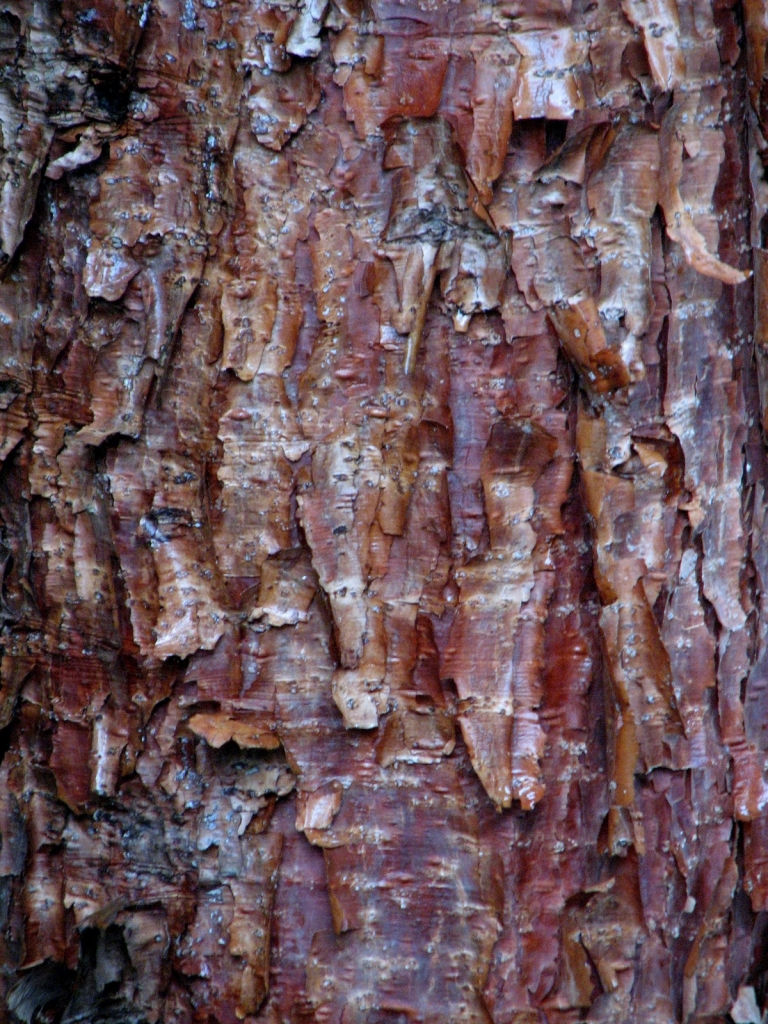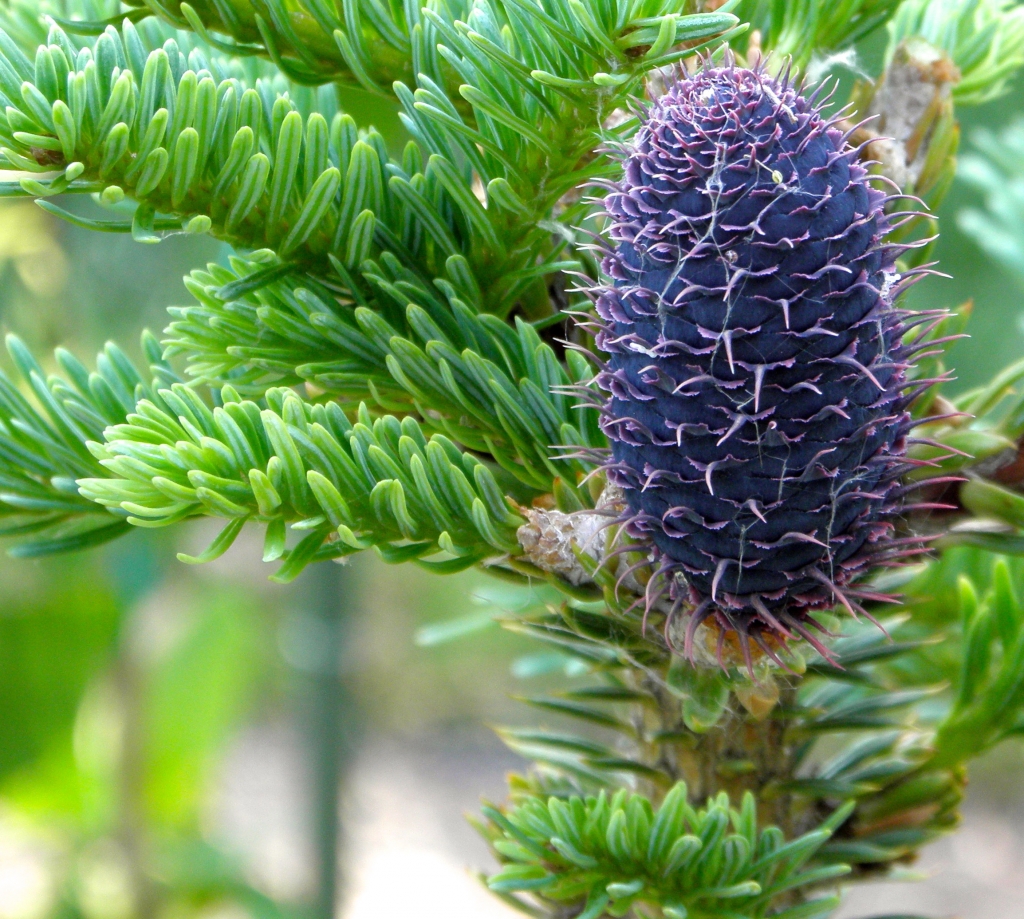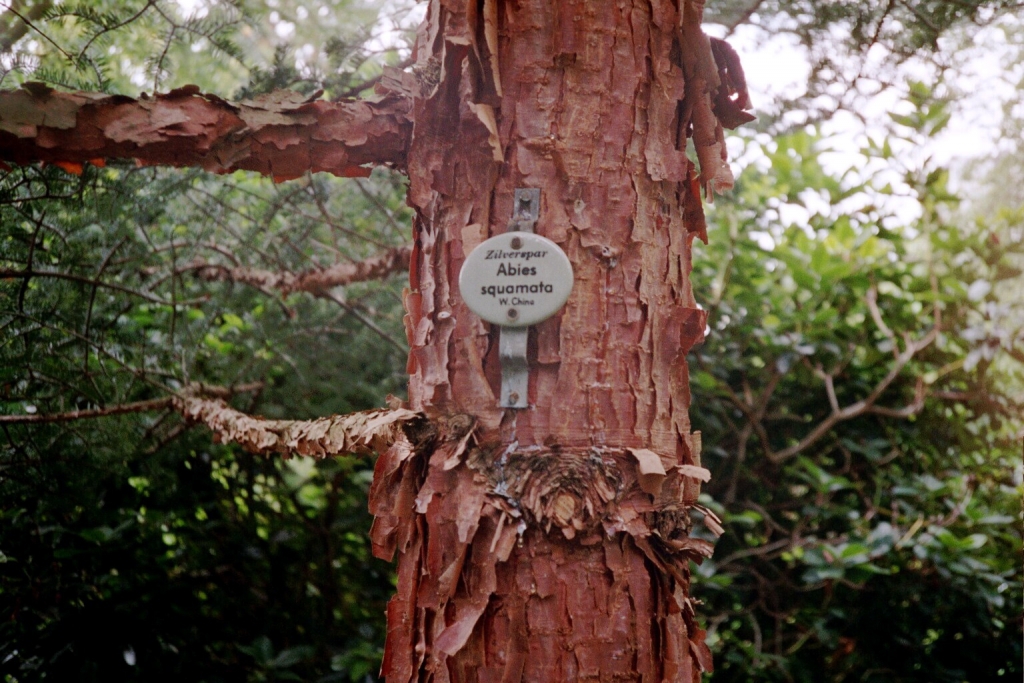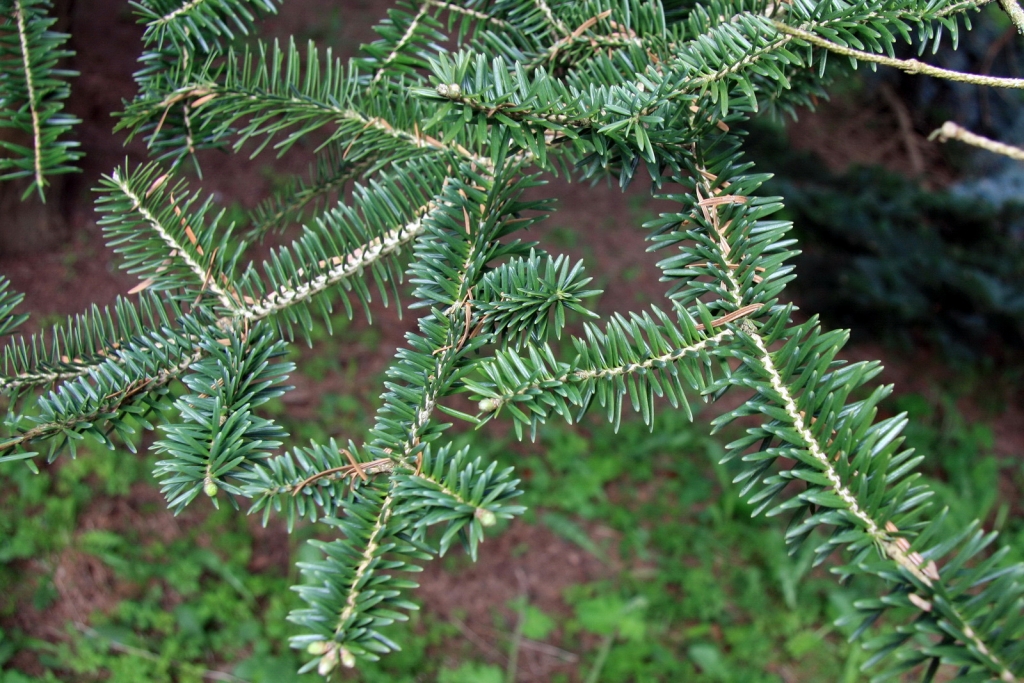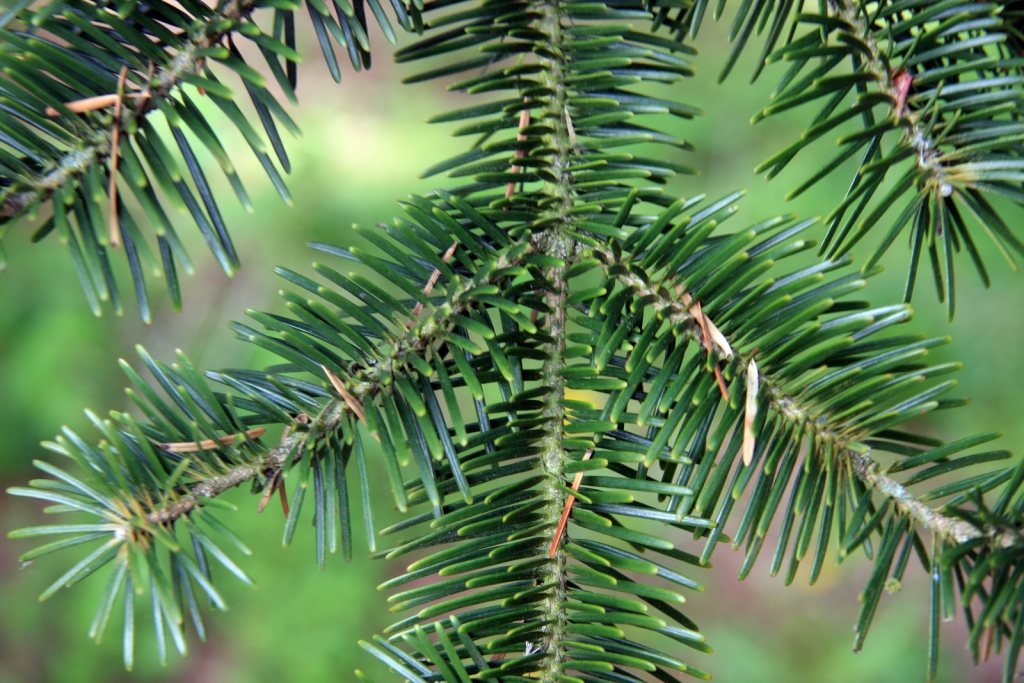