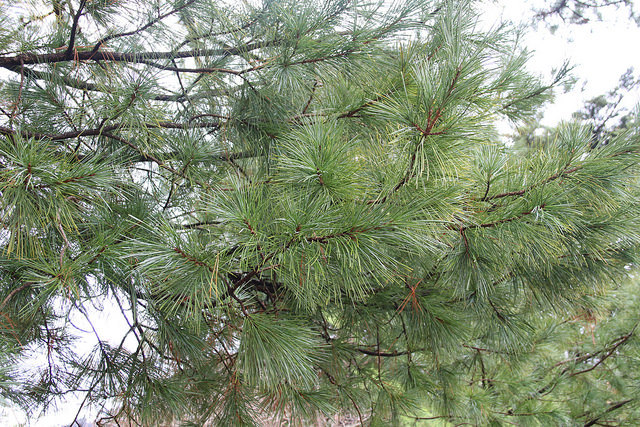
Description. Korean pine is an evergreen, coniferous species of tree which grows to mature heights of 100 feet (30 m) tall with a trunk up to 60 inches (150 cm) in diameter at breast height.
Distribution. This species is native to northeastern Korea and Japan - central Honshu island southward from Tochigi prefecture and northward from Gifu prefecture and Shikoku island - the Ussuri River basin; to China - Heilongjiang and Russia. It's native habitat is in subalpine forests at elevations of 4,200 to 8,000 feet (1,300 - 2,500 m) above sea level.
Hardy to USDA Zone 3 - cold hardiness limit between -40° and -30°F (-39.9° and -34.4°C).