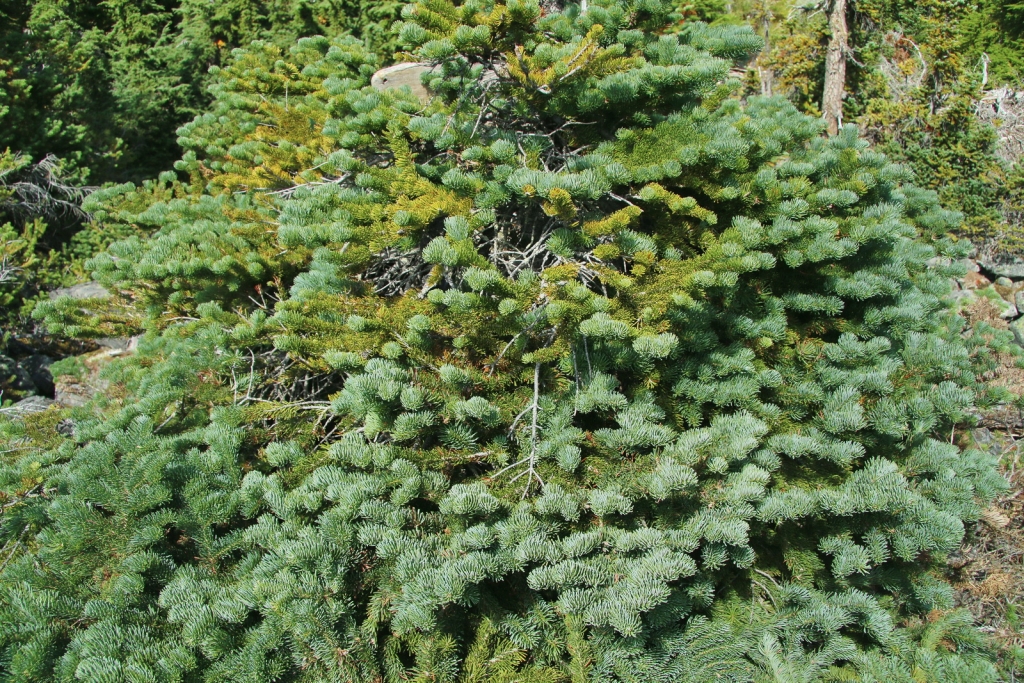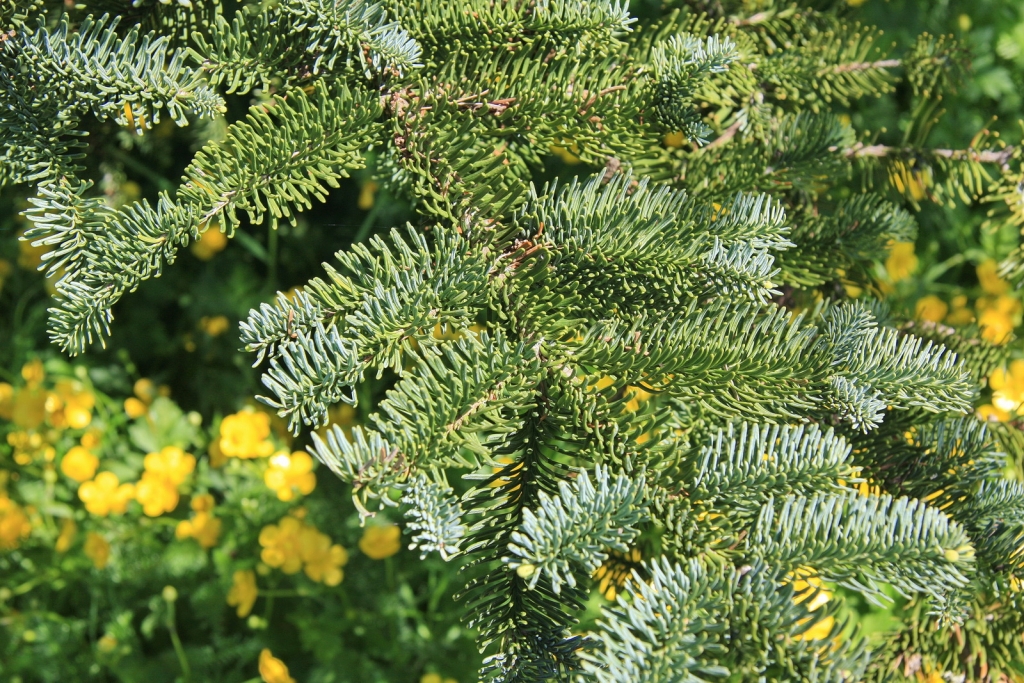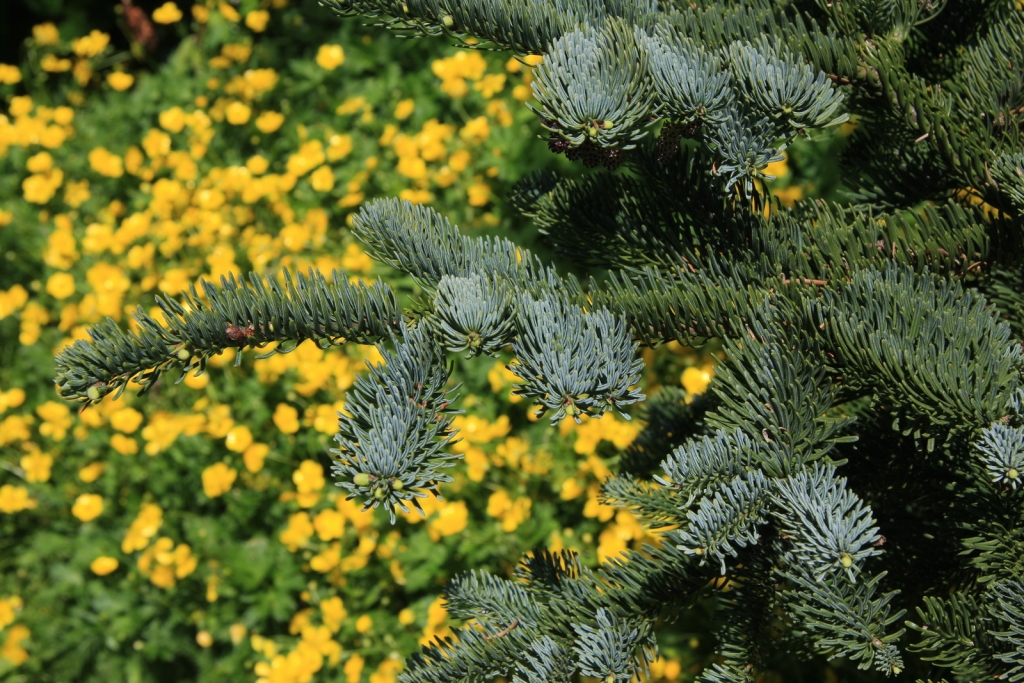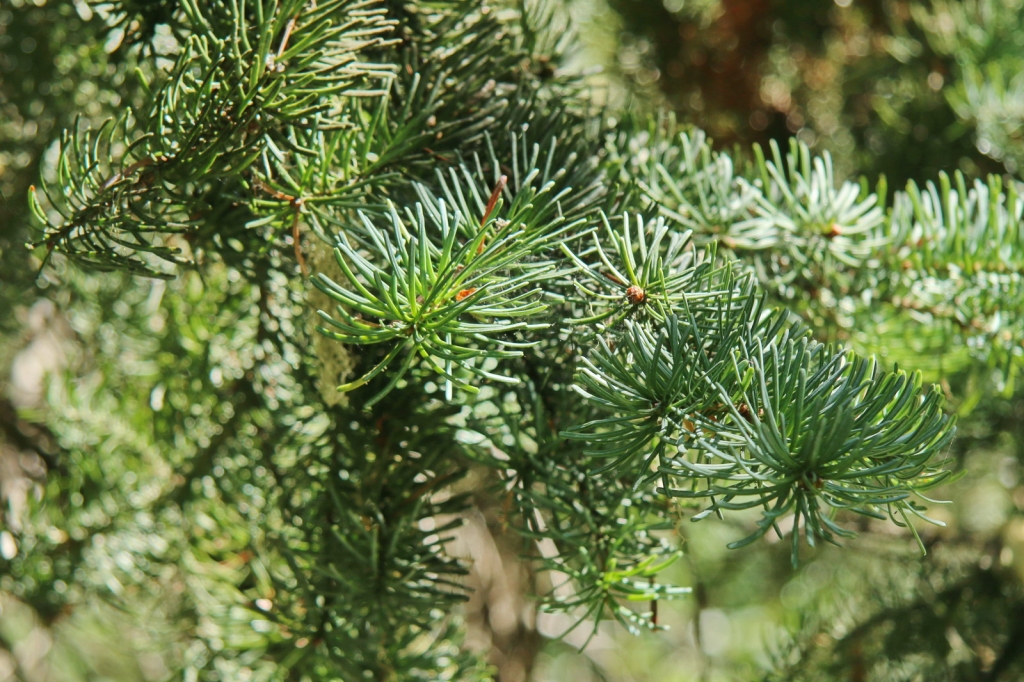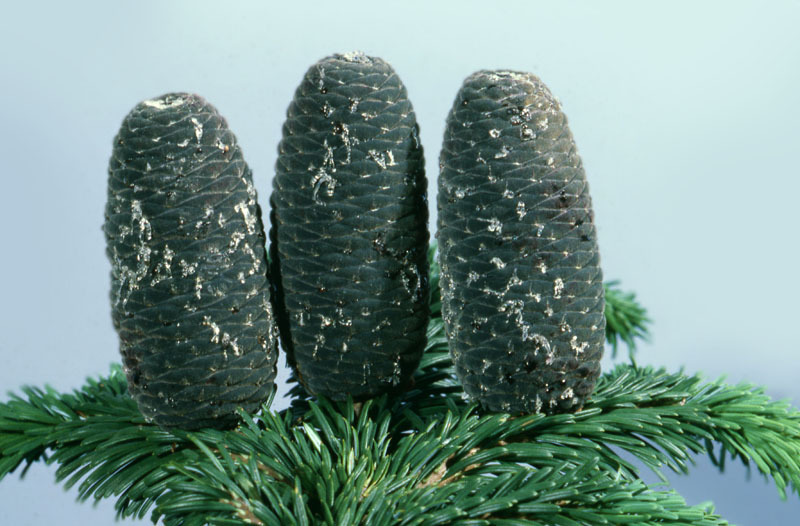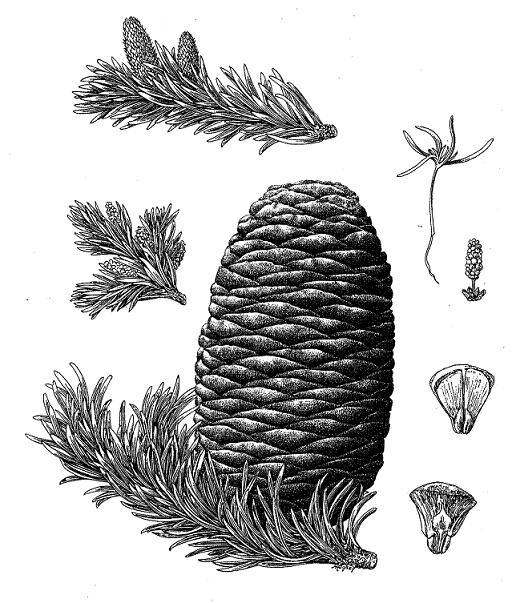
Abies amabilis, as described in 1839 by David Douglas (1798-1834) ex John Forbes (1799-1823), in Pinetum Woburnense, 125th edition, is commonly known as Pacific Silver fir, white fir, red fir, lovely fir, amabilis fir, Cascades fir; as well as sapin gracieux in the French language. In the Latin language, "amabilis" translates into "lovely," well aptly described young trees of this species.