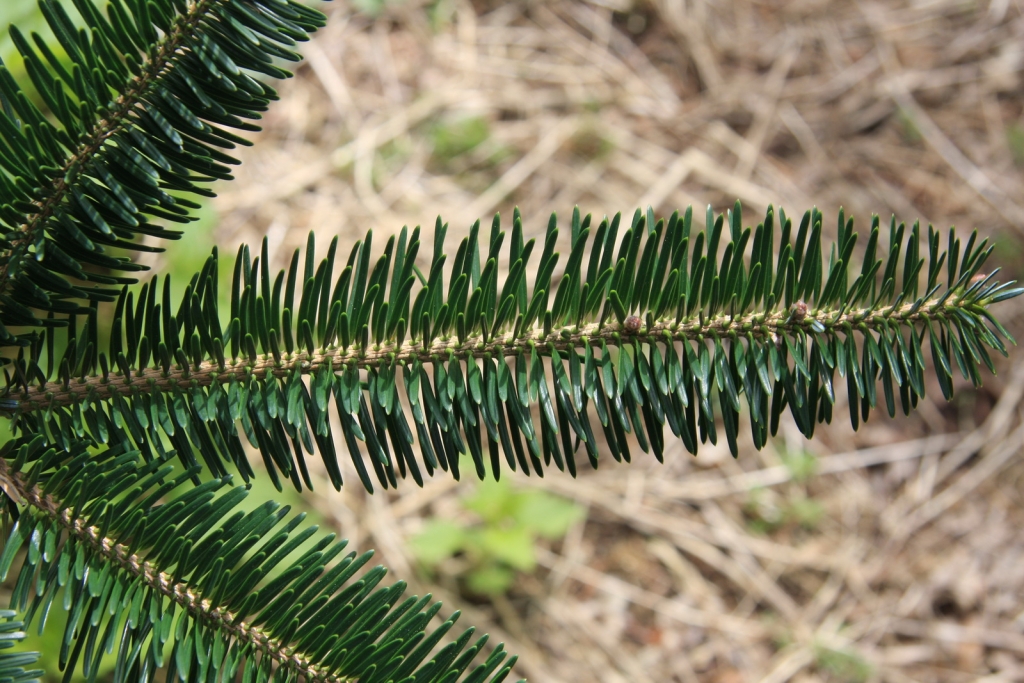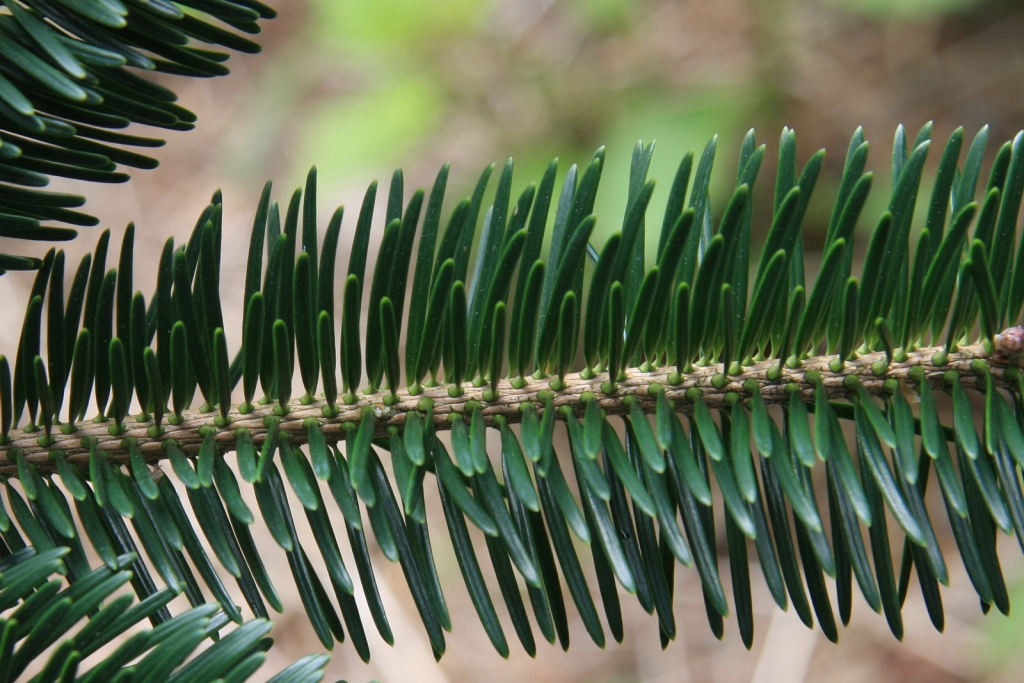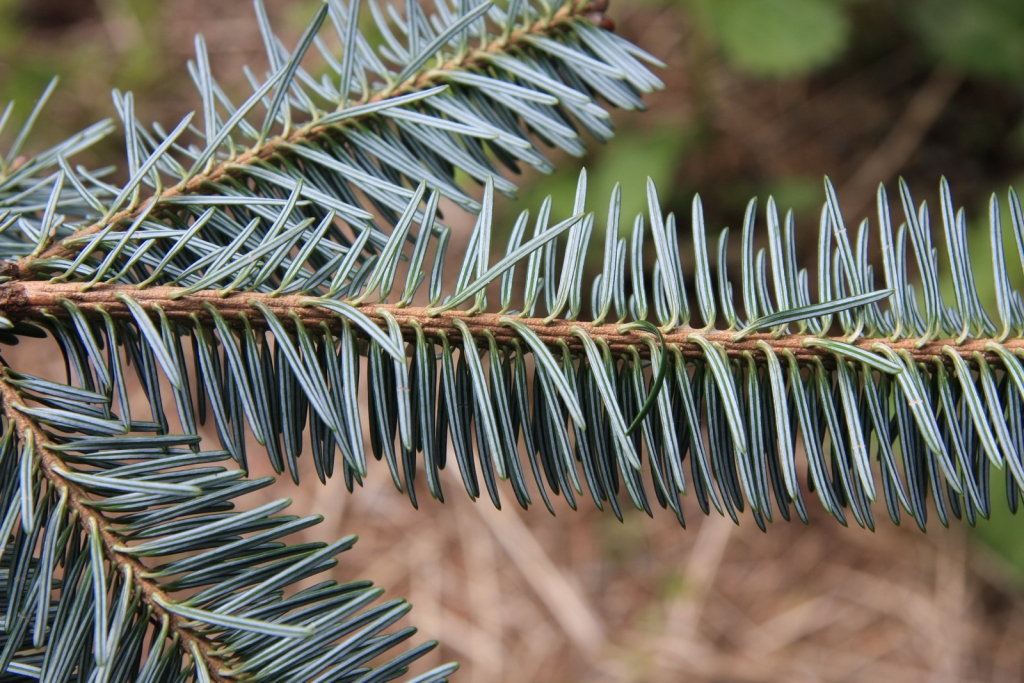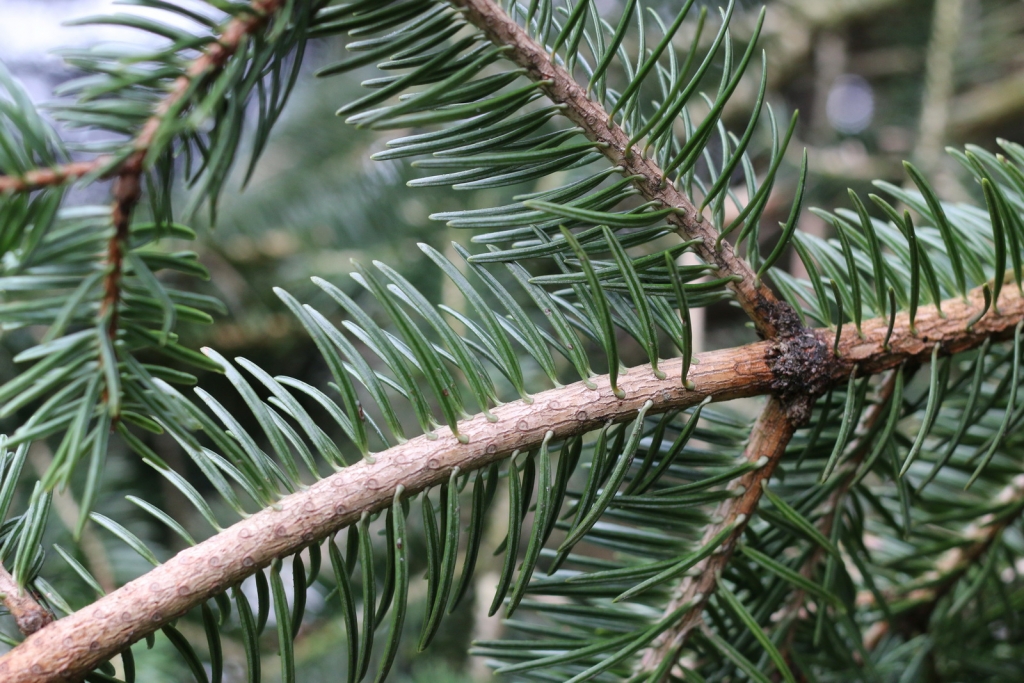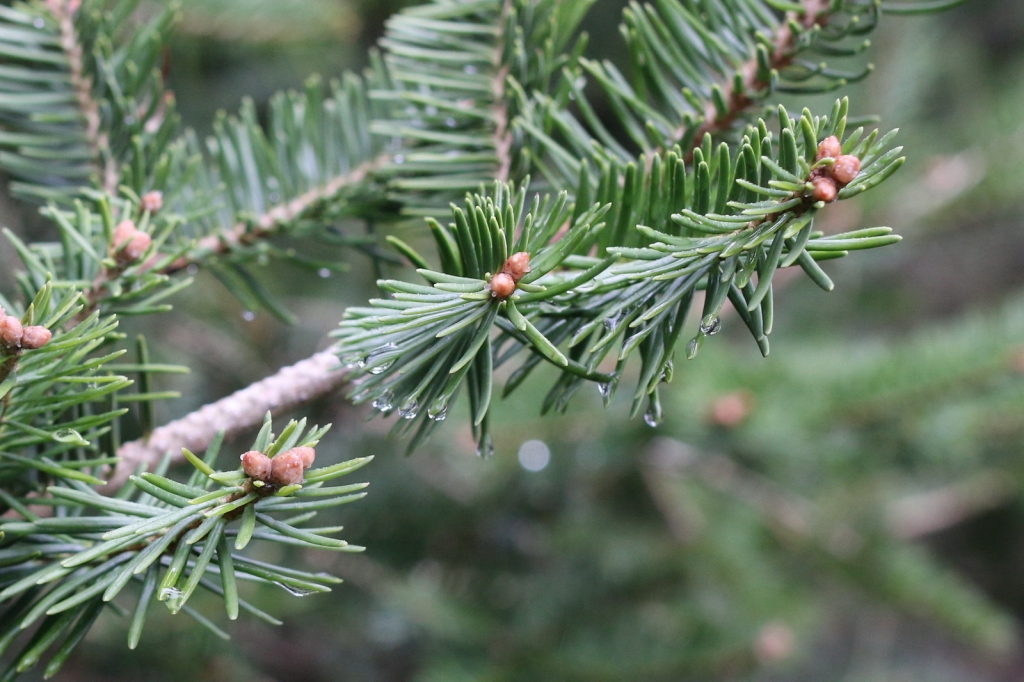