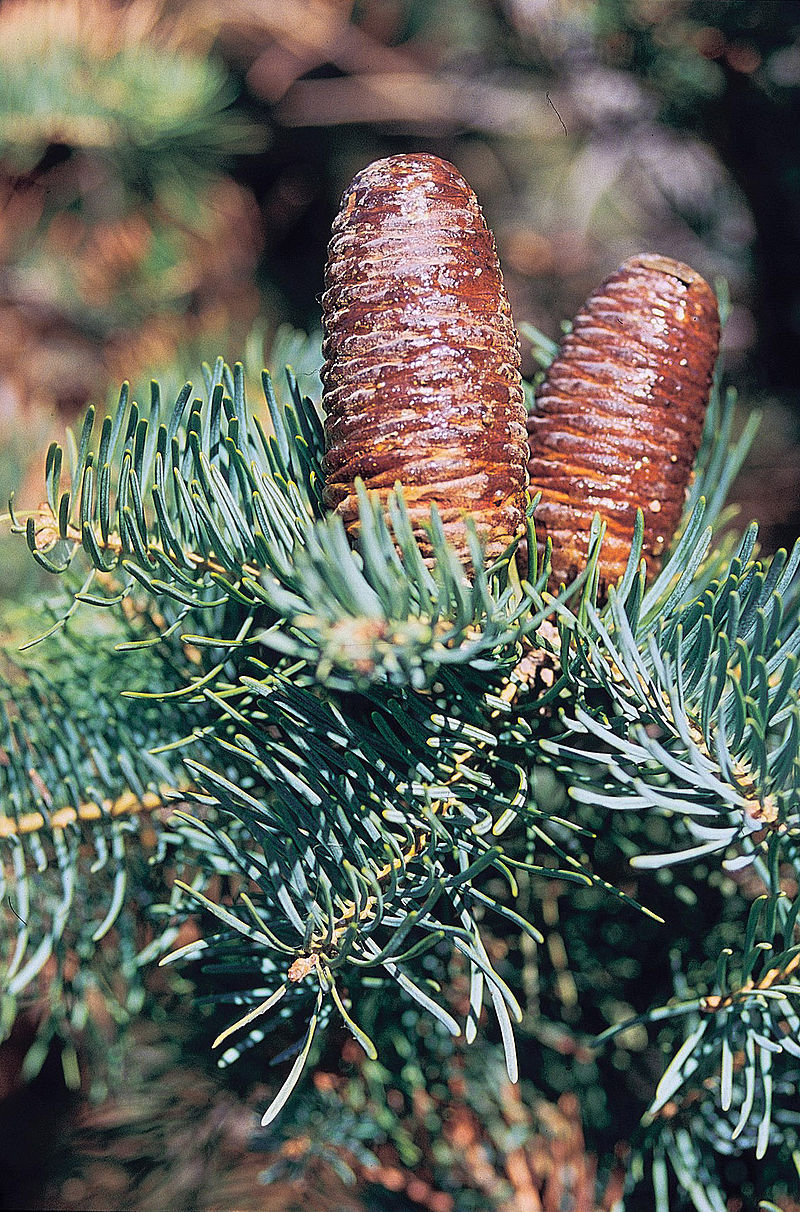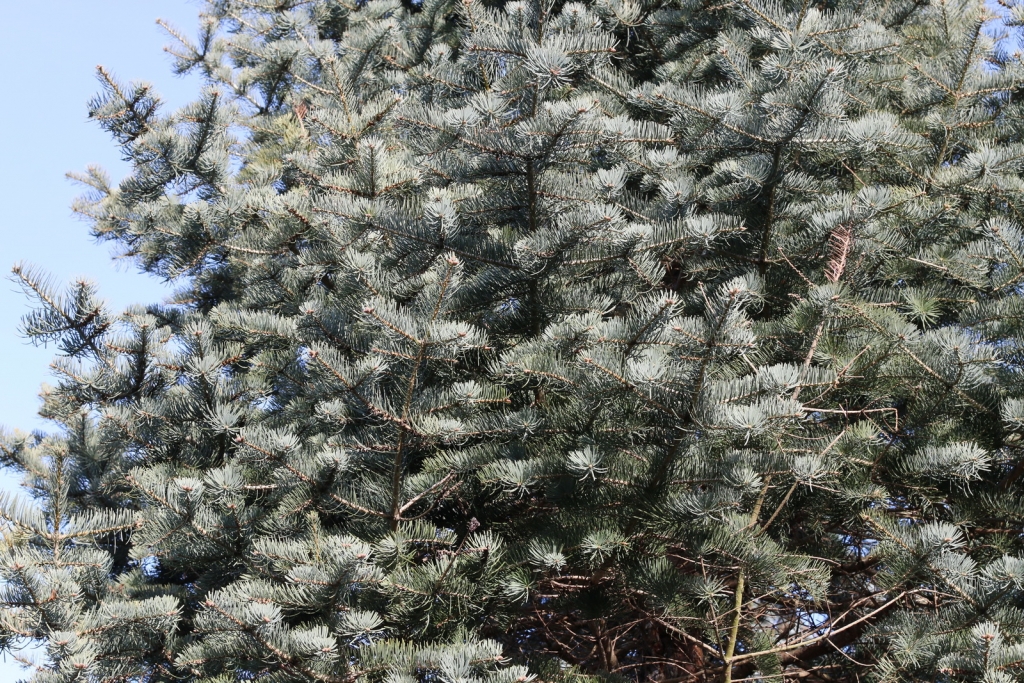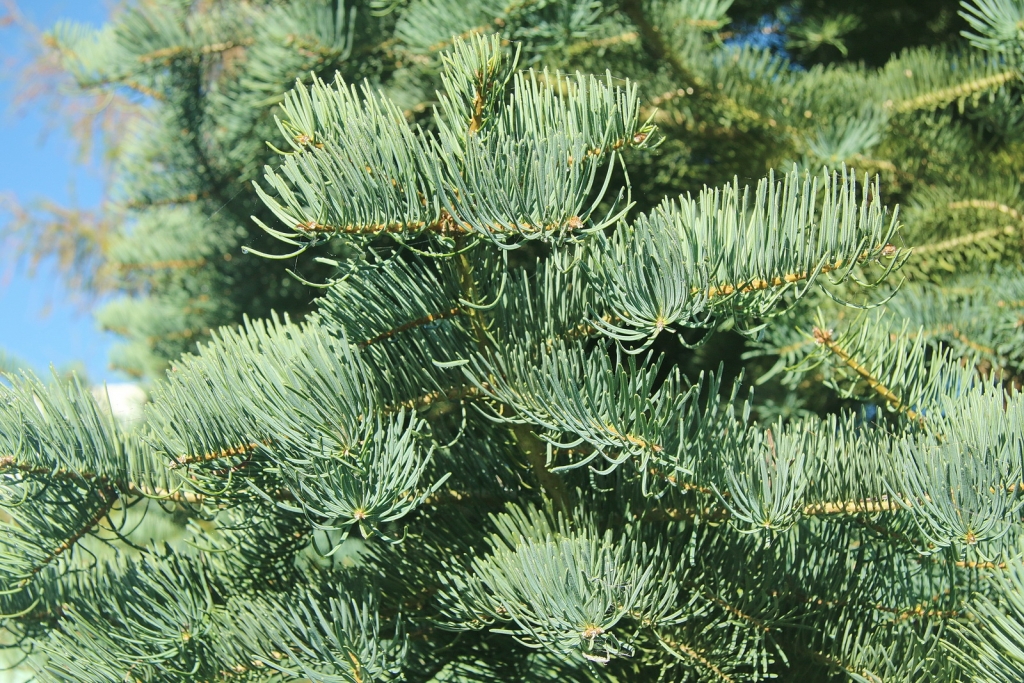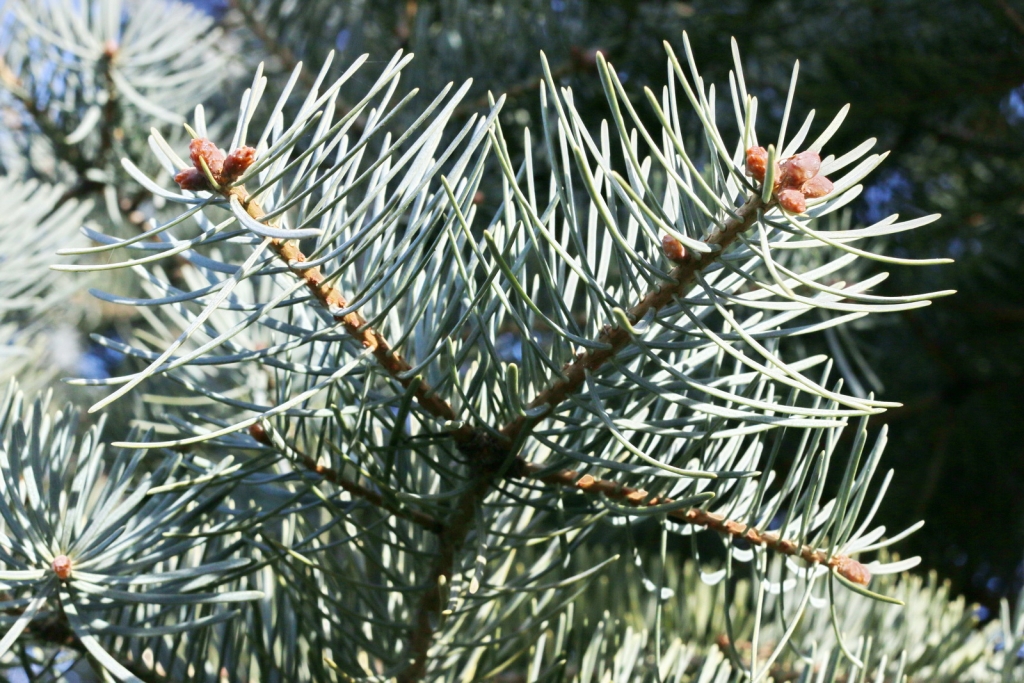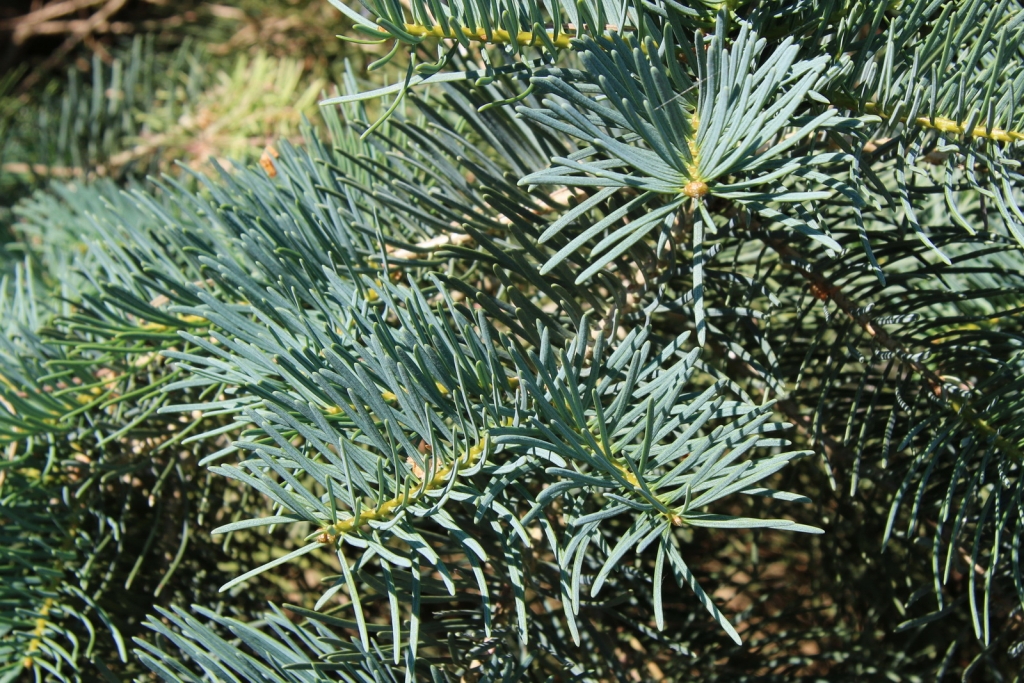