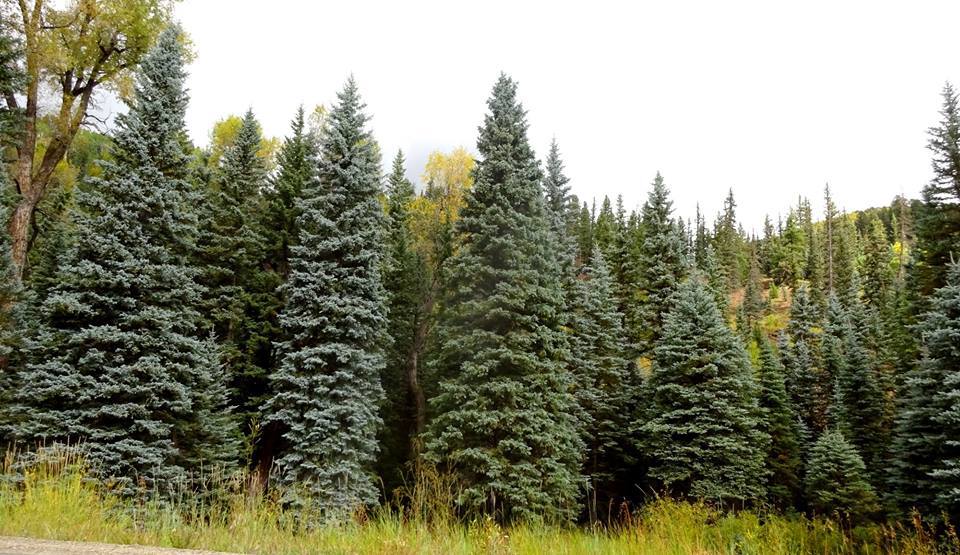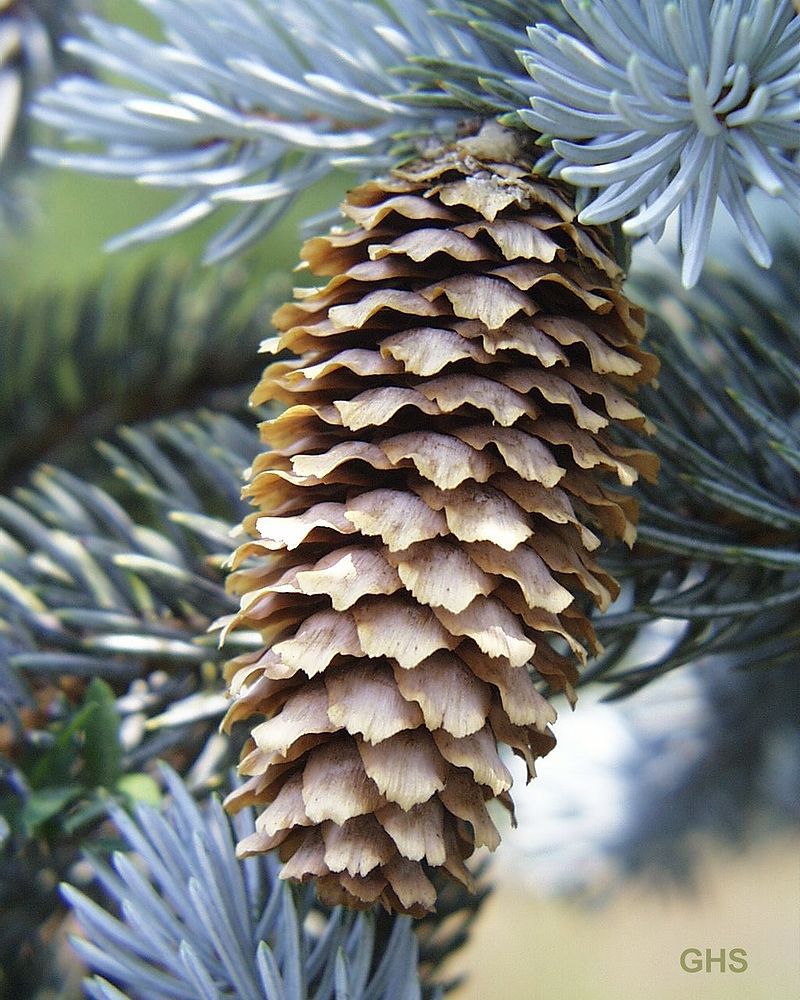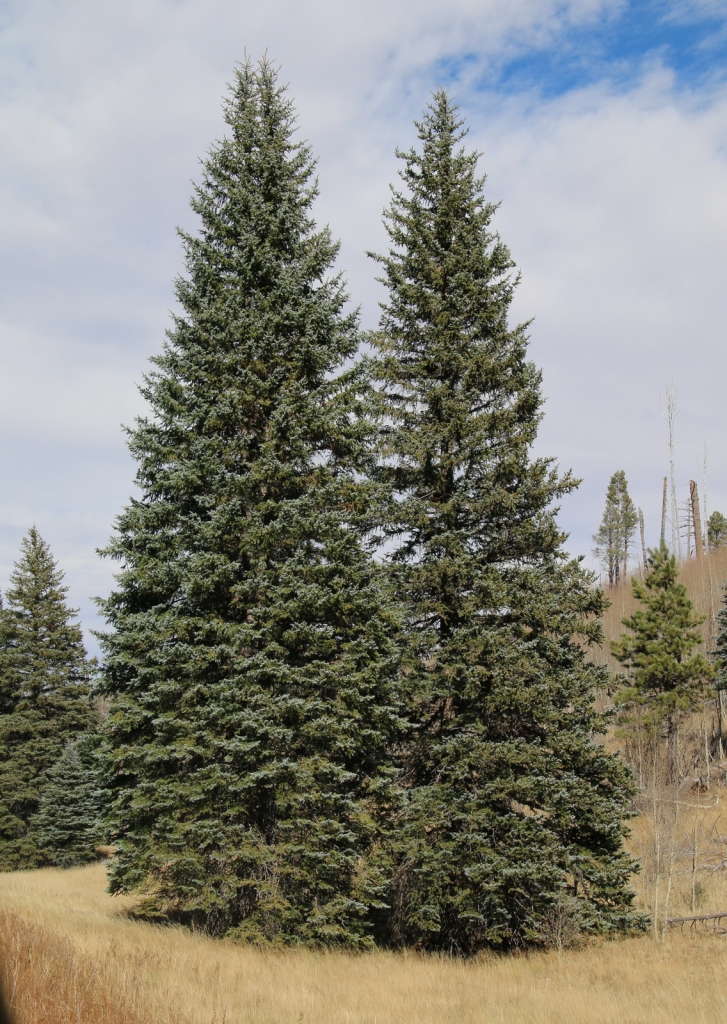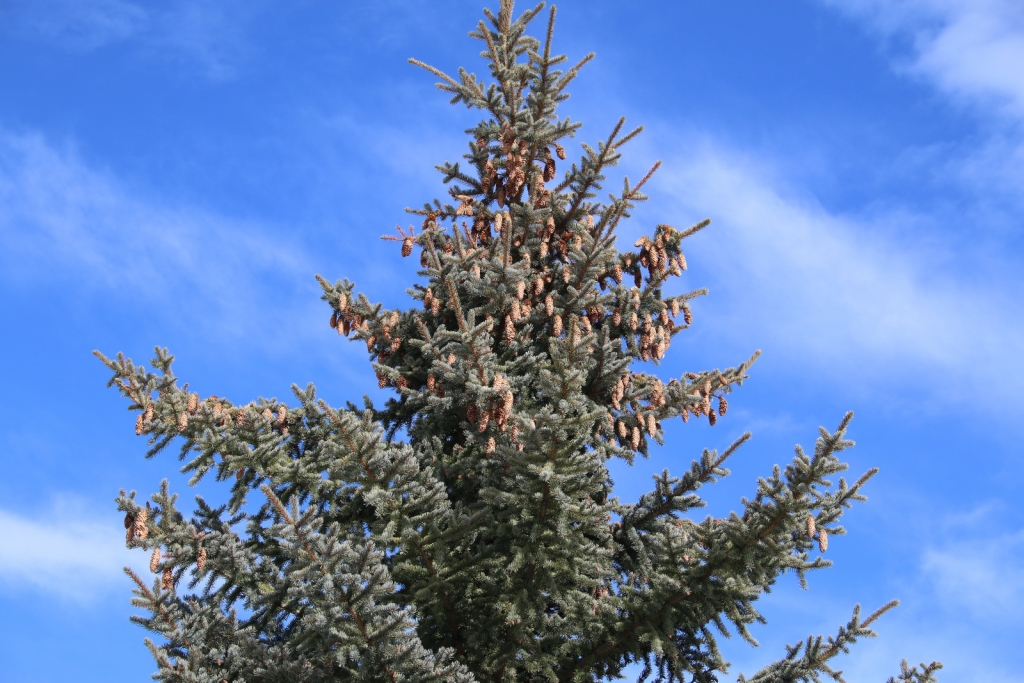