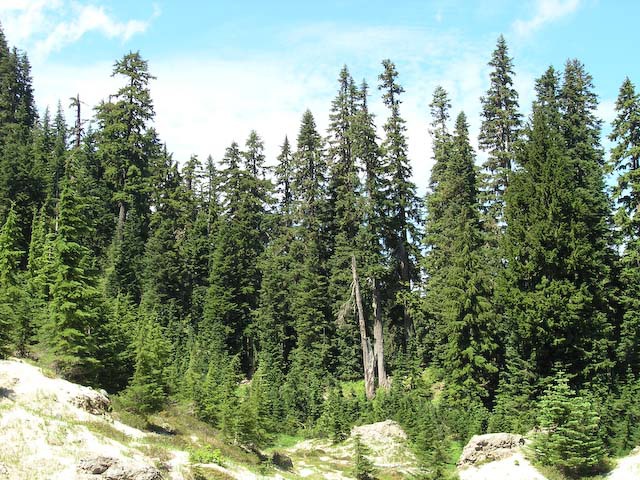
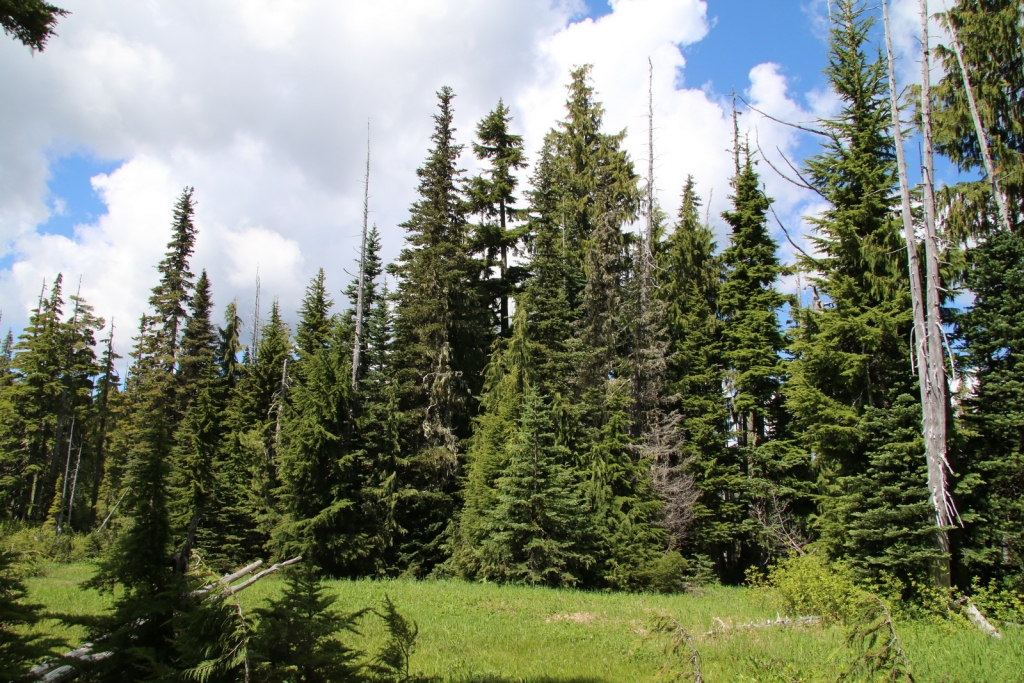
