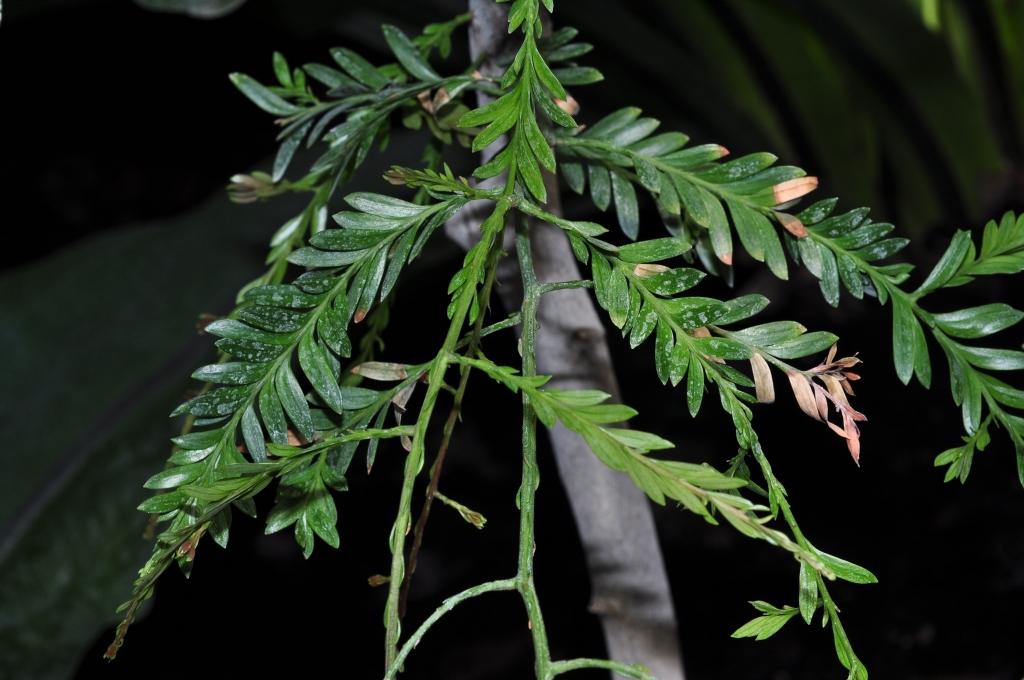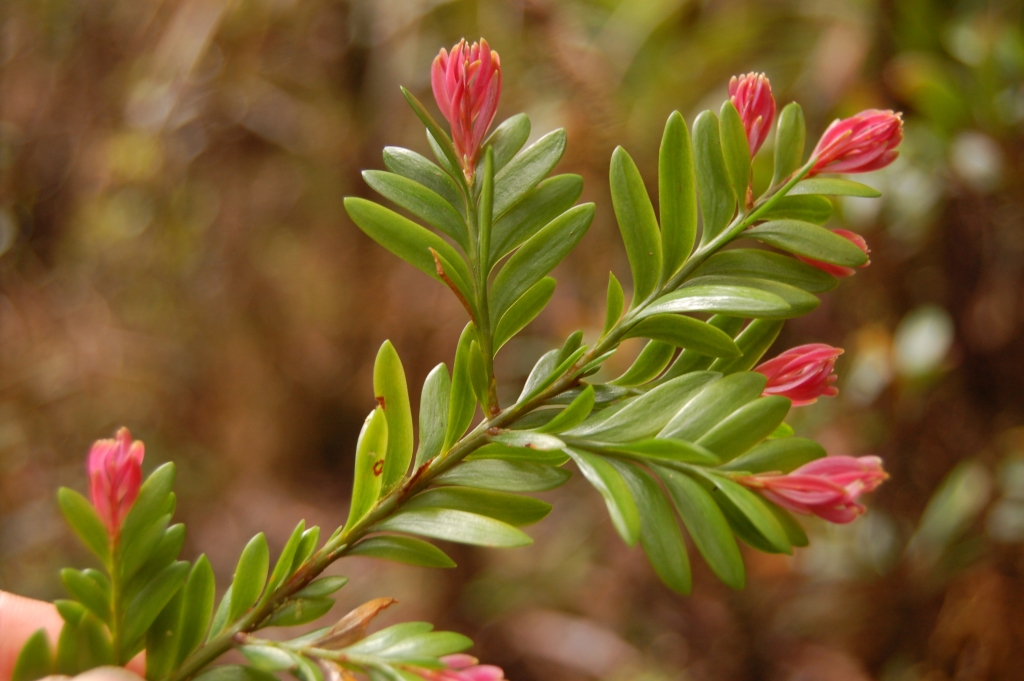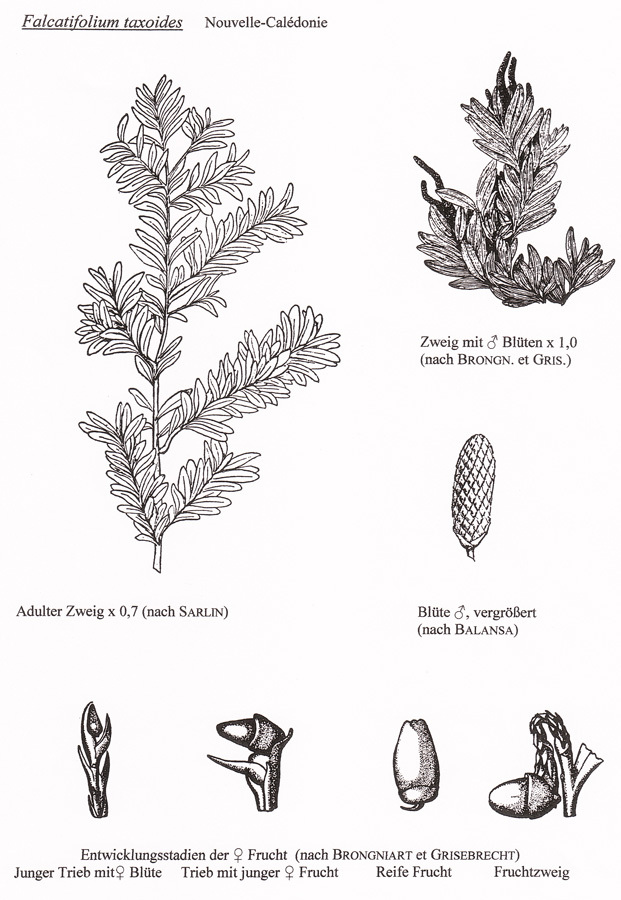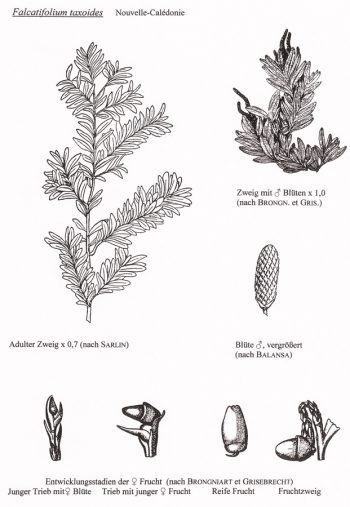
Falcatifolium taxoides, as described in 1969 by (Adolphe-Théodore Brongniart (1801-1876) and August Heinrich Rudolf Grisebach (1814-1879)) David John de Laubenfels (1925-2016), in Journal of the Arnold Arboretum, vol. 50, is commonly known as New Caledonian sickle pine. The species name describes a superficial resemblance to the Yew species (Taxus spp).
The most closely related species is F. papuanum from New Guinea. This species is also the sole host to Parasitaxus ustus, the only-known parasitic conifer. It is also the most geographically isolated member of this genus.
