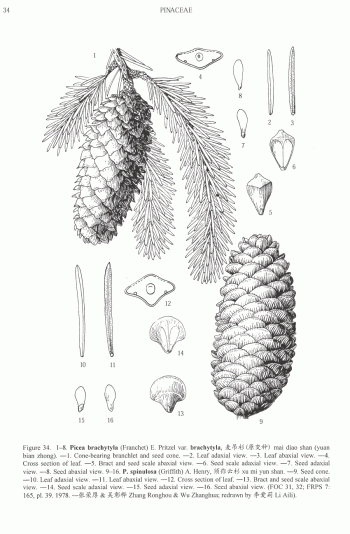
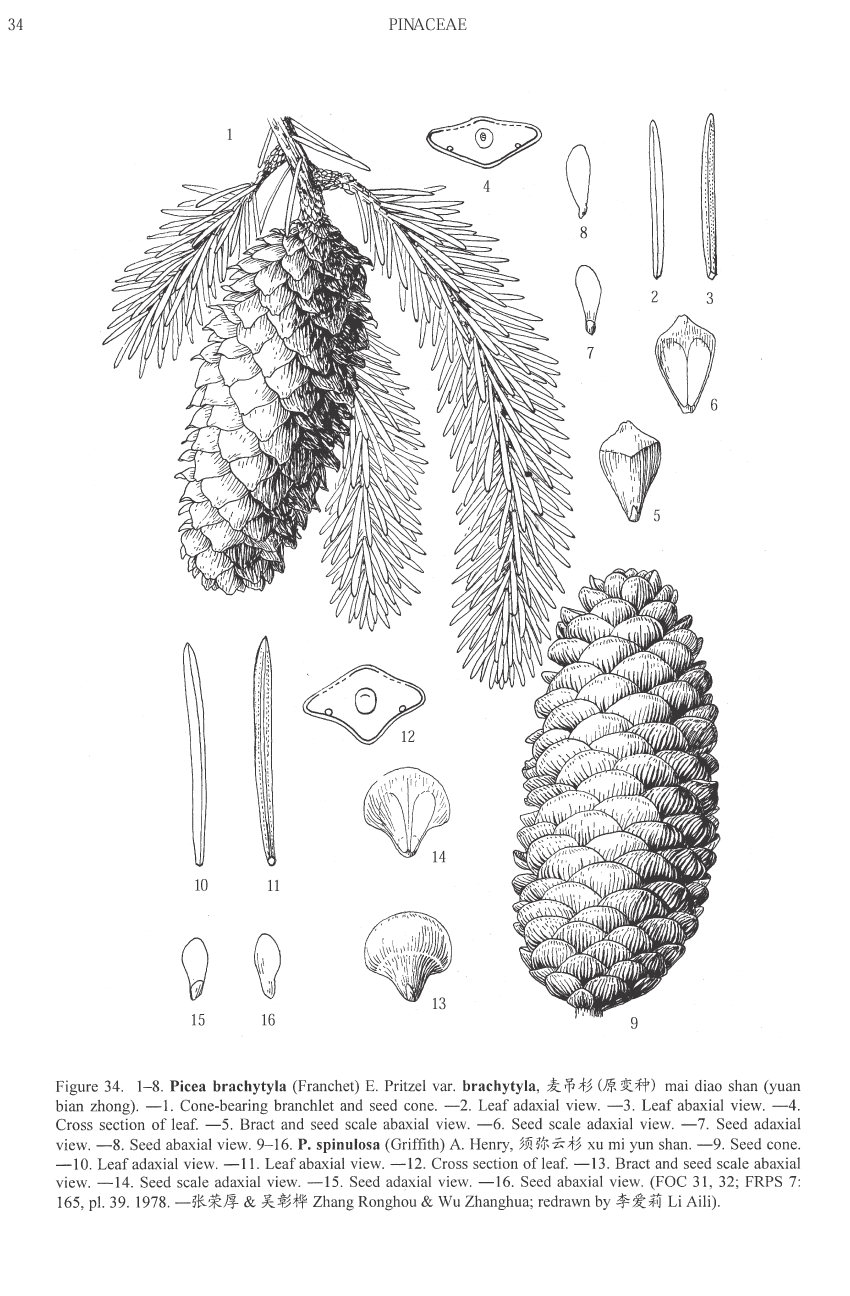
Picea brachytyla, as described in 1900 by (Franchet) Ernst Georg Pritzel (1875-1948), in the 29th edition of Botanische Jahrbüscher füsr Systematik, Pflanzengeschichte und Pflanzengeographie, is commonly known as Sargent spruce, as well as 麦ŠŠäº‘æ‰ (mai diao yunshan) in the Chinese language. The species name translates in to "short knob," and the common name honors Charles Sprague Sargent (1841-1927), the first director of Harvard University's Arnold Arboretum in Boston, Massachusetts, and held the post until his death.