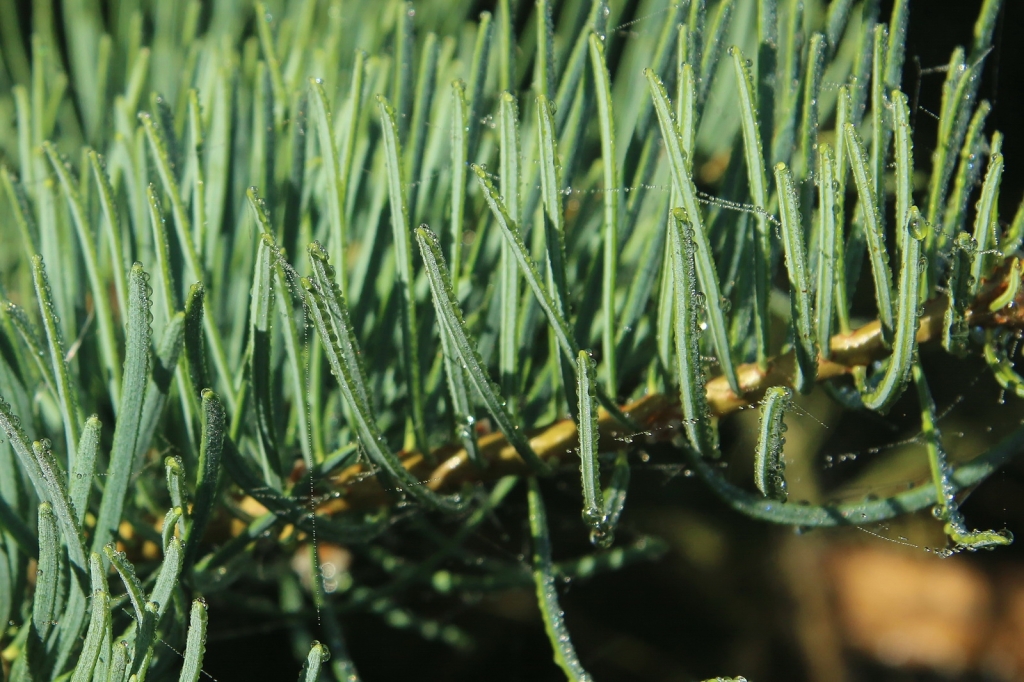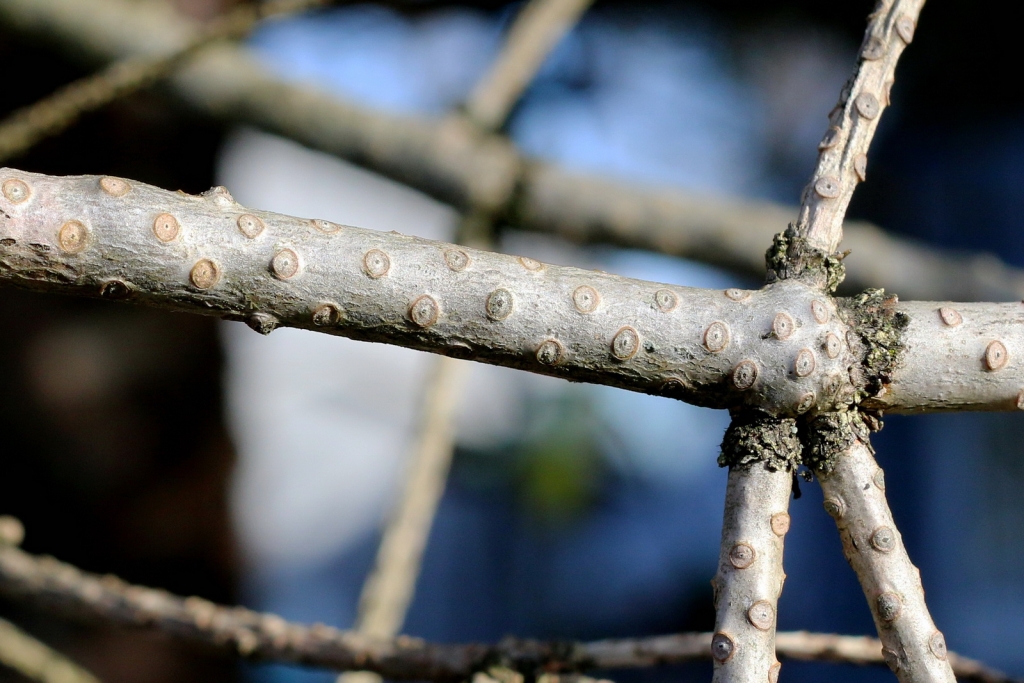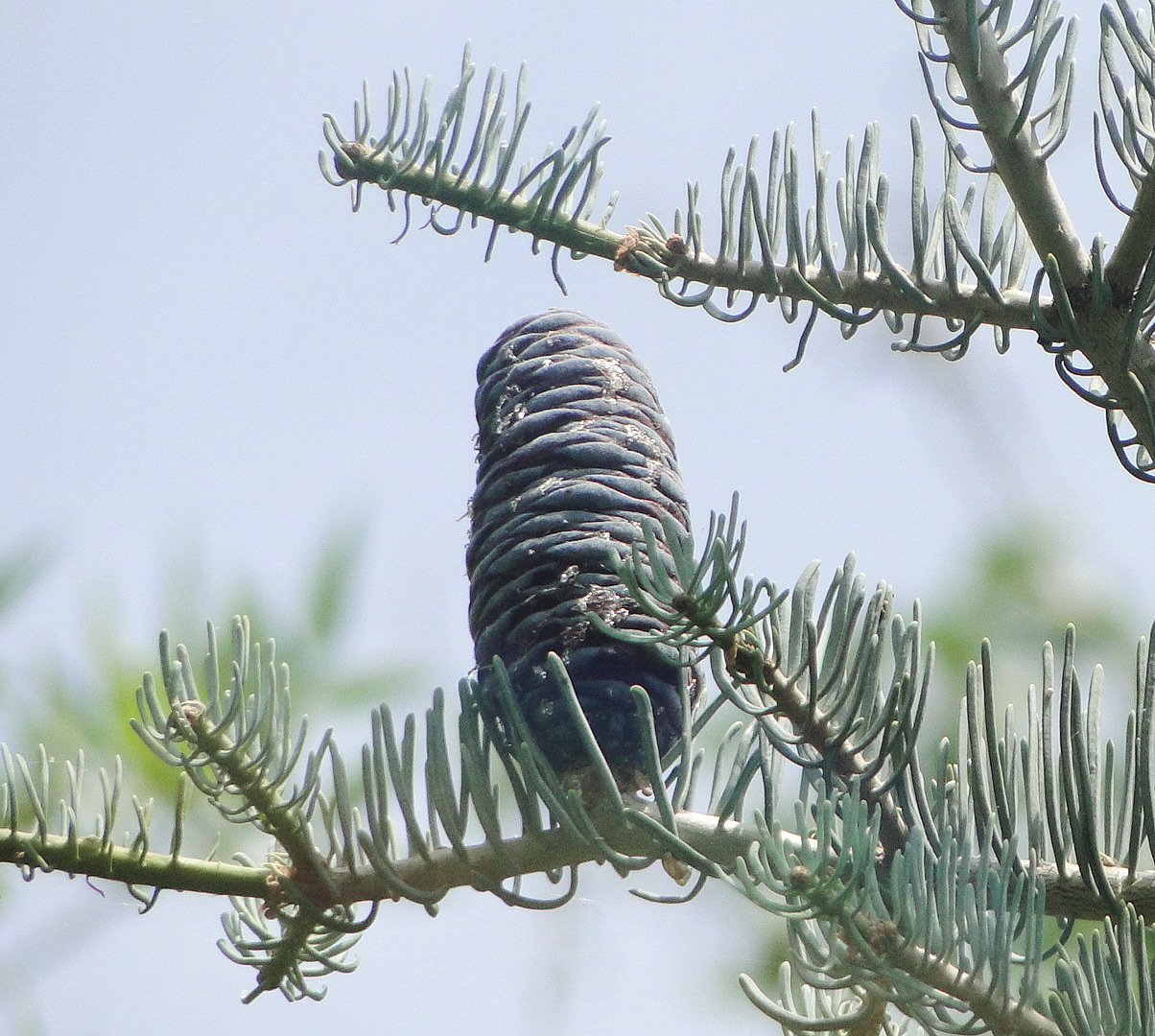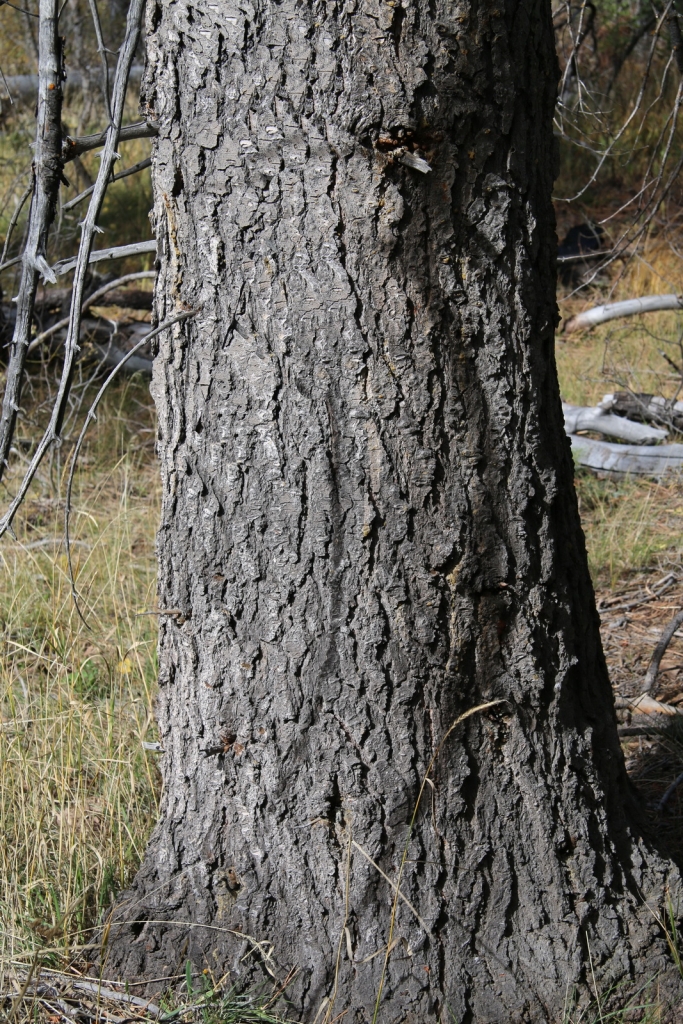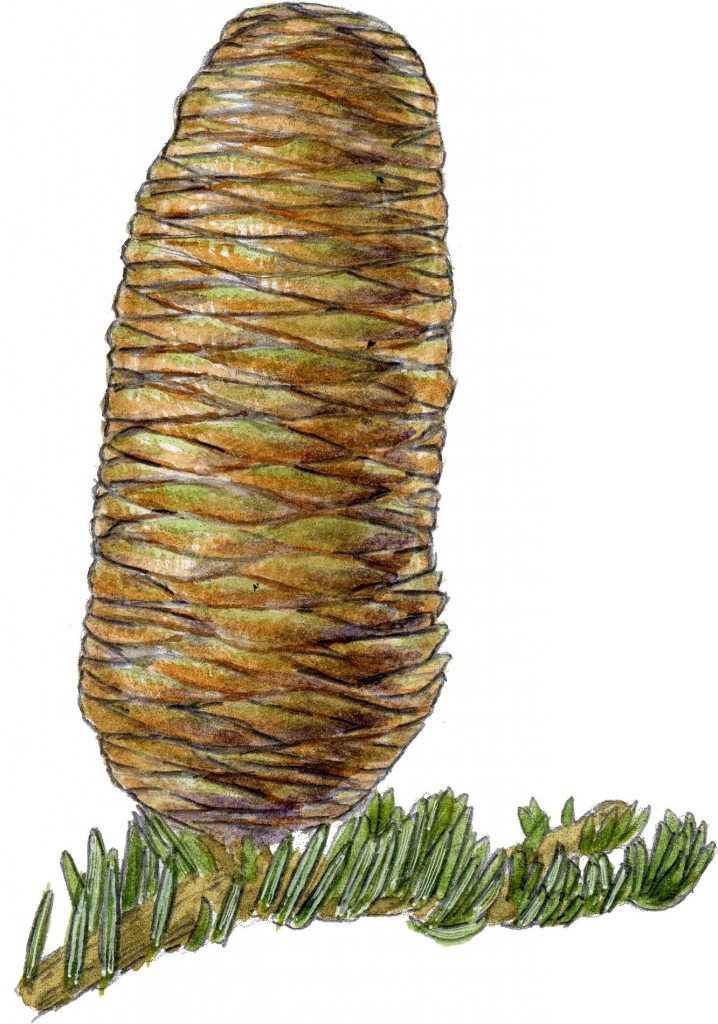