Description. New Caledonian sickle pine is an evergreen coniferous species of shrub or small tree that grows to mature heights of 7 to 50 feet (2 - 15 m).
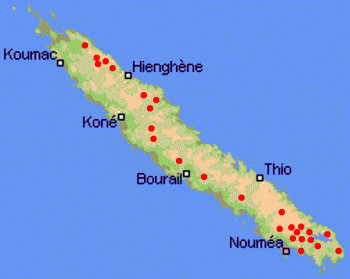
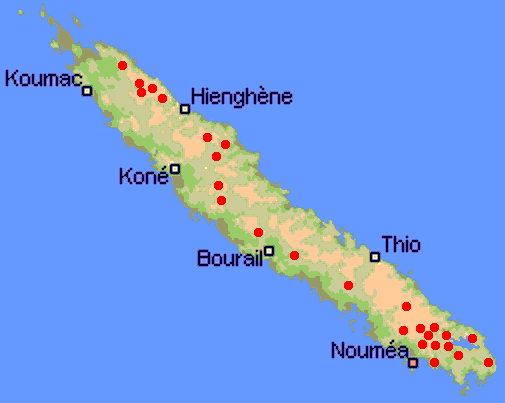
Distribution. This species is native to New Caledonia, growing at elevations from sea level to 4,500 feet (1,400 m). It is an understory tree in the wet forests of the main island. Within its range, mean annual temperature is 68.7ºF (20.4°C), with an average minimum in the coldest month of 56.3ºF (13.5°C), and a mean annual precipitation of 74 inches (1,848 mm). The IUCN reports that the population status is stable.
Hardy to USDA Zone 10, cold hardiness limit between 30º and 40ºF (-1° and +4.4°C).