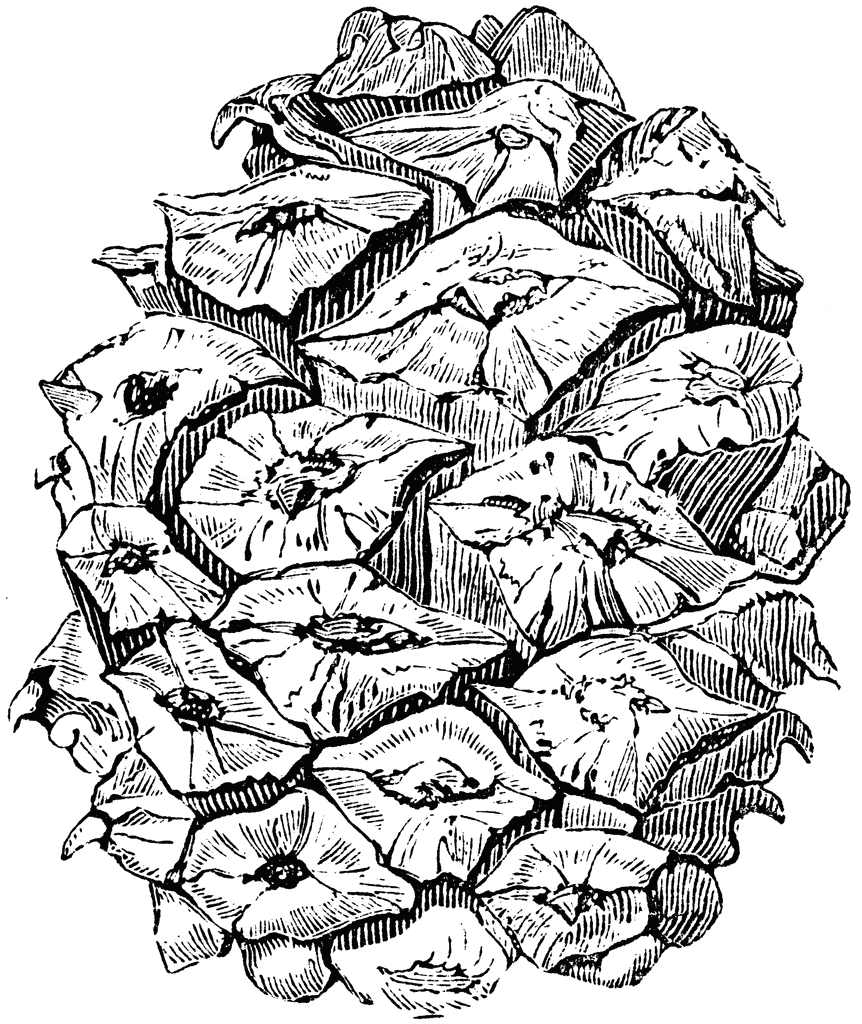
subgenus Strobus (Lemmon), section Quinquefoliae (Duhamel), subsection Gerardianae (Loudon)
Pinus bungeana, as described in 1847 by Joseph Gerhard Zuccarini (1790-1848) ex Stephan Friedrich Ladislaus Endlicher (1804-1849), in Synopsis Coniferarum, vol. 166; is commonly known as lacebark pine, as well as ç™½çš®æ¾ (bai pi song) in the Chinese language. The species name honors Alexander A. von Bunge (1803 - 1890), who collected the type specimen in 1831, while serving as Russian envoy to the imperial court of Beijing, and later wrote about the collections he made in northern China and Mongolia.