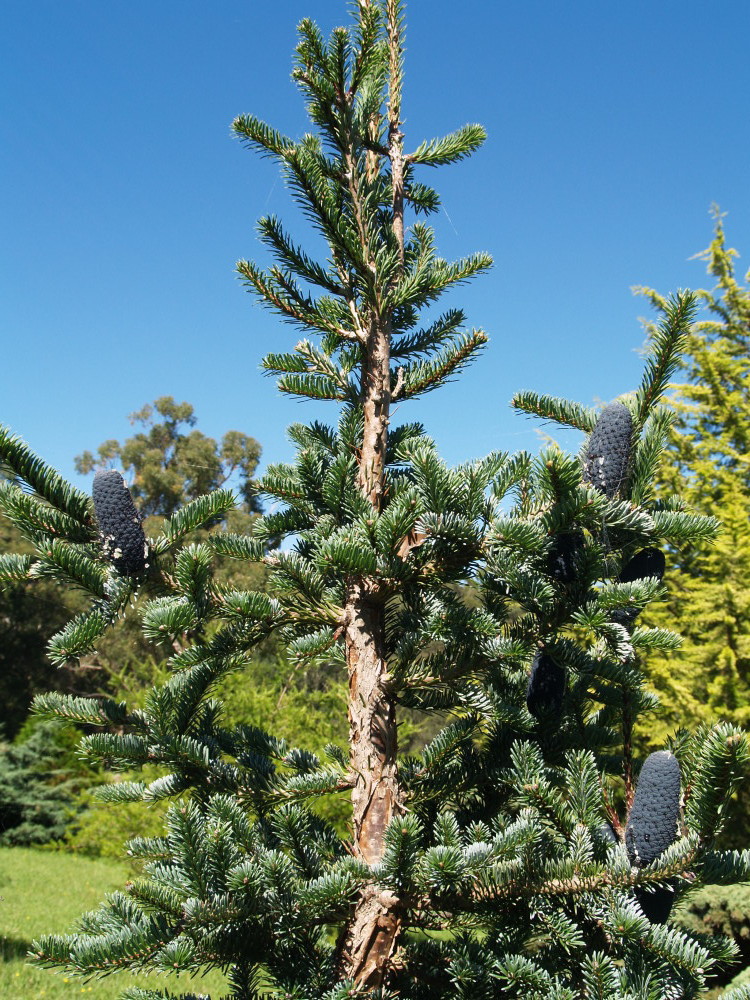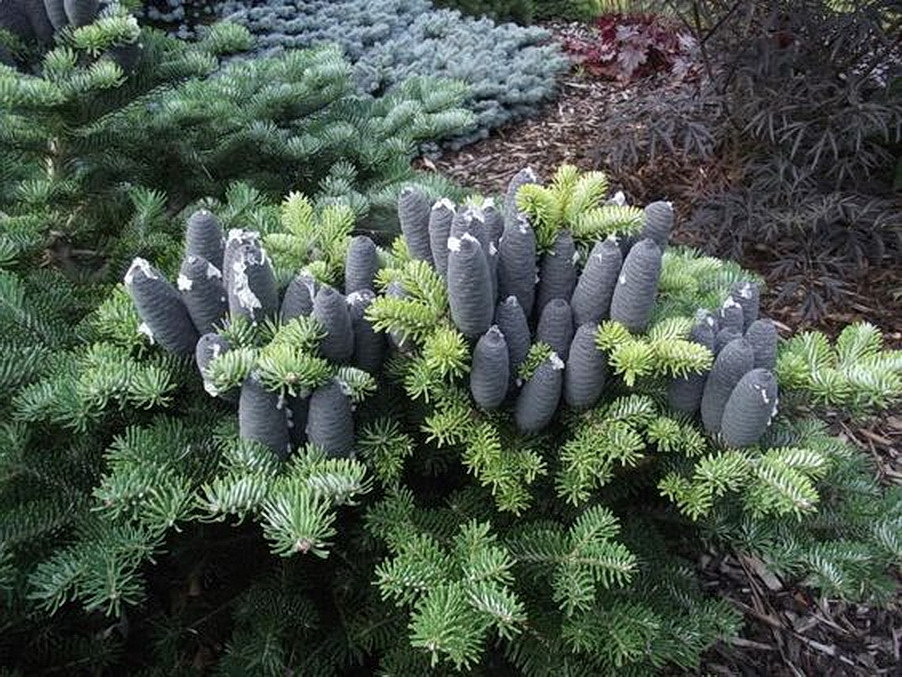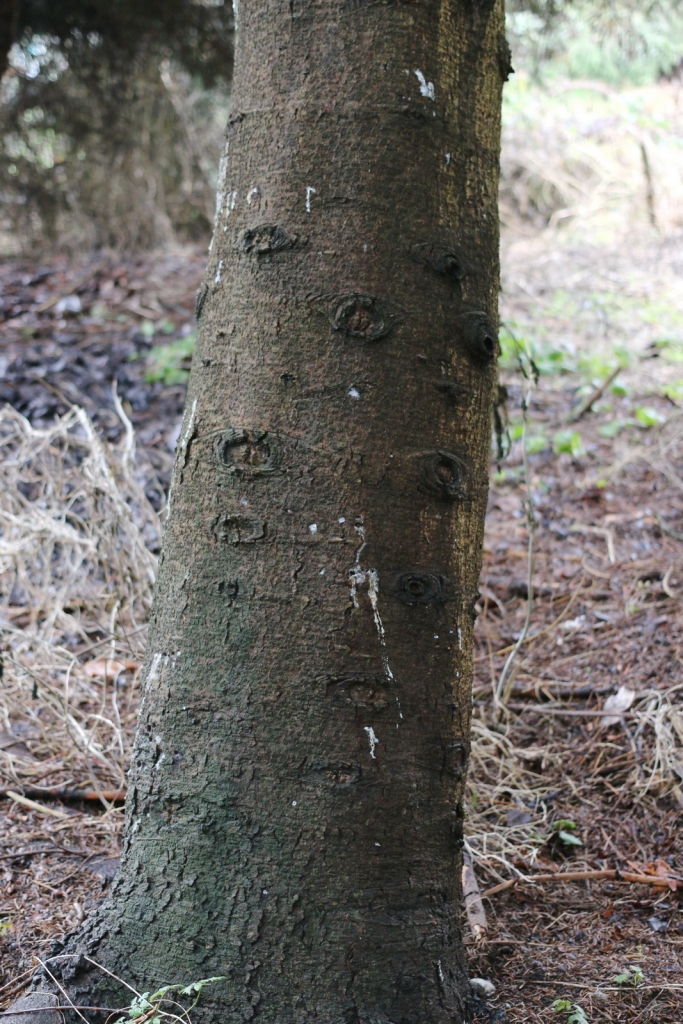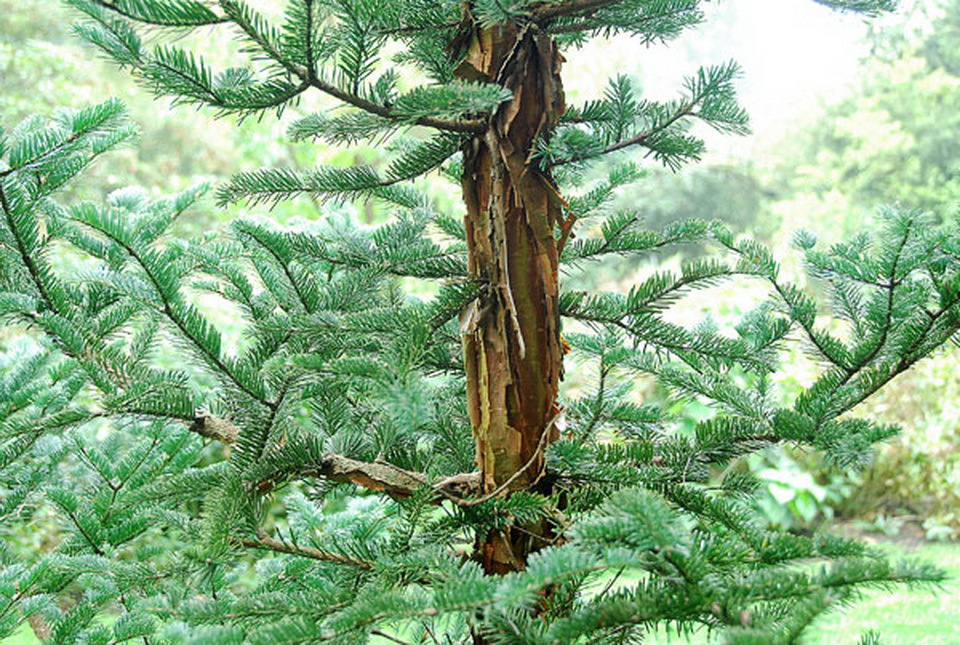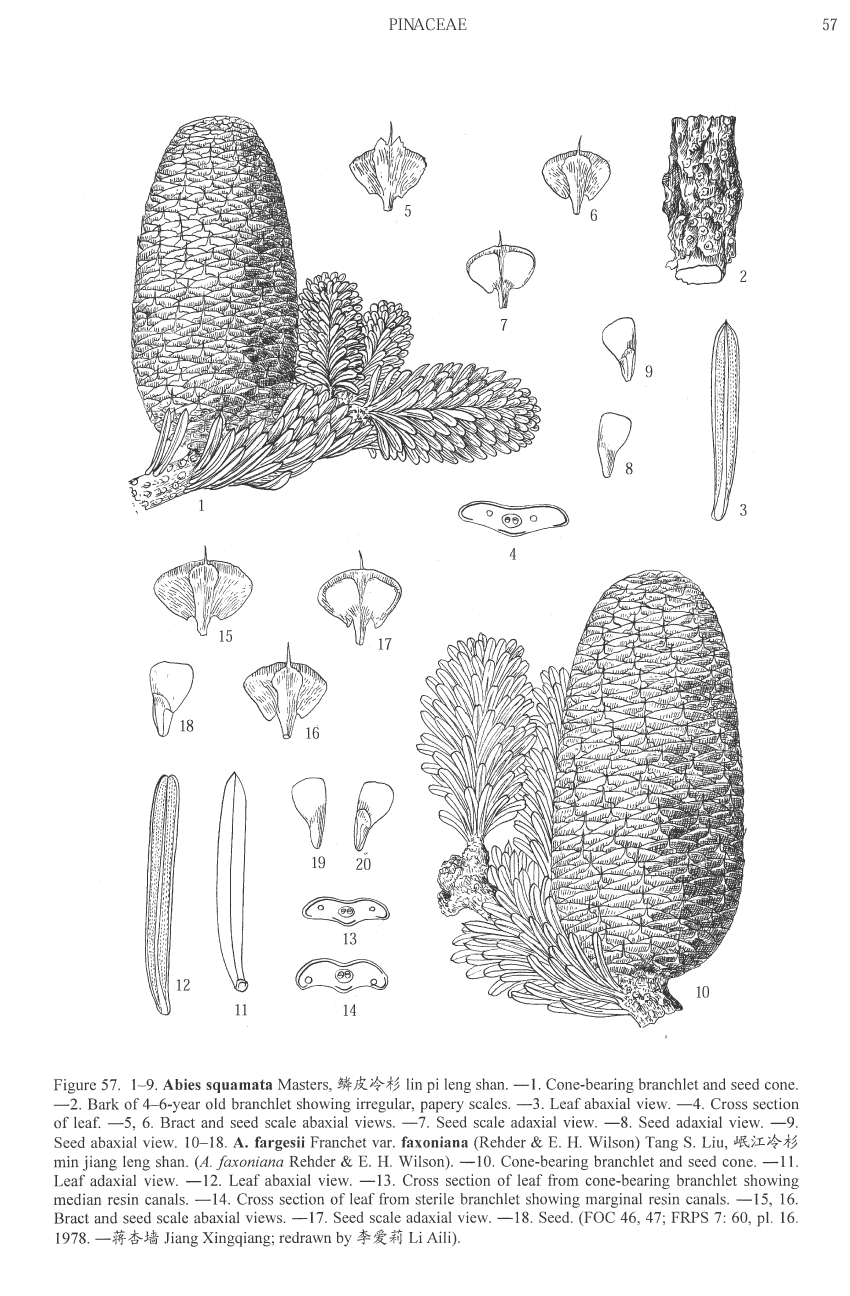
