Calocedrus macrolepsis, first described in 1873 by Wilhelm Sulpiz Kurz (1834-1878), is commonly known as Chinese incense-cedar, as Bách xanh, Tùng hÆ°Æ¡ng, PÆ¡ mu giả, Trắc bách diệp núi in the Vietnamese language, or as Š´”æŸ (CuÄ« bÇŽi) in Chinese. This is still sometimes seen listed and remains a synonym for Libocedrus macrolepis.
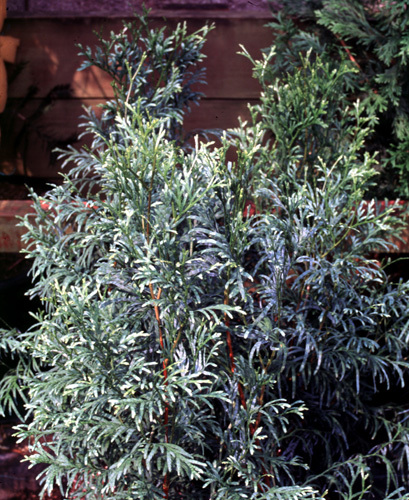
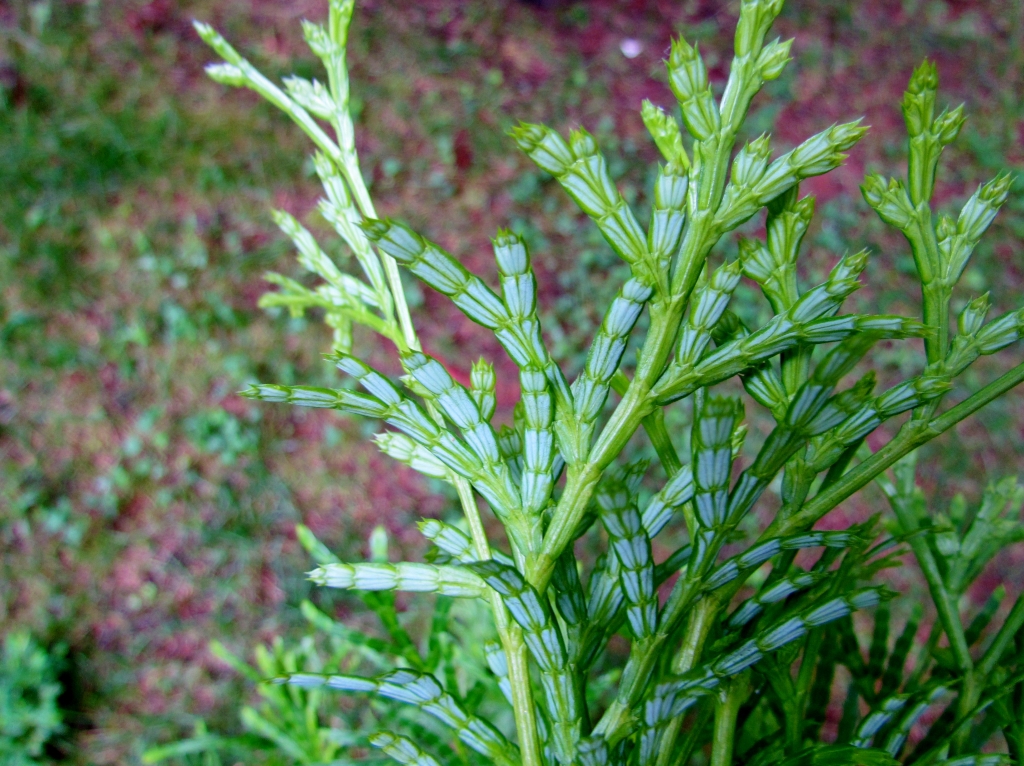
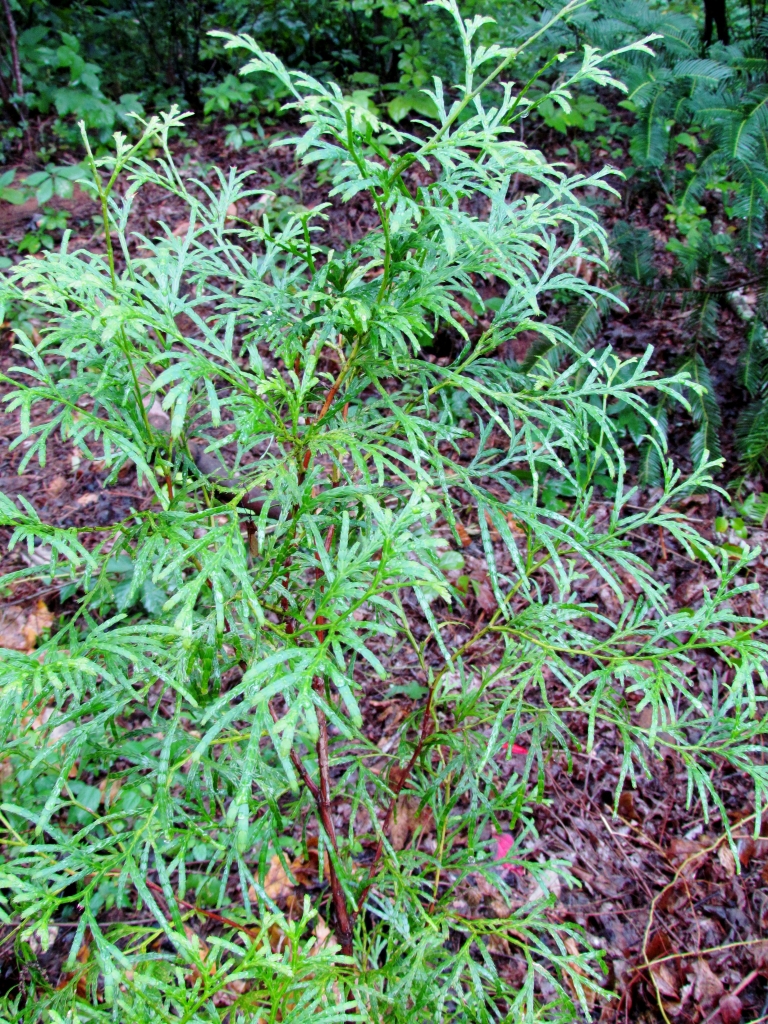
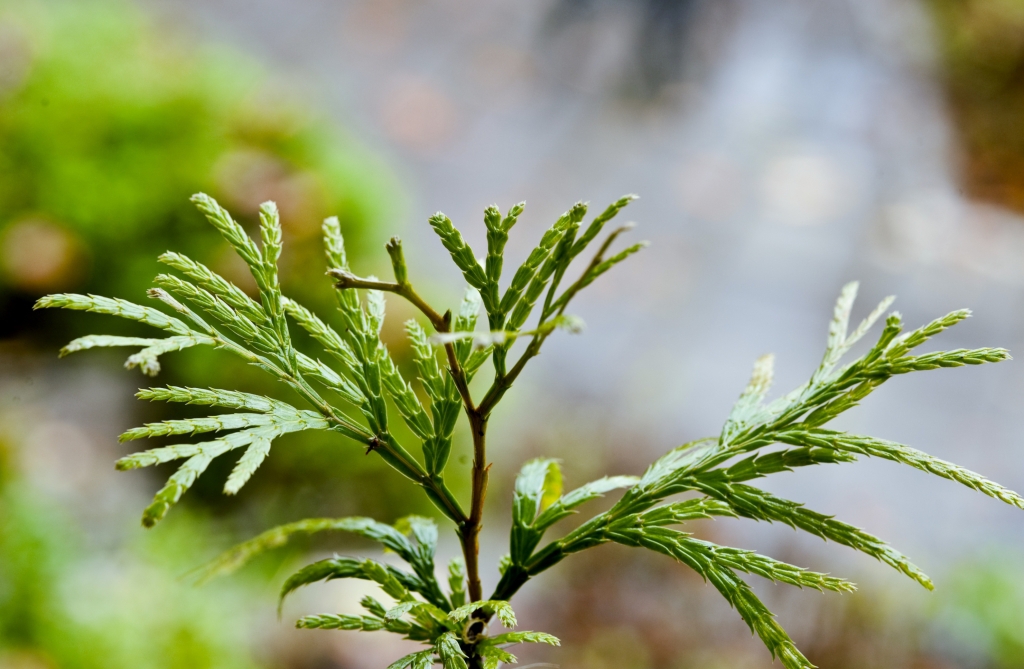
Description. Chinese incense-cedar is an evergreen coniferous species of tree which will grow to a mature height of 50 to 80 feet (15 - 25 m) tall with a 24 to 32 inch (60 - 80 cm) diameter trunk at breast height. It's bole is straight when young, but often becoming twisted once over 30 feet (10 m) high. It's bark is dark brown with longitudinal fissures. It is well branched when young, with big branches growing nearly horizontal, producing an oviform crown. Leaves are scaly and closely inserted on twigs into nodes, each node with two large leaves and two smaller opposite leaves. Female cones are oval, very small, green when young, becoming violet-brown, lignified and opening into 3 fragments when mature with the middle fragment bearing 2 big winged seeds which mature in October-December.
Distribution. This species is native to
At the JCRA, we are always on the lookout for new screening evergreens. In this regard, we have seen C. decurrens (California incense-cedar) used successfully in several southern and mid-Atlantic states. However, it is only through recent plant expeditions conducted by Heronswood Nursery (Kingston, WA) that new germplasm of this sister Chinese species has become available. Chinese incense-cedar forms an upright evergreen tree or tall hedge/screen with rich Blue-green foliage. We have been pleasantly surprised with the performance of several Asian Cupressaceae and expect nothing less from this species.