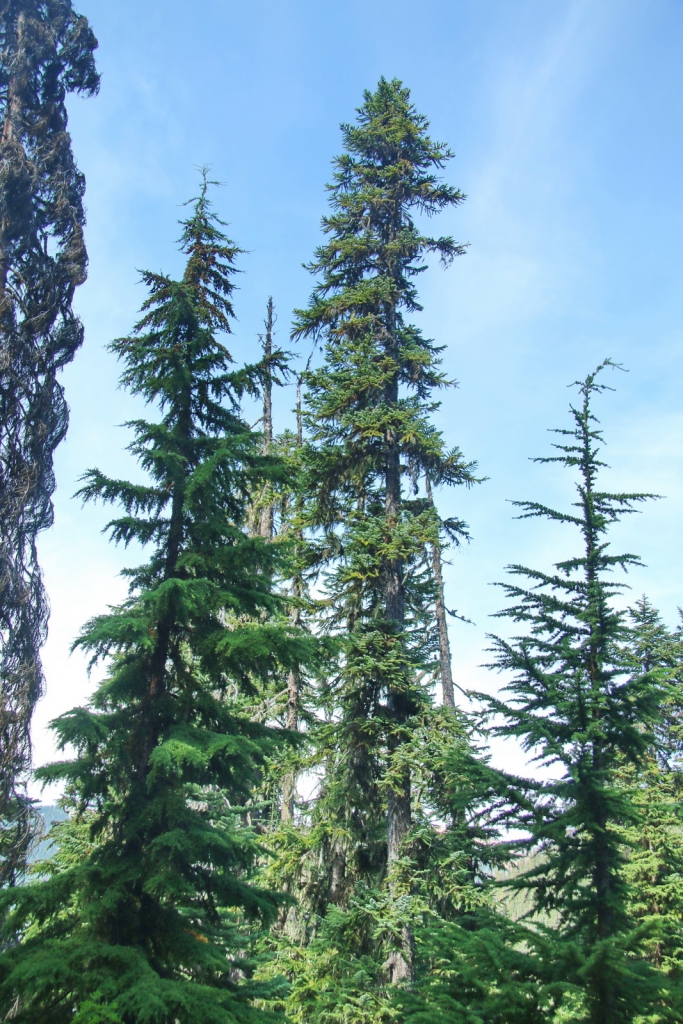
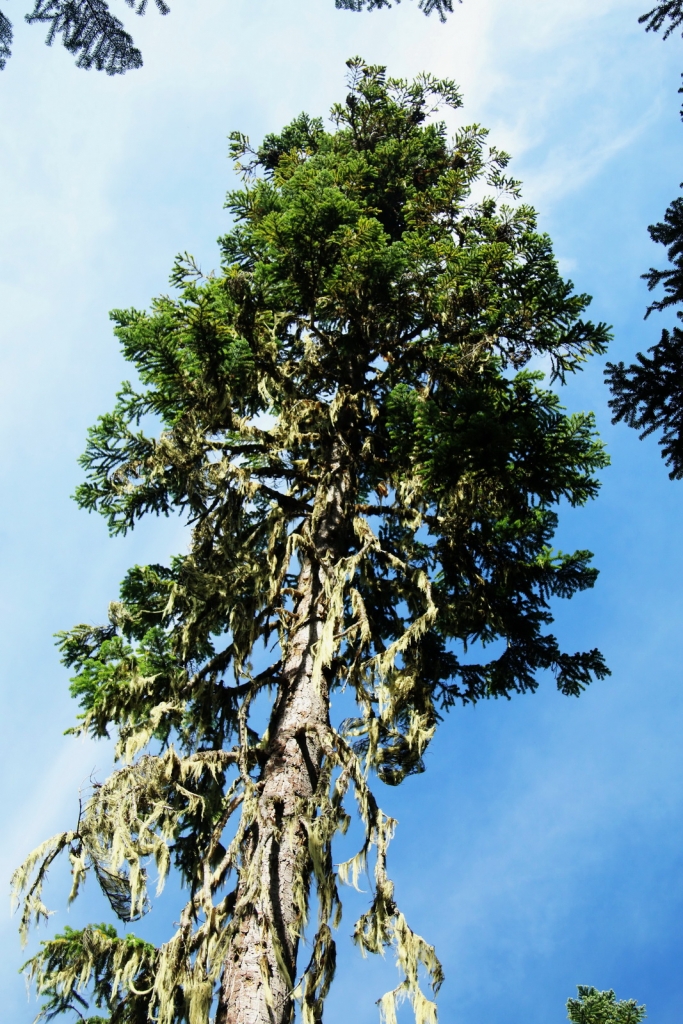