Abies squamata, as described in 1906 by Maxwell Tylden Masters (1833-1907), in The Gardeners' Chronicle: a weekly illustrated journal of horticulture and allied subjects, is commonly known as flaky fir; as well as 鳞皮Š†·æ‰ (lin pi leng shan) in the Chinese language. Local Tibetans know this fir as "bollo", but that term is a general term for firs and spruces. The species name, Latin for scaly, refers to this conifer's papery, peeling bark.
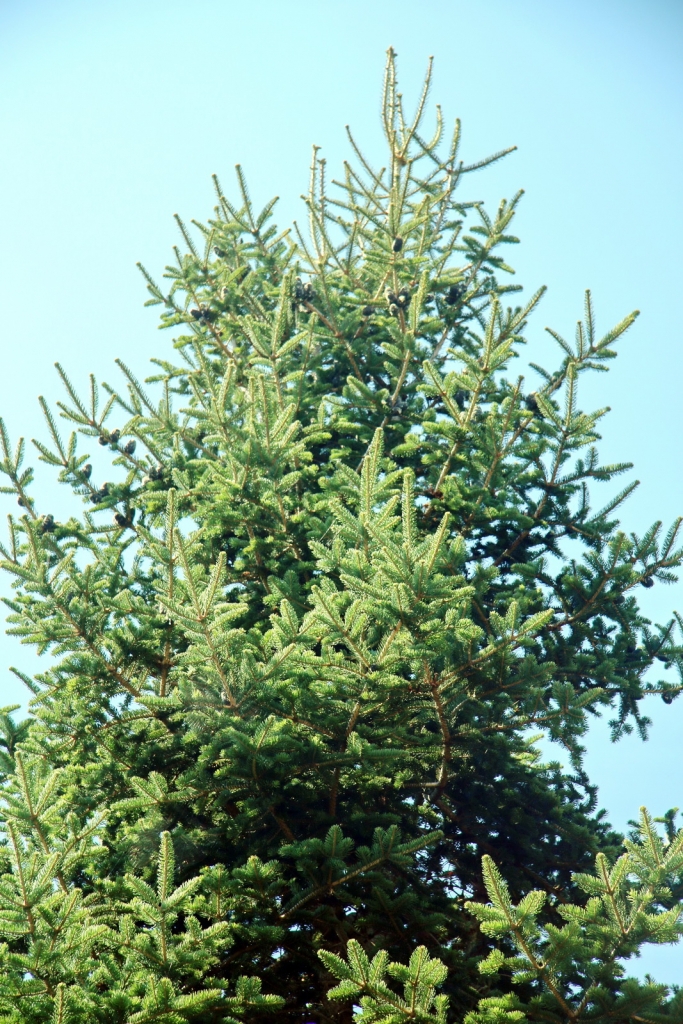
Description. Flaky fir is an evergreen coniferous species of tree which grows to mature heights of 120 feet (40 m) tall; with trunk up to 