Ethnobotany. An important timber species within its native range, it is also cultivated for afforestation.
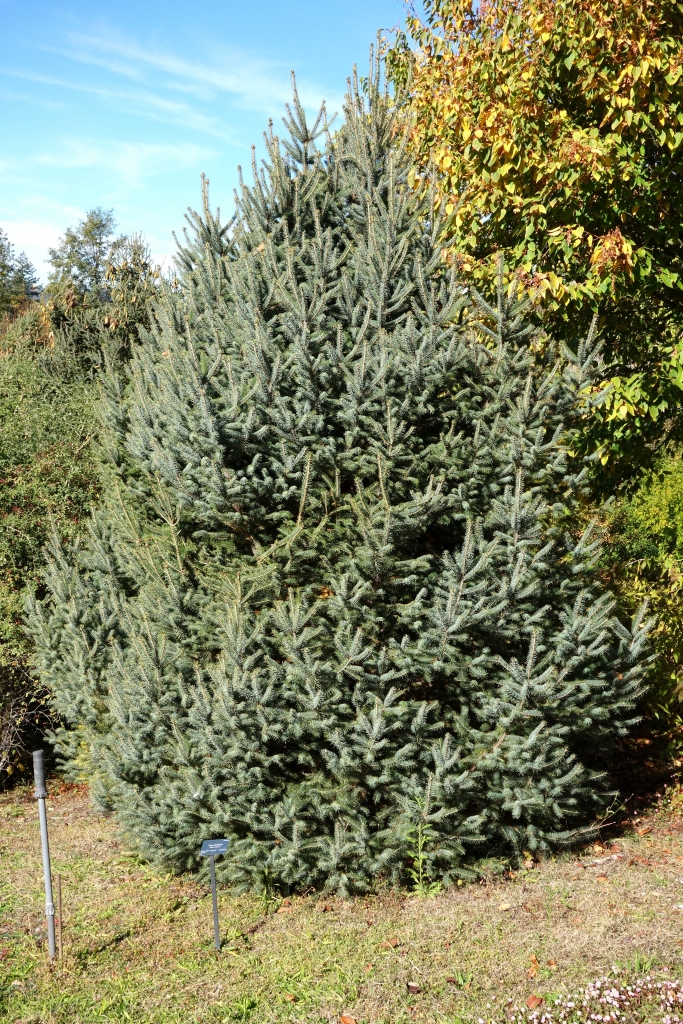
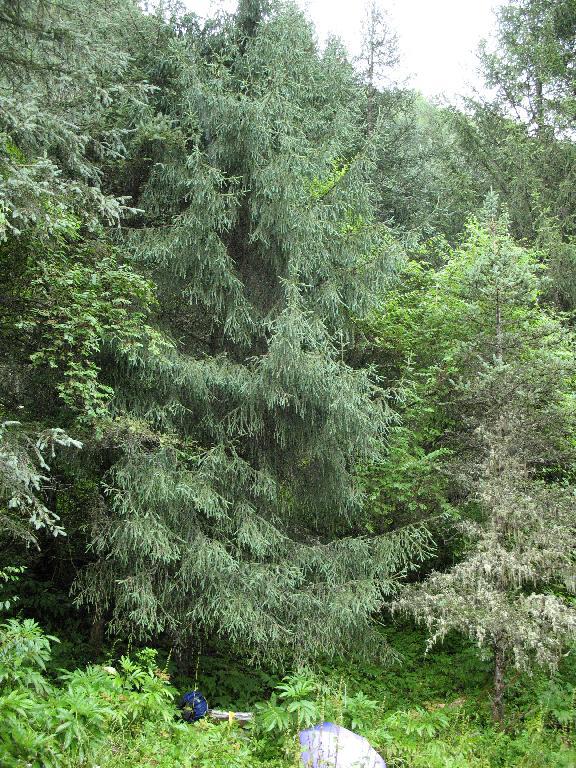
Description. Sargent spruce is an evergreen coniferous species of tree that grows to mature heights of 100 feet (30 m) with a trunck up to 40 inches (100 cm) in diameter, measured at breast height. Exceptional specimens will reach heights of 165 feet (50 m) tall with trunk up to 80 inches (200 cm) in diameter. Crown is pyramidal, becoming cylindrical and somewhat irregular with age.
- Bark is gray or gray-brown in color and longitudinally fissured into thick, square plates or irregularly flaking.
