Cephalotaxus griffithii, as described in 1888 by William Jackson Hooker (1785-1865) in The Flora of British India, 5th edition, is commonly known as Griffith's plum-yew; as well as 西ŠŒç‰ˆçº³ç²—榧 (hai nan cu fei) in the Chinese language. The species name honors William Griffith, a British botanist who collected widely in India and neighboring lands before dying of a tropical disease at the age of 35.
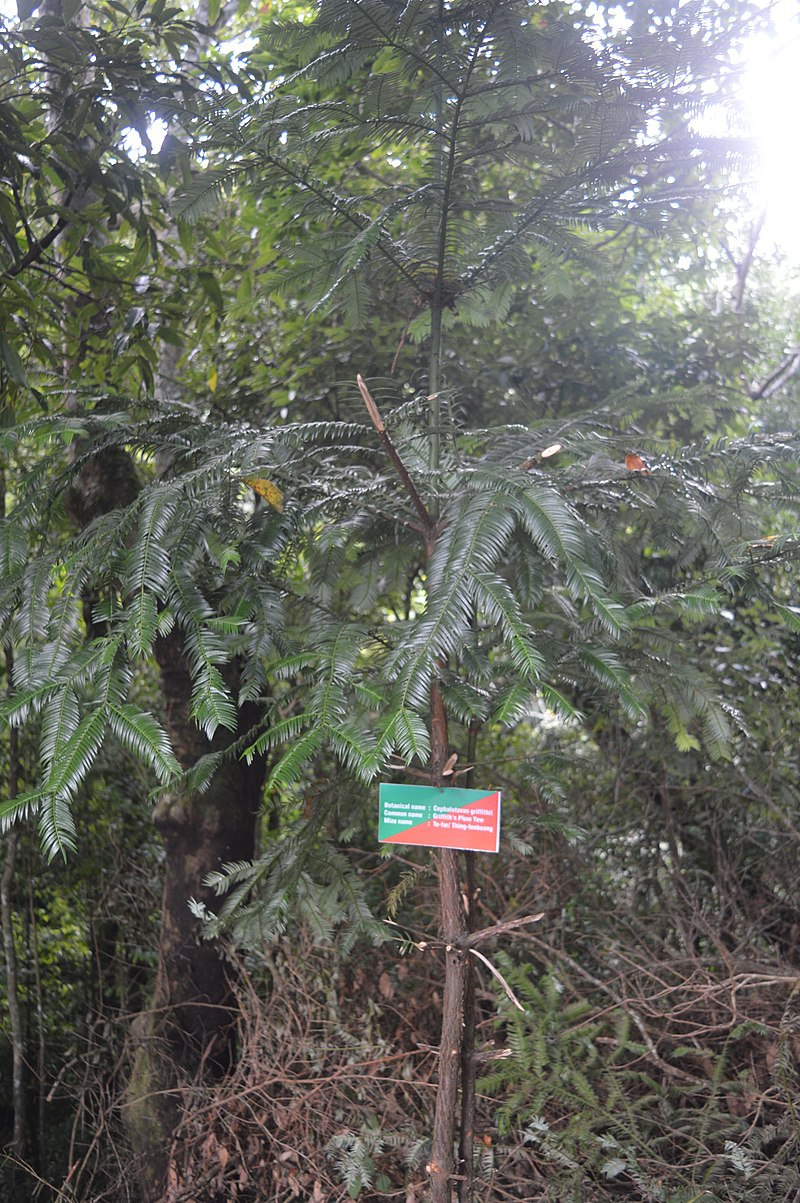
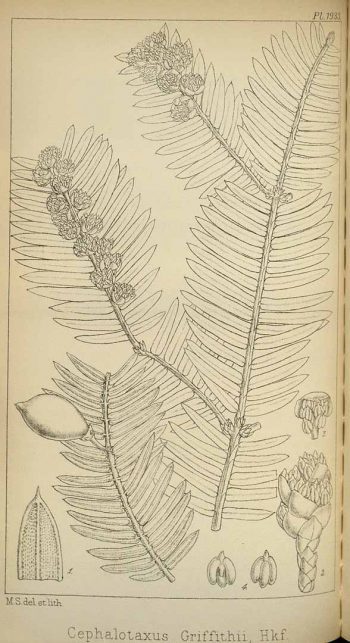
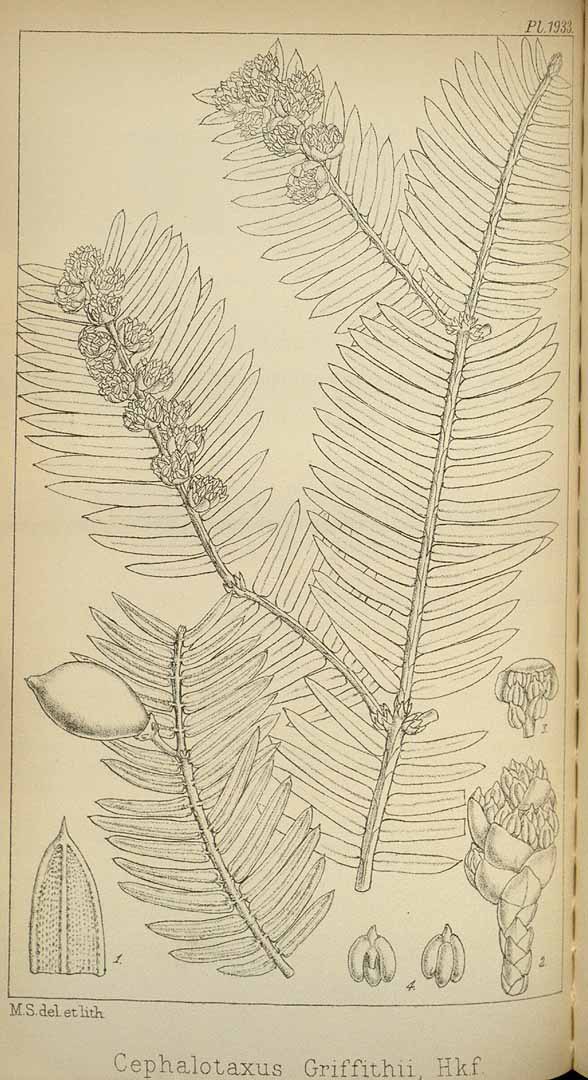
Description. Griffith's plum-yew is an evergreen, coniferous species of tree that grows to mature heights of 65 feet (20 m) tall with a trunk up to 20 inches (50 cm) in diameter, measured at breast height.
- Bark light to reddish brown in color, flaking off with age.
- Leafy branchlets have an elliptic or oblong-elliptic outline, measuring 3.2 to 7.2 inches (8 - 19 cm) long and 1.8 to 3.2 inches (4.5 - 8 cm) wide, about half as wide as long.
- Leaves are held at 45 to 80° angles to the branchlet axis. Petioles are more-or-less absent to 0.02 (0.5 mm) wide. Leaf blades are dark green or shining olive-green adaxially, with a linear or linear-lanceolate outline, and are usually straight, occasionally slightly falcate and flat. Individual needles measure (0.6 to 1.6 inches (1.5 - 4 cm) long and 0.08 to 0.16 inch (2.5 - 4 mm) wide, with leathery texture. A relatively thin midvein is prominent adaxially; measuring 0.08 to 0.12 inch (0.2 - 0.3 mm) wide. Abaxially, stomatal bands are white or bluish white in color, often indistinct and green