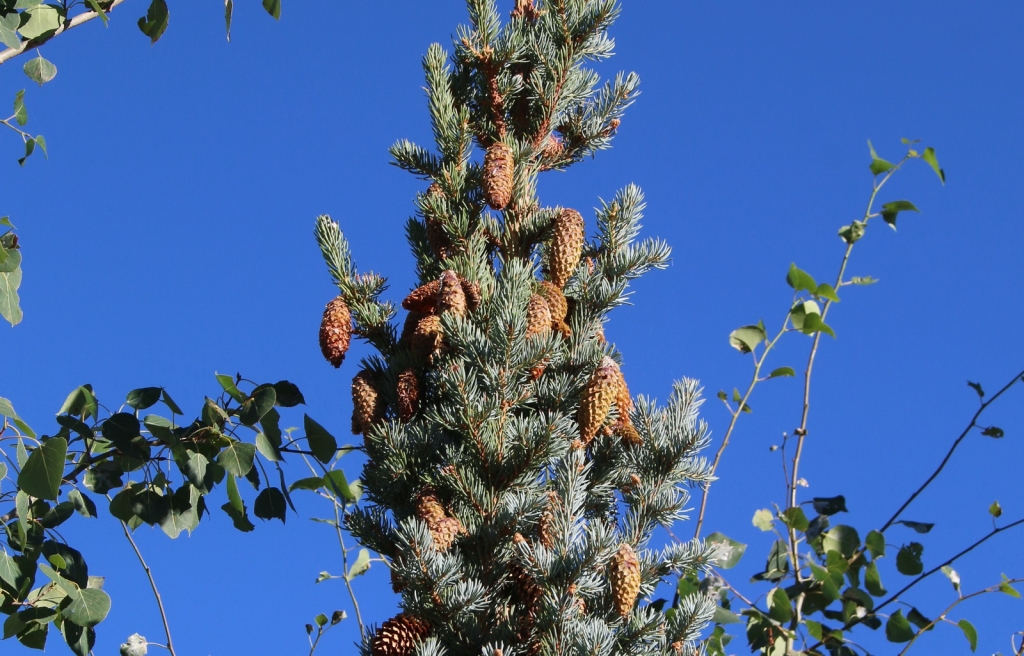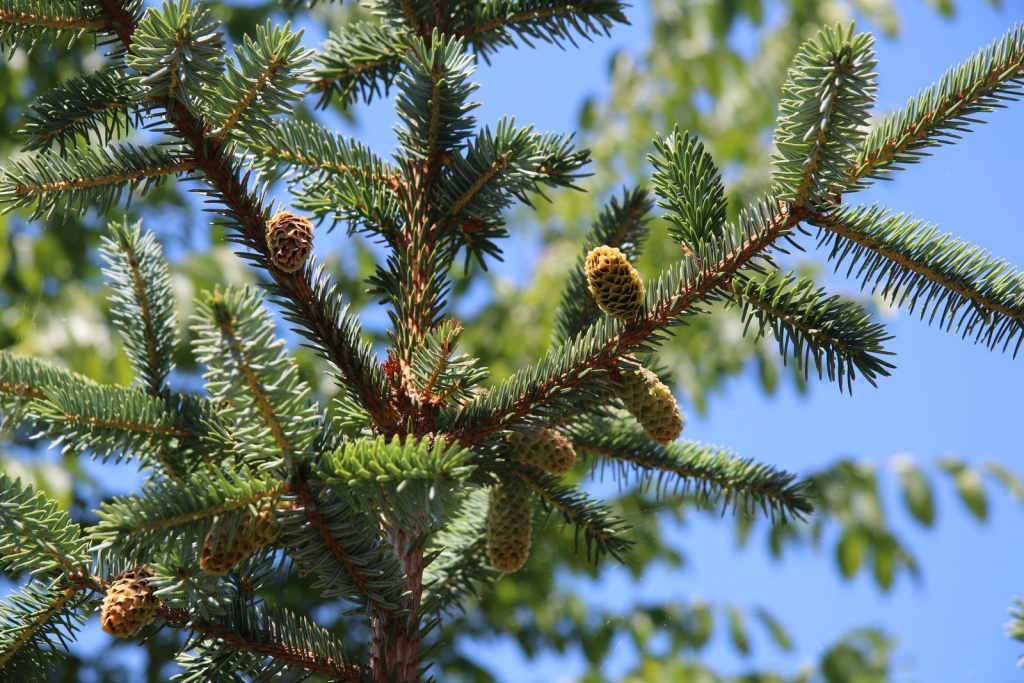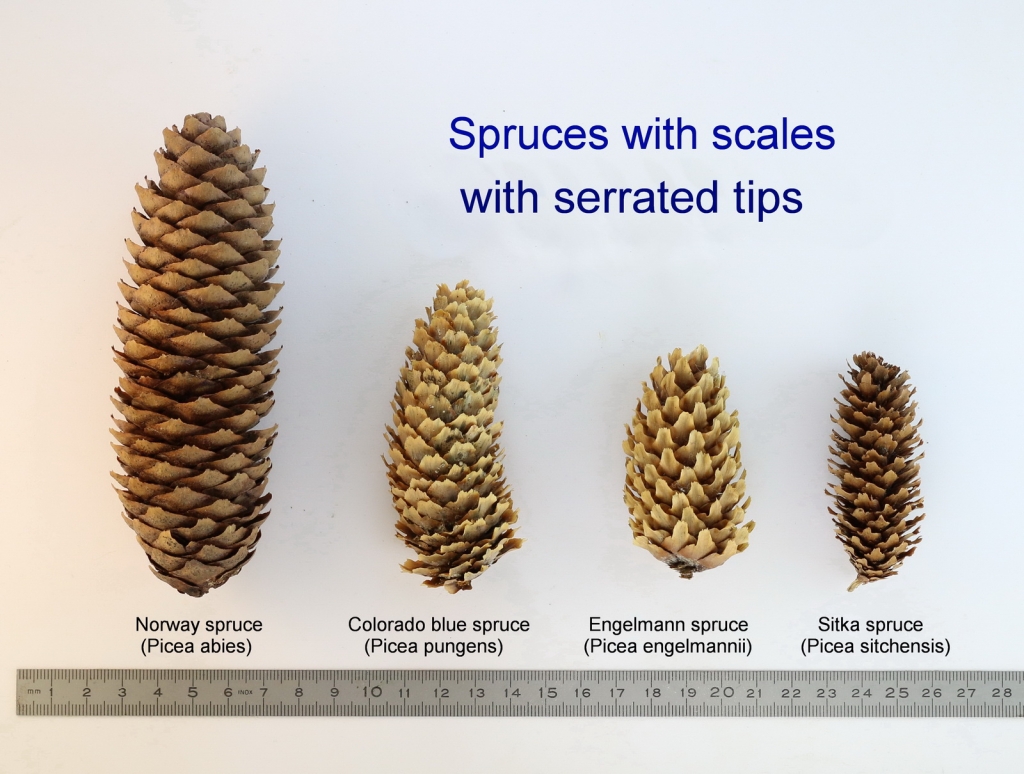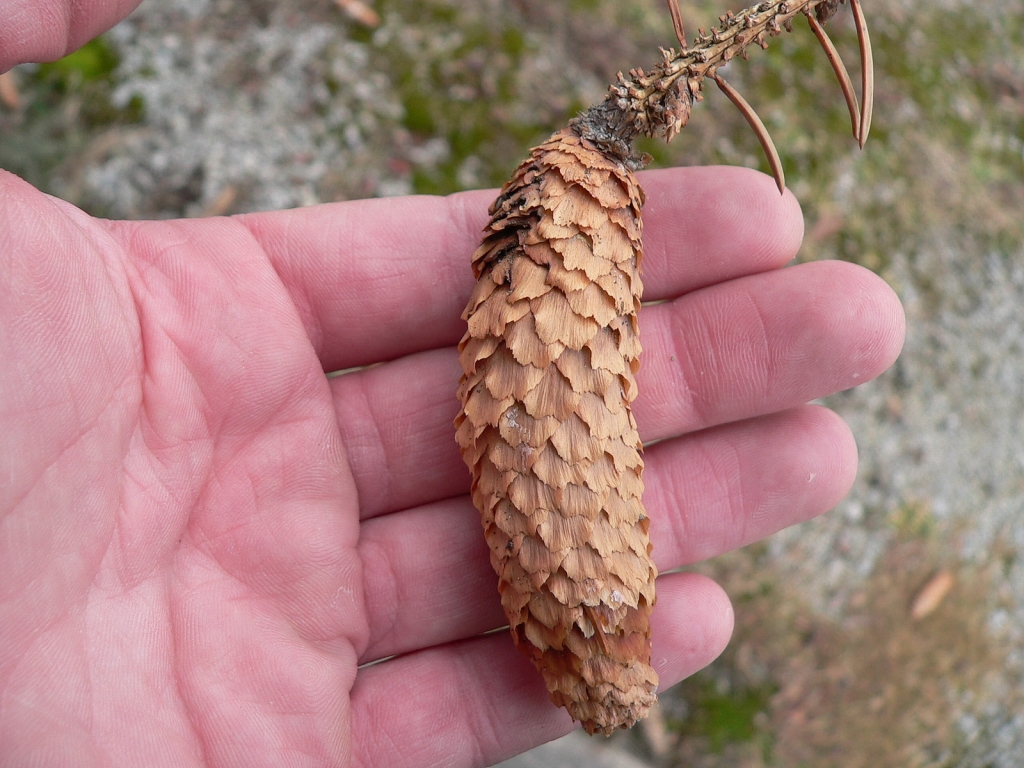