40 inches (1 m) in diameter, measured at breast height.
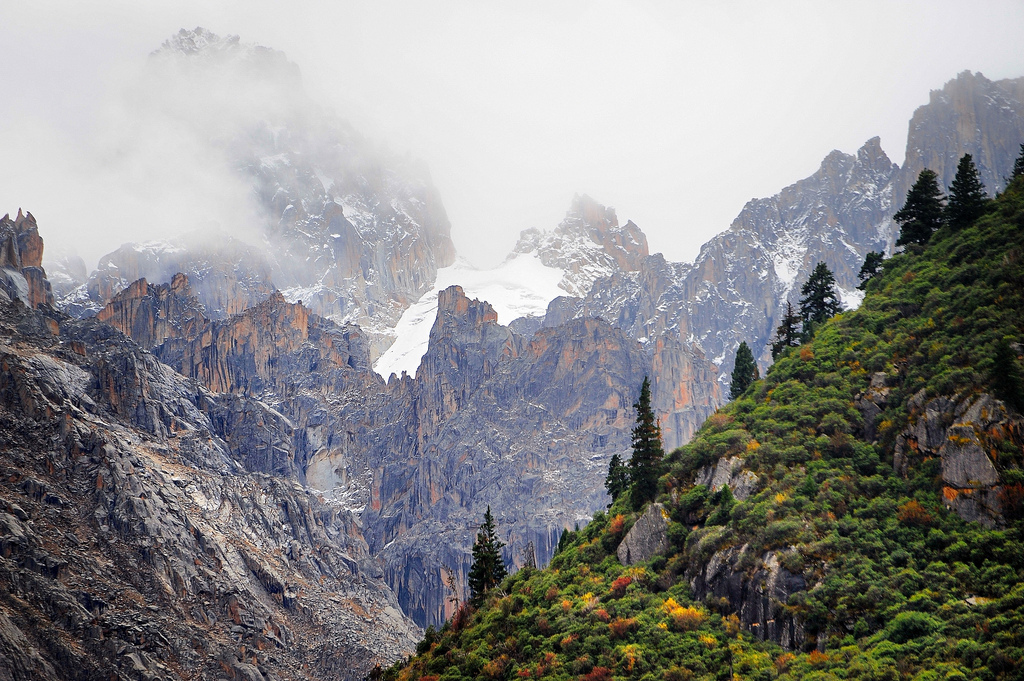
Distribution. This species is native to China - western Sichuan, growing the alpine zone at elevations of 11,200 to 12,800 feet (3,500 - 4,000 m) above sea level; also in southern Qinghai province, as well as eastern Tibet.
Hardy to USDA Zone 6 - cold hardiness limit between -10° and 0°F (-23.2° and -17.8°C).