Ethnobotany. In Korea these conifers are used for lumber and their seeds and oil are eaten. Naturalist, Tom Velardi reports, "In Korea, a few trees grow in such areas as Seoul, Goyang and Icheon in Gyeonggi-do, Miryang in Gyeongsangnam-do, Boeun in Chungcheongbuk-do, and Yesan in Chungcheongnam-do. The largest of these trees are designated and protected as natural monuments"
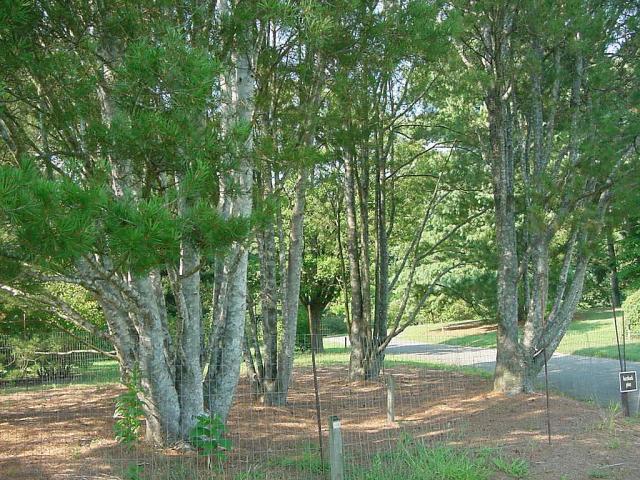
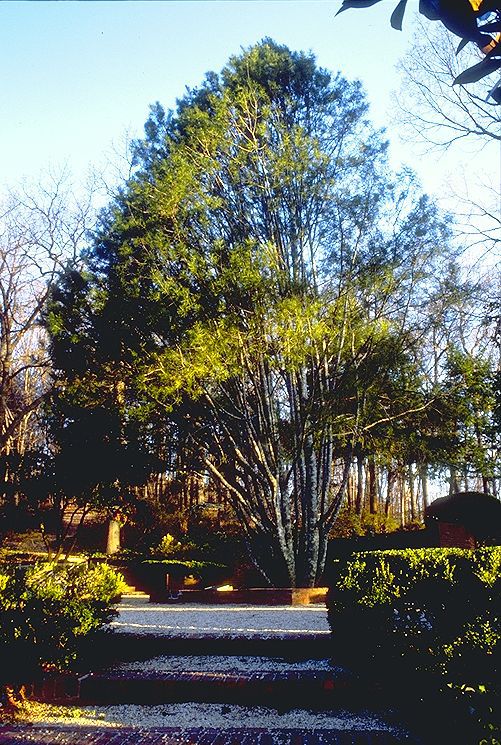
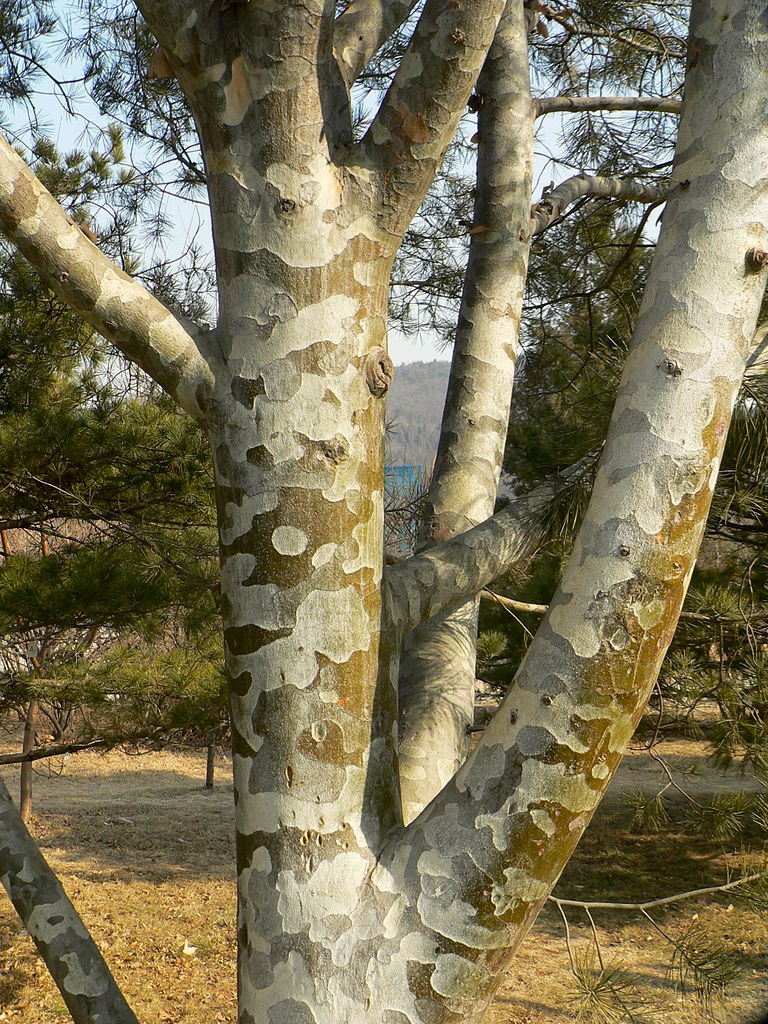
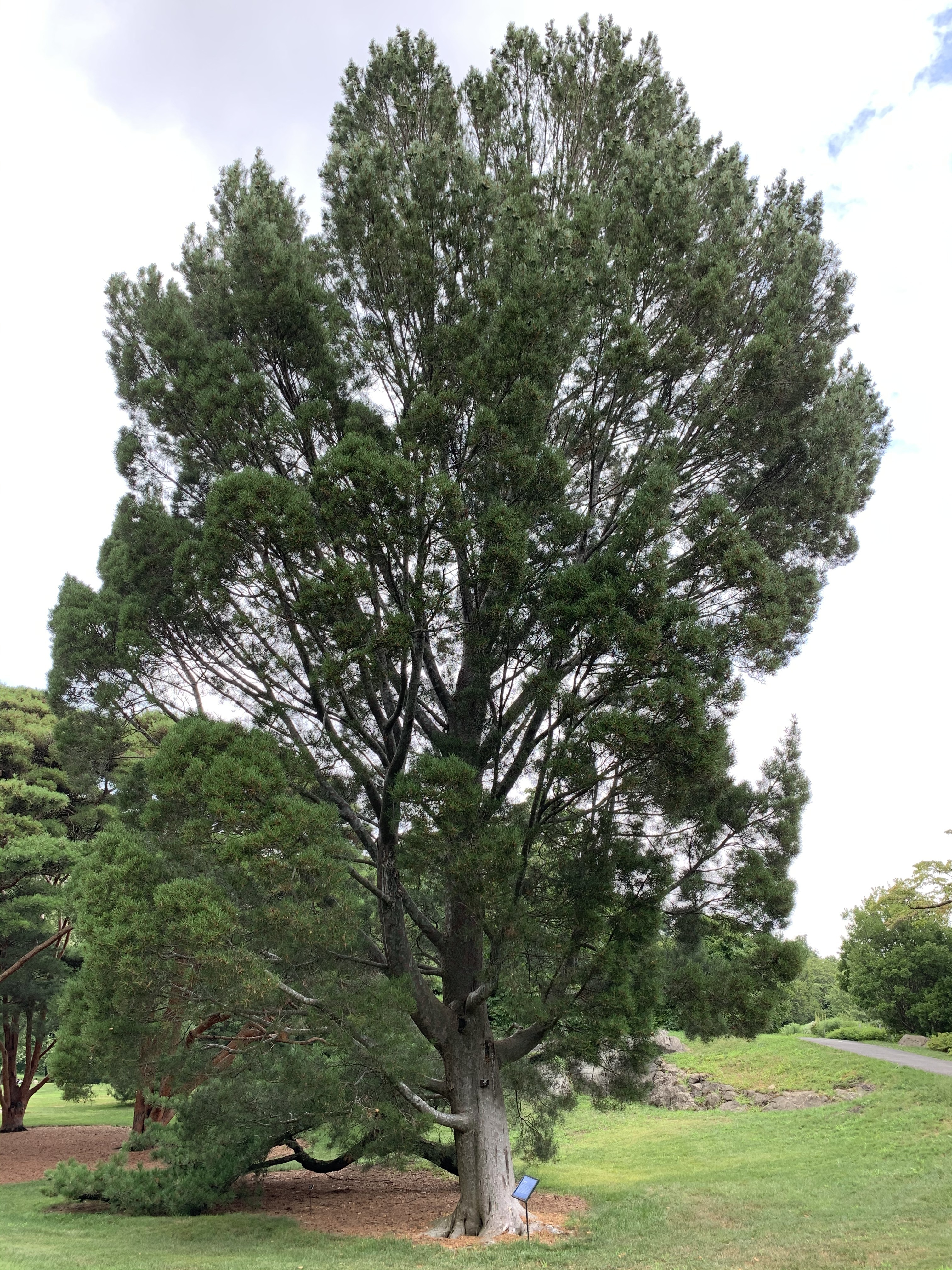
Description. Lacebark pine is an evergreen coniferous species of tree that grows to mature heights of 75 to 100 feet (24 - 30 m) with a trunk up to 46 inches (116 cm) in diameter, measured at breast height.