- Branchlets are pendulous, pale yellow or brownish yellow in color, turning brownish yellow or brown, and finally gray.
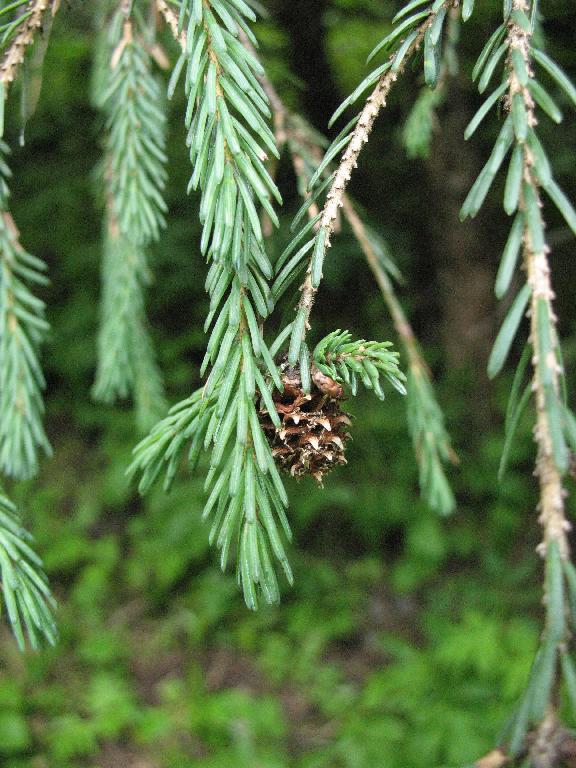
- Leaves (needles) are directed forward and closely appressed along upper sides of branchlets, spreading and almost pectinate on lower side; linear, slightly curved or straight, and flattened. Individual needles measure 0.4 to 1 inch (10 - 25 mm) long by 0.04 to 0.06 inch (1 - 1.5 mm) thick; and are slightly keeled on both sides, bearing 5 to 7 stomatal lines in each of 2 white or pale bands adaxially. Needle apices acute or mucronate.
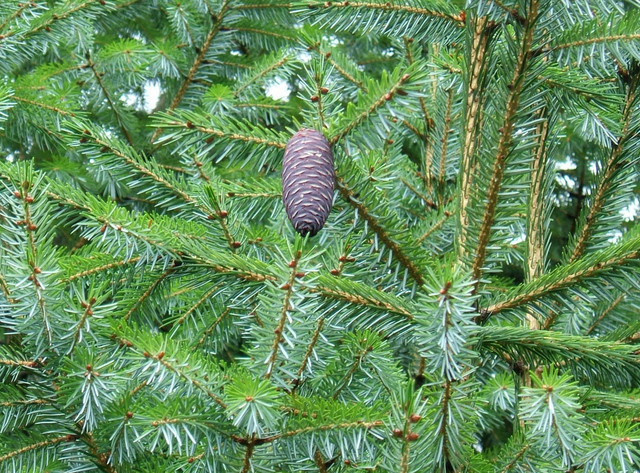
- Seed cones are colored green, red- or purple-brown, maturing dull brown or brown tinged purplish, with an ovoid-oblong shape, measuring 2.4 to 4 inches (6 - 10 cm) long by 1.2 to 1.6 inches (3 - 4 cm) broad.
- Seed scales have an obovate-oblong or rhombic outline, measuring 0.56 to 0.88 inch (1.4 - 2.2) by 0.44 to 0.52 inch (1.1 - 1.3 cm), with a cuneate base, and usually recurved, sometimes elongate distal margins.
- Seeds measuring circa 0.48 inch (12 mm) long, including wing. Pollination takes place in April to May, seed maturity is in September and October .
Distribution. This species is native to China - southern Gansu, southern Shaanxi, northwestern Hubei, western Sichuan, northwestern Yunnan and southeastern Xizang provinces; as well as northern Burma; and the Assam Himal of India. This species forms a prominent forest belt in moist mountains of southwestern China at elevations of 8,500 to 10,000 feet (2,600 - 3,100 m) above sea level. Across its broad range, it can be found at 4,400 to 12,250 feet (1,300 - 3,800 m) elevation, typically growing in a cold and wet monsoonal climate with annual precipitation of 40 to 100 inches (1,000 - 2,500 mm) (wetter to the south) on grey-brown mountain podzols. It is commonly found with
Abies spp.,
Picea likiangensis,
Tsuga spp. and
Larix potaninii .
Hardy to USDA Zone 8 - cold hardiness limit between 10° and 20°F (-12.1° and -6.7°C).