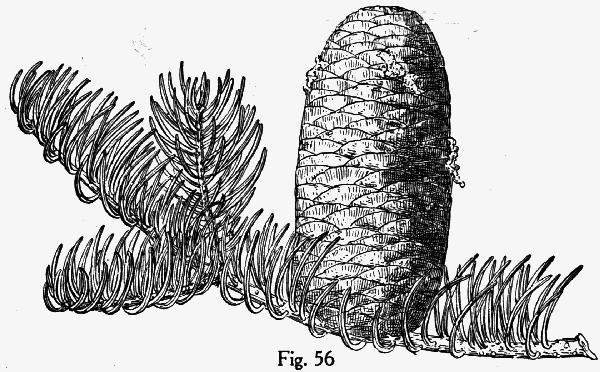
Abies concolor, as described in 1861 by (Gordon and Glendinning) William (Wilhelm) Hillebrand (1821-1886), in Verhandlungen des Naturhistorischen Vereines der Preussischen Rheinlande und Westphalens, 18th edition, is commonly known as white fir, Colorado white fir, or Rocky Mountain white fir; as well as abeto del Colorado, or pino real blanco in the Spanish language. The species name, "concolor," means "same color" in the Latin language, referring to needles having the same color on the adaxial and abaxial sides.
Ethnobotany. White fir is a preferred construction species because of its nail-holding ability, lightness in weight, and resistance to split, twist, and pitch. It is straight-grained, non-resinous, fine-textured, stiff, and strong.