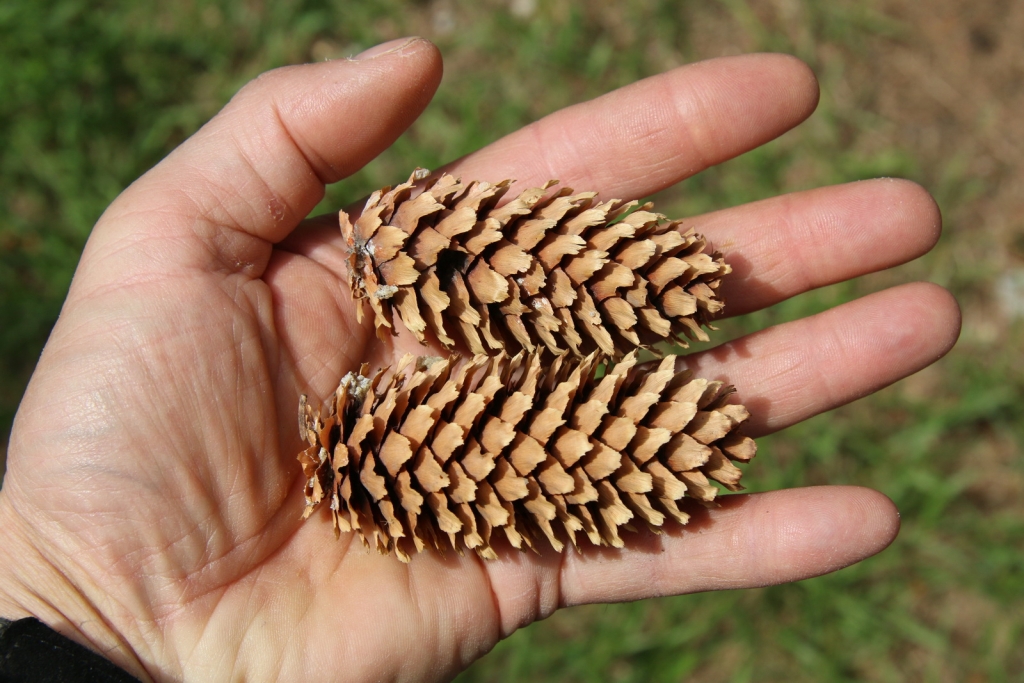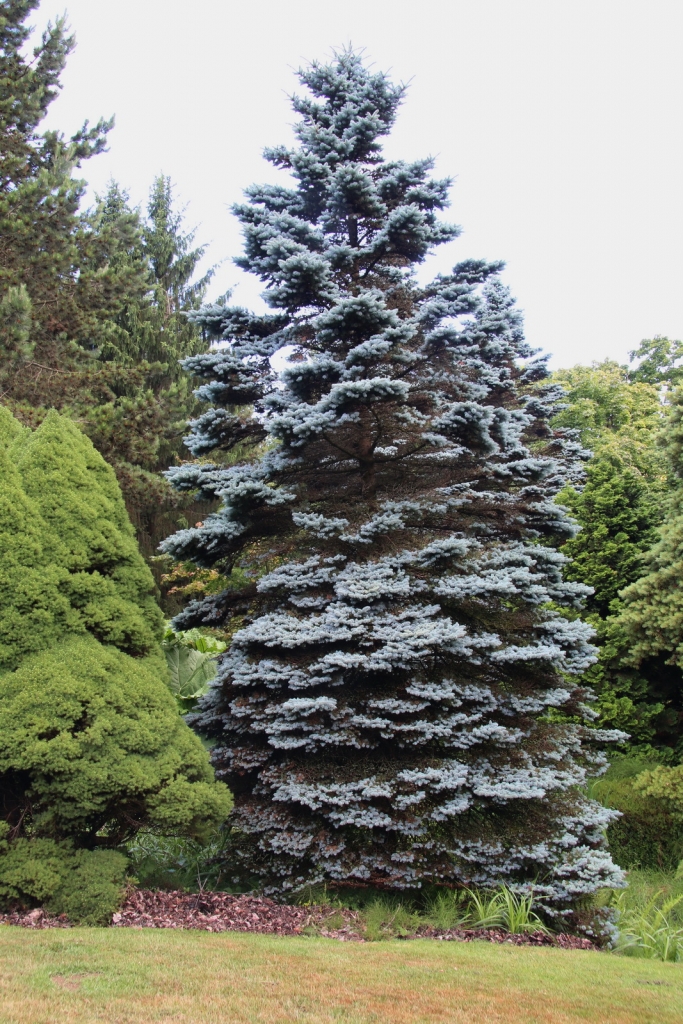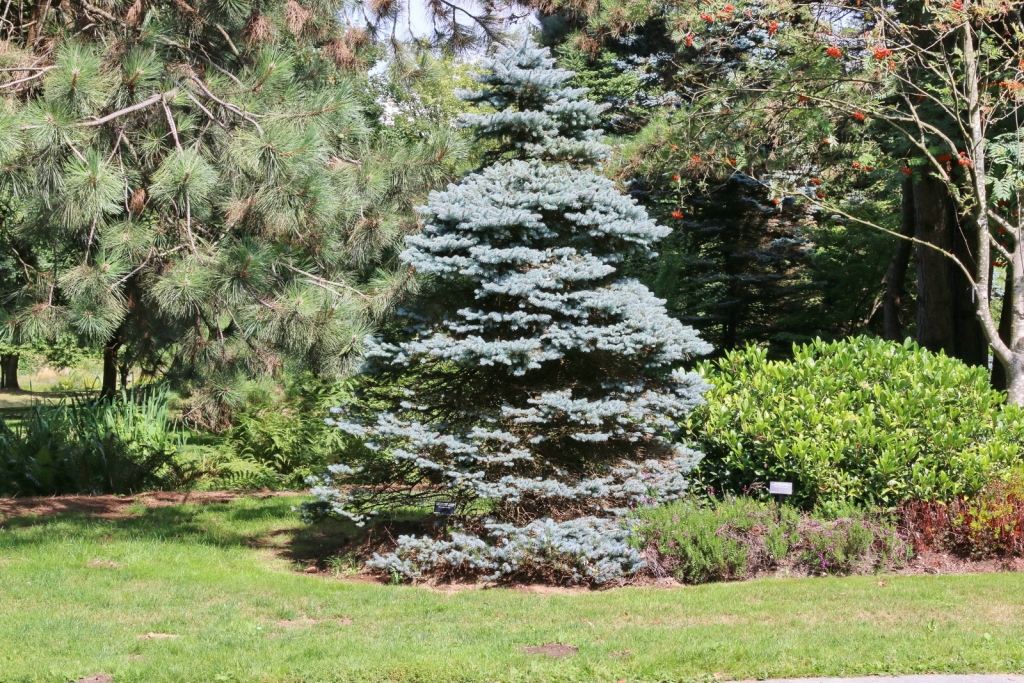