when dry because of white powder being shed. The bands measure 0.28 to 0.64 inch (0.7 - 1.6 mm) wide and are comprised of 19 to 23 rows of stomata, 2.5 to 8 time as wide as midvein. Marginal bands measure 0.04 to 0.12 inch (0.1 - 0.3 mm) wide with a very broadly obtuse or obtusely truncate base. Needle apex is cuspidate (with leaf tapered into apex from at least middle, often from base), or abruptly and very shortly mucronate.
- Pollen cones are borne in clusters of 6 to 8, colored pale yellow, with globose shape, measuring 0.16 to 0.18 inch (4 - 4.5) mm in diameter with a 0.16 to 0.2 inch (4 0 5 mm) long peduncle, usually with at least 10 bracts. Microsporophylls number 7 to 13, each with 3 or 4 pollen sacs.
- Seed cones are solitary or borne in clusters of 2 or 3, with a 0.24 to 0.4 inch (6 - 10 mm) long peduncle. Arils are green in color initially, turning red when ripe and measure 0.88 to 1.2 inches (2.2 - 3 cm) long and 0.44 to 0.48 inch (1.1 - 1.2 cm) wide.
- Seeds are obovoid-ellipsoid or obovoid shaped, sometimes laterally compressed, measuring 0.88 to 1.12 inches (2.2 - 2.8 cm), with a shortly mucronate or cuspidate apex.
Distribution. This species is native China - southwestern Guangdong (Xinyi Xian), Guangxi (Rong Xian), Hainan (Jianfeng Ling, Limu Ling, Wuzhi Shan), southeastern Xizang, southern and western Yunnan provinces; as well as in northeastern India, Laos, northern Myanmar, northern Thailand, and northern Vietnam. It naturally grow in mixed forests and forested ravines at elevations of circa 3,600 feet (1,100 m) above sea level.