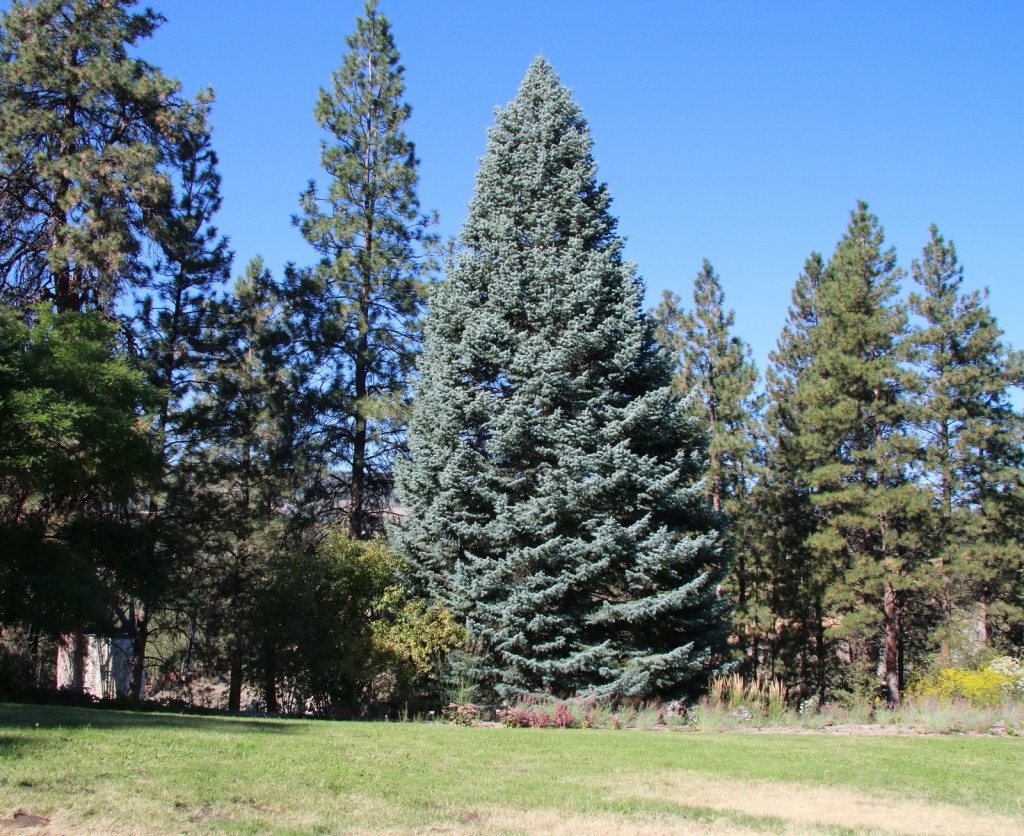
White fir is popular as a Christmas tree and for Christmas decoration owing to its soft needles, generally excellent needle retention and abundance. It is often marketed as concolor or white fir.
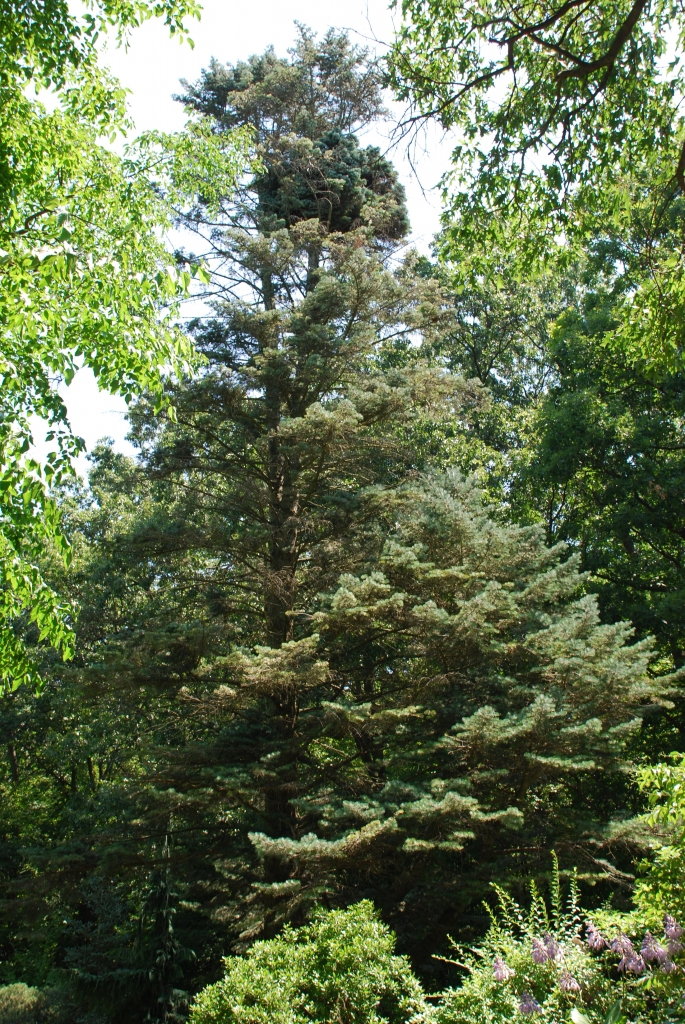
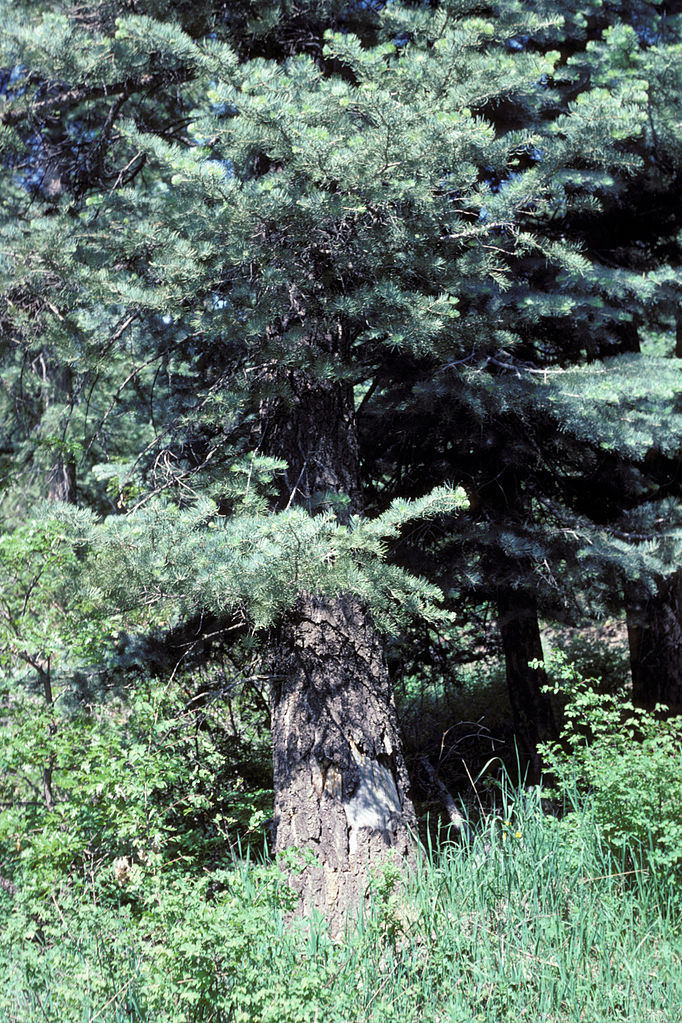
Description. White fir is an evergreen coniferous tree which grows to mature heights of 130 feet (40 m) tall and with a trunk 35 inches (90 cm) in diameter, measured at breast height.