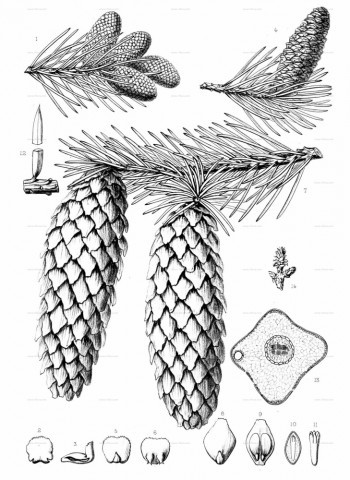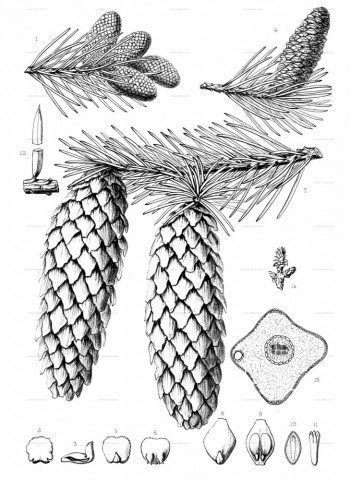
Picea pungens, as described in 1879 by Georg Engelmann (1809-1884), in The Gardeners' Chronicle, new series 11, is commonly known as Blue spruce, Colorado spruce, white spruce, silver spruce, or Parry spruce; as well as épinette bleue in French Canadian; and as pino real in Spanish. The species name described this conifer's exceptionally spiny needles. It is the state tree of Colorado.
