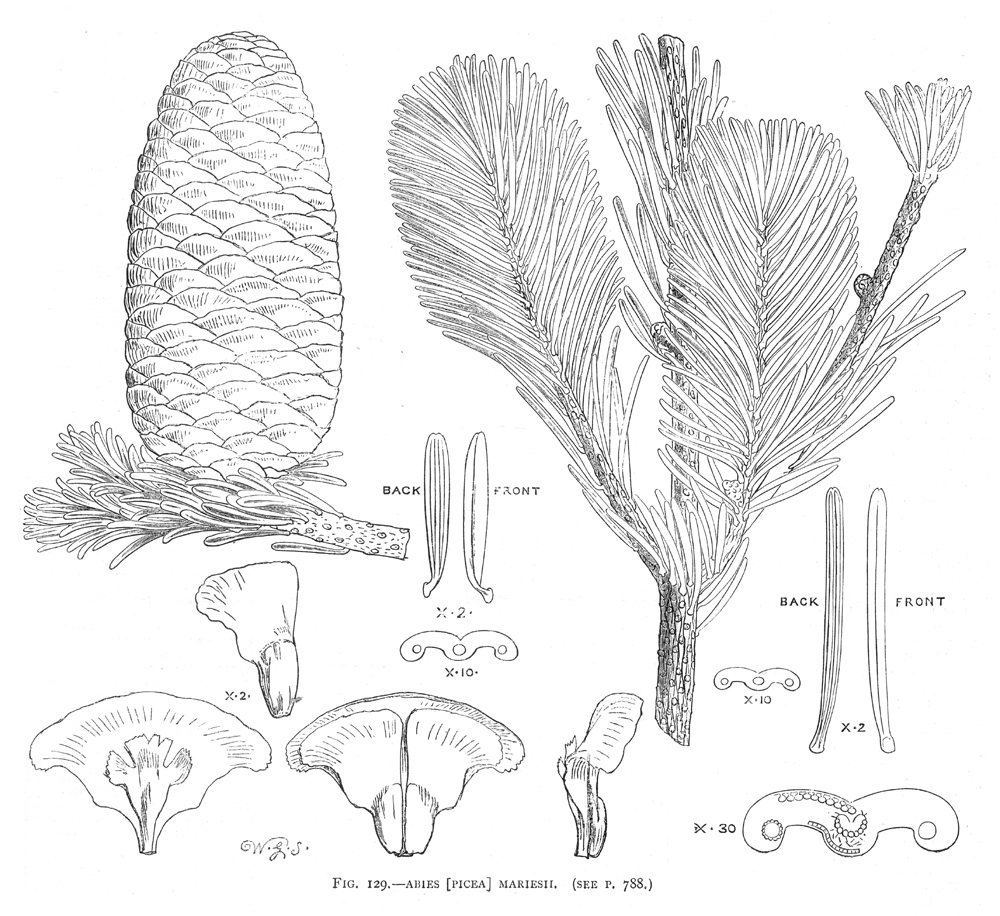
Abies mariesii, first described in 1879 by Maxwell Tylden Masters (1833-1907), is commonly known as Maries' fir or as オオシラビソ or アオモリトドマツ (Oh-shirabiso, or Aomori-todomatsu) in the Japanese language. Maries' fir is named after the English plant collector Charles Maries (1851-1902), who introduced the species to Britain in 1879. According to the account in "Hortus Veitchii", whilst waiting at Aomori on the main island (HonshŠ«) for a steamer to convey him to Hakodate on the island of HokkaidŠ:
Maries noticed a conifer new to him growing in a garden, and learnt that it could be found in quantity on a neighbouring mountain. He went in search, and had reached a height of 3,500 ft., when it became obvious that the bamboo scrub formed an impassable barrier on that side of the mountain, and he reluctantly had to turn back, although the object of his search could plainly be seen. The following day he again made the ascent, but this time from the north side, and he succeeded in procuring cones of a new species, since named by Dr. Masters, Abies mariesii.