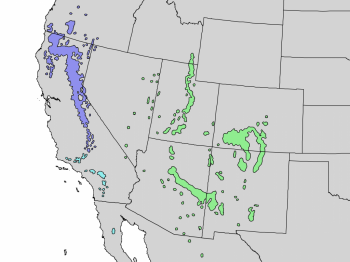
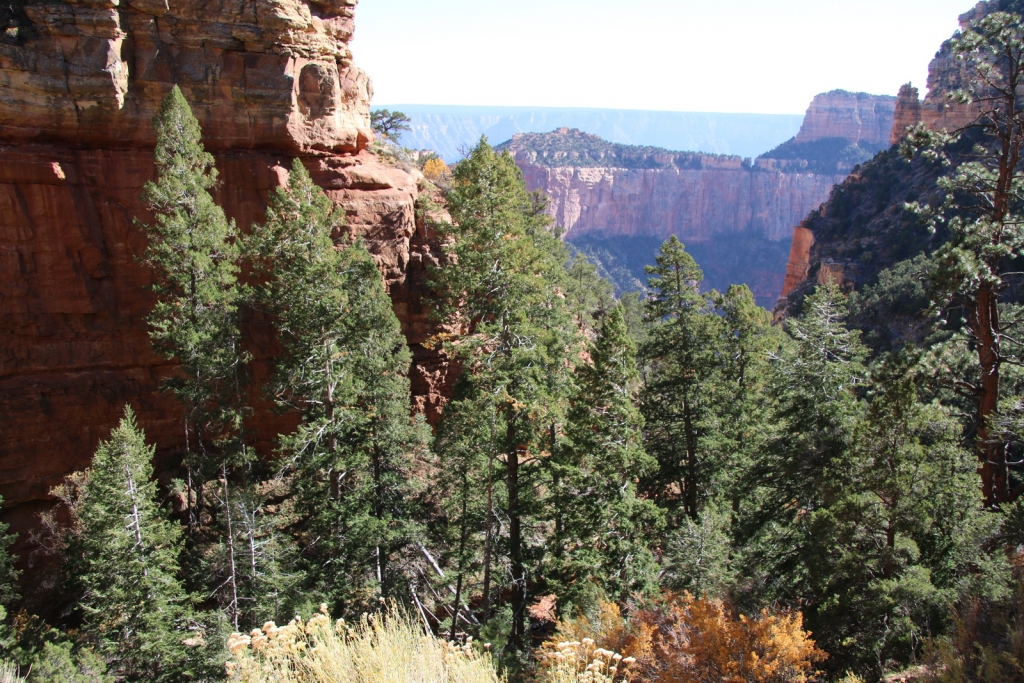
Distribution. This species is native to USA - the states of Idaho, Oregon, California, Nevada, Utah, Colorado, New Mexico, and Arizona as well as Mexico - Baja California Norte and Sonorawestern, growing at elevations of 3,000 to 10,000 feet (920 - 3050 m) above sea level.
Hardy to USDA Zone 4 - cold hardiness limit between -30° and -20°F (-34.3° and -28.9°C). This conifer has evolved to thrive in Semiarid steppe and Mediterranean climates.
