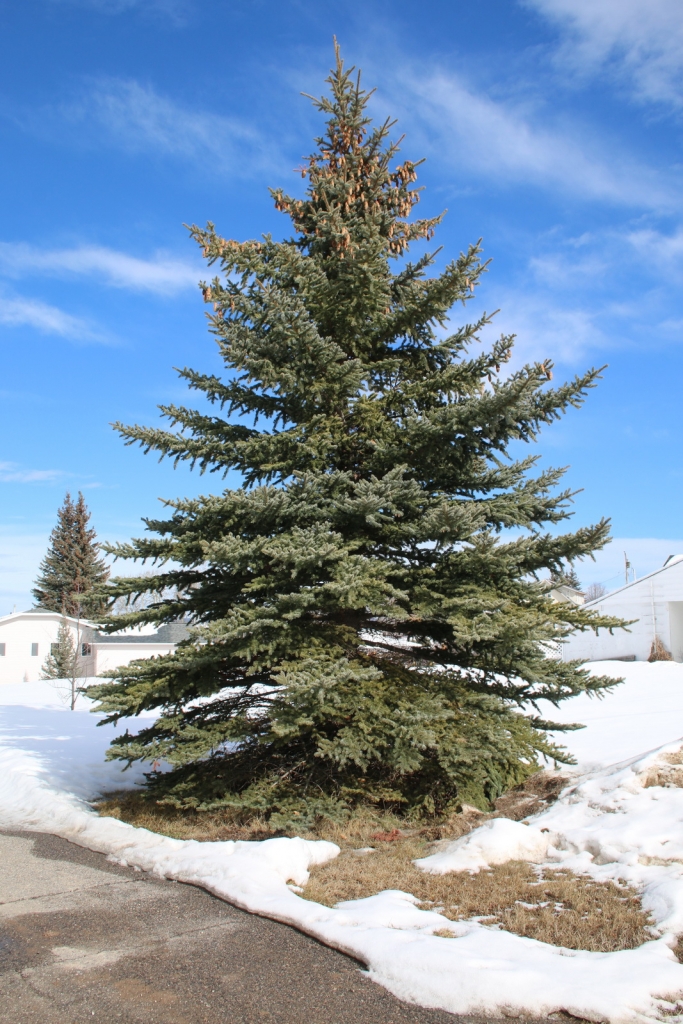
Description. Colorado spruce is an evergreen coniferous species of tree that grows to mature heights of 165 feet (50 m) tall with a trunk 5 feet (150 cm) in diameter, measured at breast height.
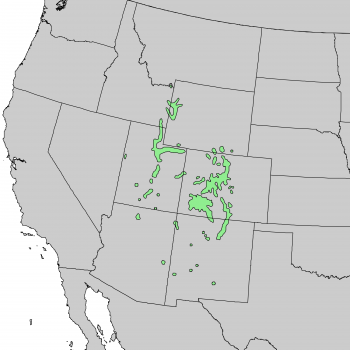
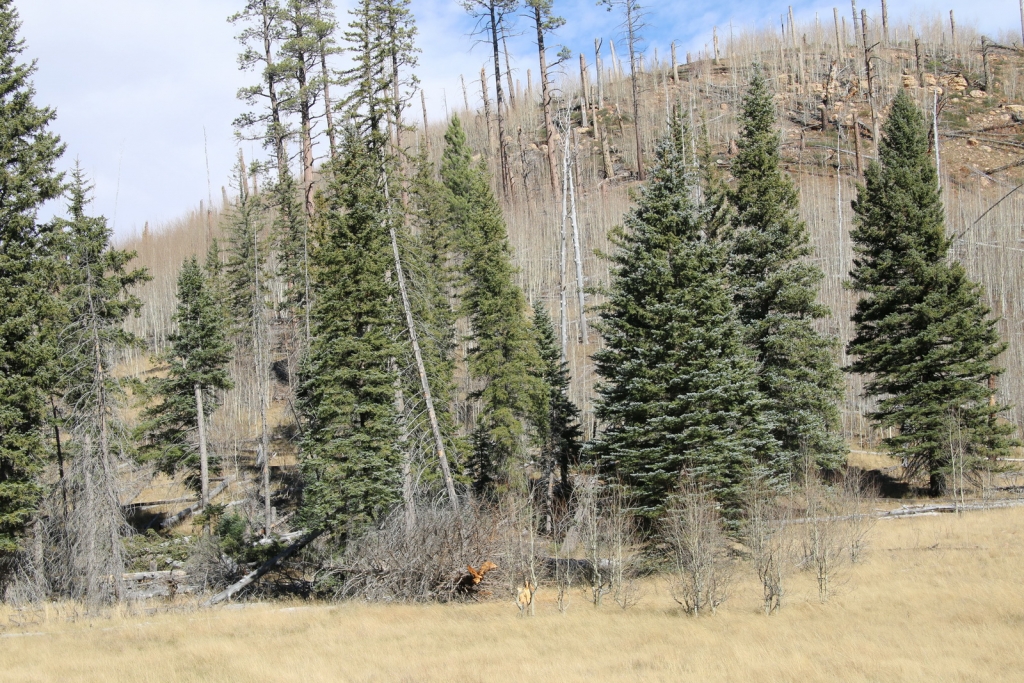
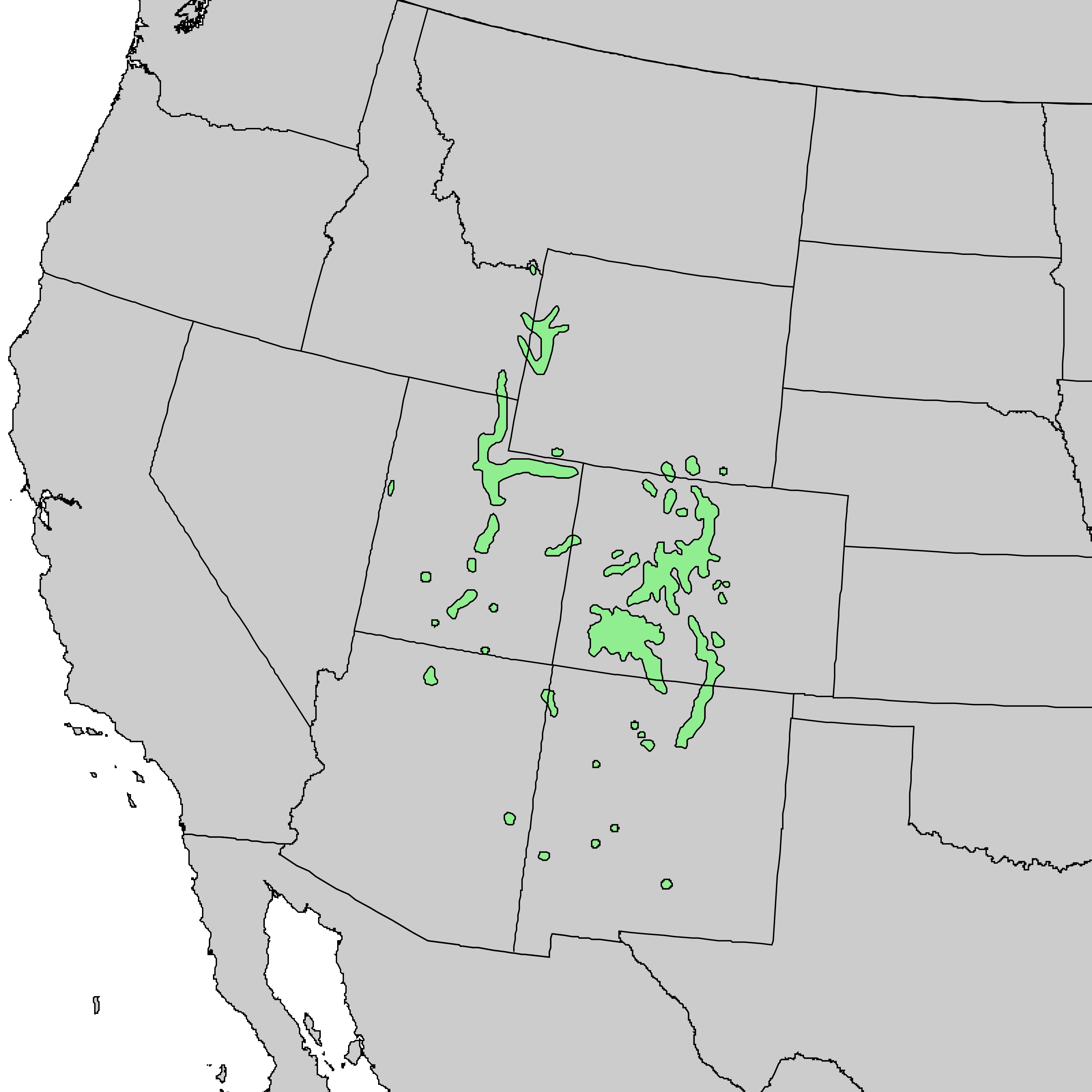
Distribution. This species is native to USA - Idaho, Wyoming, Utah, Colorado, New Mexico and Arizona, growing in the montane zone at elevations varying from 5,800 to 8,800 feet (1,830 - 2,740 m) above sea level in the northern range of the species, and from 6,800 to 9,800 feet (2,130 - 3,050 m) in southern areas. It prefers conditions where the climate is cool and summer-wet, with mean winter minimum temperatures of 12 to 48°F (-11.1 - 8.9°C) and mean summer maximum temperatures of 70 to 72° F (21.1 - 22.2°C). Average annual precipitation varies from 18 to 24 inches (460 - 610 mm), with half of the annual precipitation falling during the growing season. It is the most drought-tolerant species of Picea in North America.
Hardy to USDA Zone 3 (cold hardiness limit between -40 and -30° (-39.9° and -34.4°C).