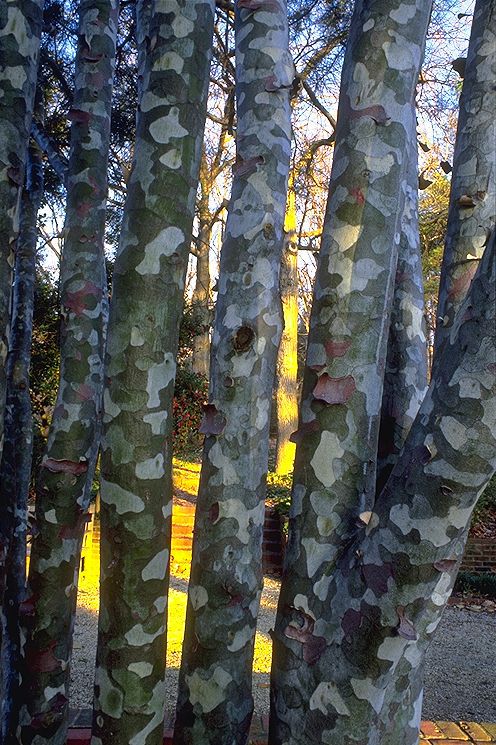
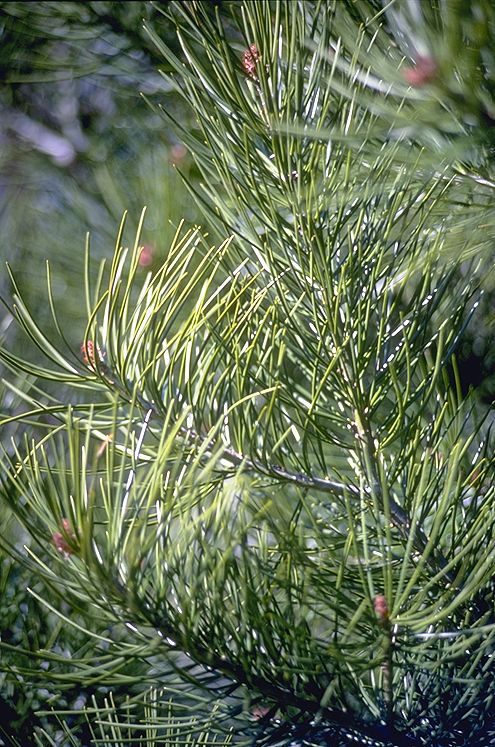
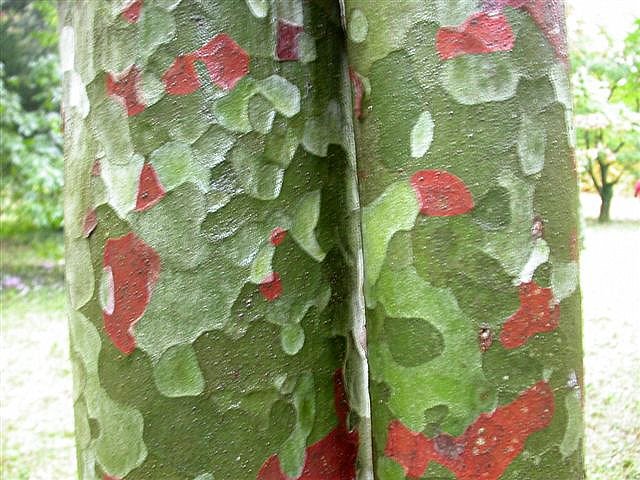
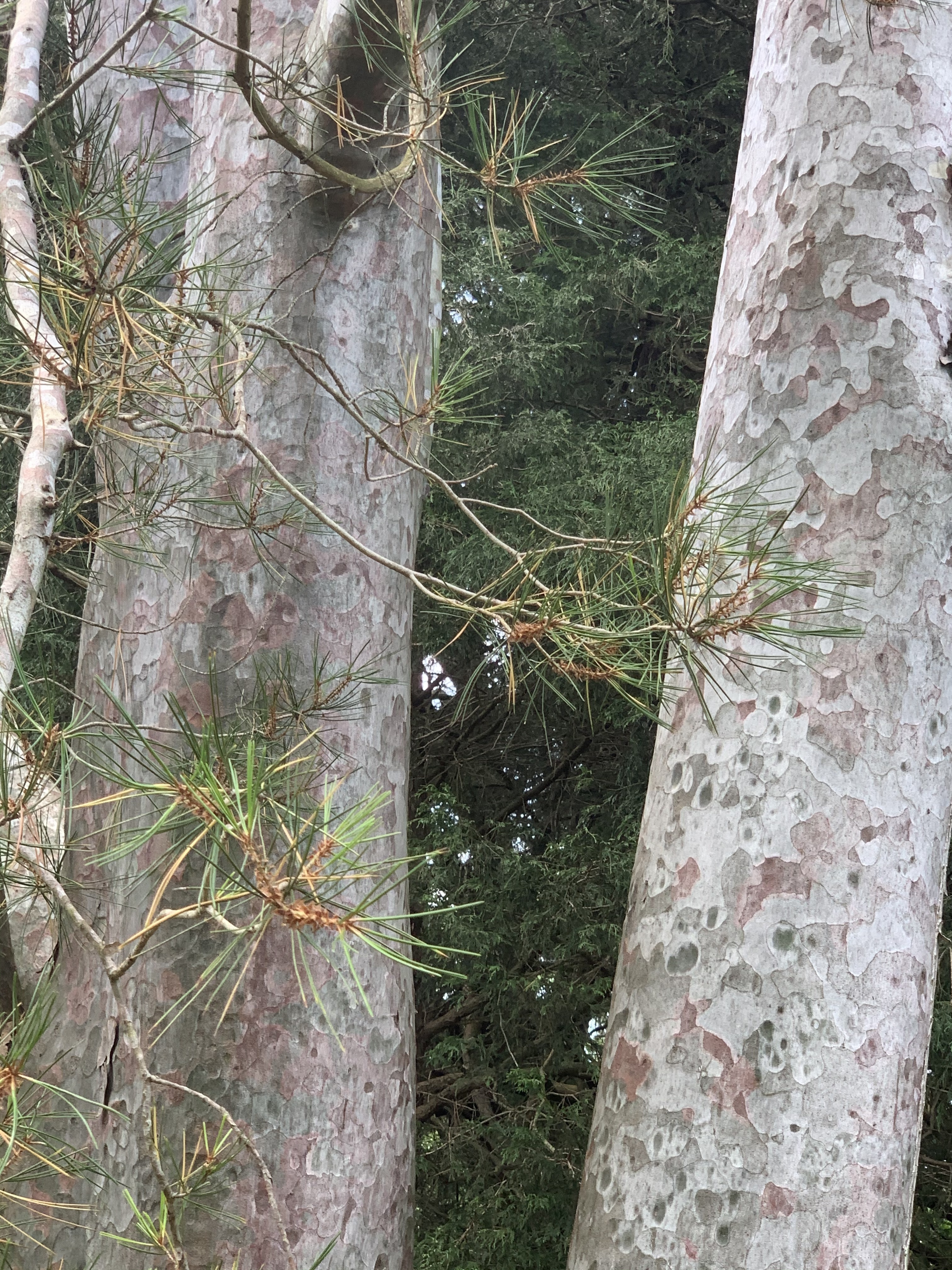
According to Dallimore, P. bungeana "closely resembles P. gerardiana, from which it is distinguished by its smaller cones and stiffer leaves. From other three-leaved pines it is separated by its smooth, scaling bark, sparsely arranged foliage, peculiar habit, and the strong odor of its bruised leaves.
Distribution. This species is native to northwestern China. It is hardy to USDA Zone 5 - cold hardiness limit between -20° and -10°F (-28.8° and -23.3°C).