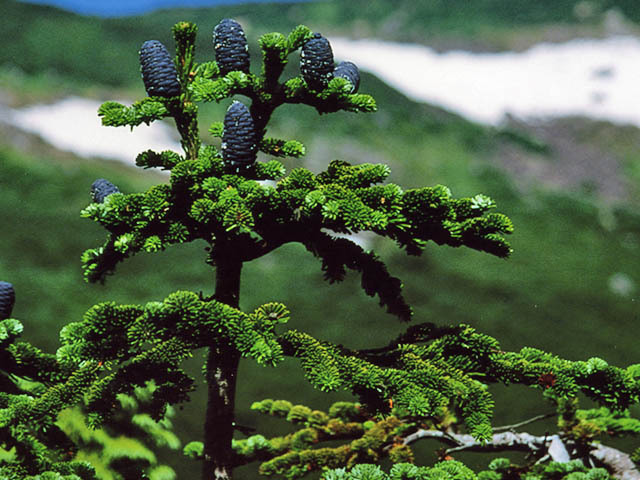
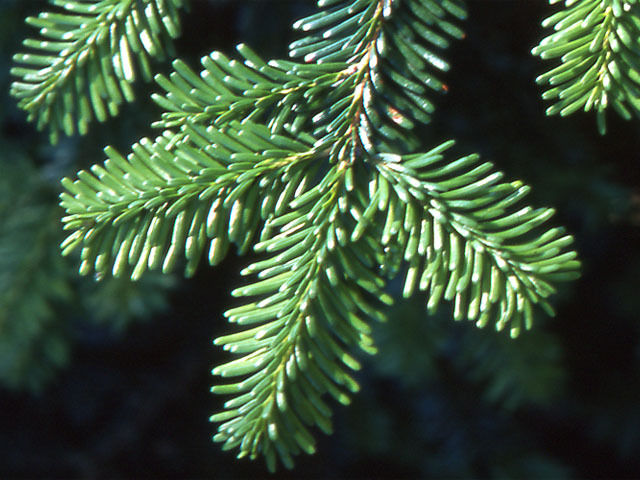
Description. Maries' fir is an medium-growing, evergreen coniferous species of tree which will grow to heights of 50 to 100 feet (15 - 30 m) tall with a trunk diameter of up to 3 feet (0.8 m), although smaller and sometimes shrubby at tree line. The leaves are needle-like, flattened, 0.6 to 1 inch (1.5 - 2.5 cm) long and 0.08 inch (2 mm) wide by 0.02 inch (0.5 mm) thick, matt dark green above, and with two white bands of stomata below, and slightly notched at the tip. The leaf arrangement is spiral on the shoot, but with each leaf variably twisted at the base so they lie flat to either side of and above the shoot, with none below the shoot. The shoots are orange-red with dense velvety pubescence. The seed cones are 2 to 4.4 inches (5 - 11 cm) long and 1.2 to 1.6 inches (3 - 4 cm) broad, dark purple-Blue when young, maturing brown; the scale bracts are short, and hidden in the closed cone. The winged seeds are released when the cones disintegrate at maturity about 6 to 7 months after pollination. Maries' fir is very closely related to Pacific silver fir (A. amabilis) from the Pacific coast of North America, which is distinguished by its slightly longer leaves 0.8 to 1.8 inches (2 - 4.5 cm) and larger cones 3.6 to 6.8 inches (9-17 cm long).
Distribution. This species is native to Japan - central and northern HonshŠ« island, where it grows at altitudes of 2,400 to 6,100 feet (750 - 1,900 m) above sea level in northern HonshŠ«, and 5,800 to 9,300 feet (1,800 - 2,900 m) in central HonshŠ«, always in temperate rain forest with high rainfall and cool, humid summers, and very heavy winter snowfall.