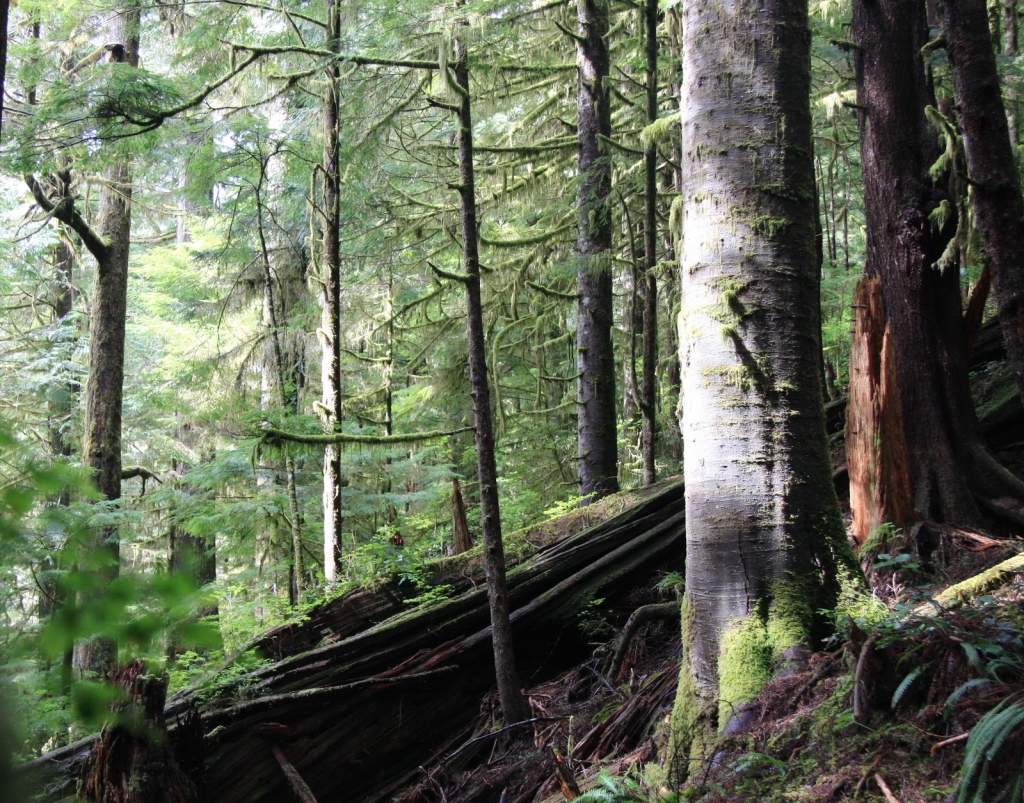
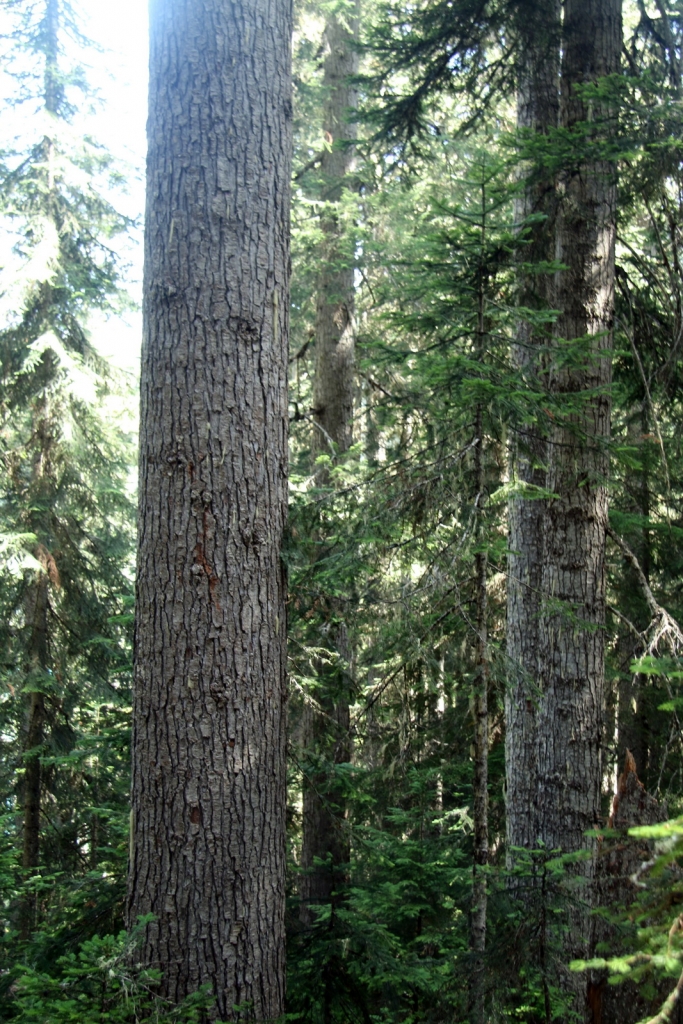
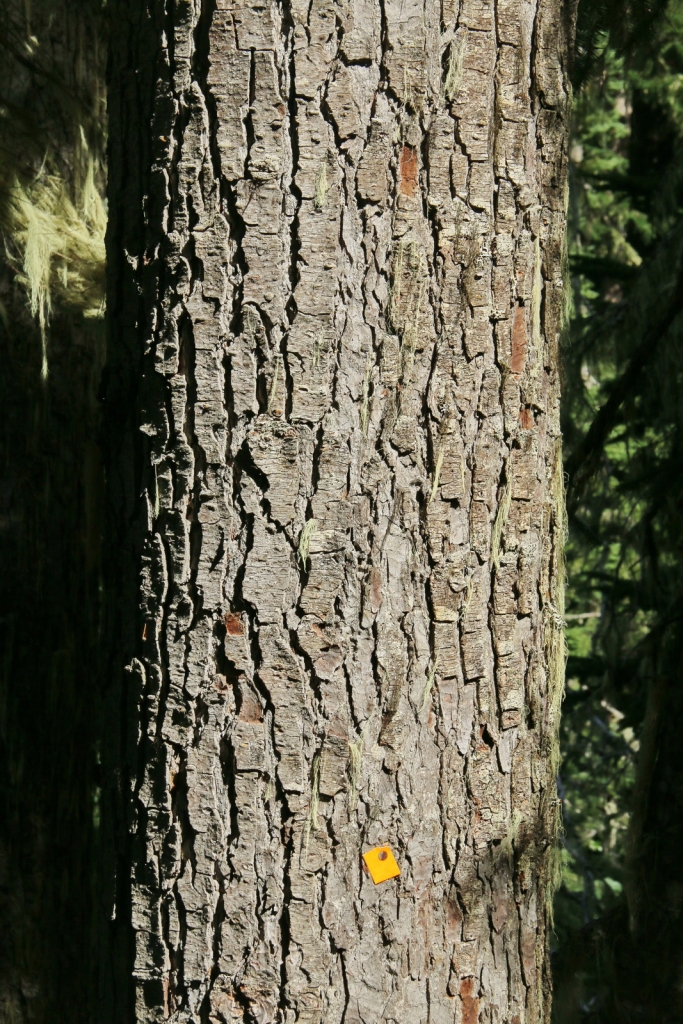
Description. Pacific Silver fir is a large, evergreen, coniferous species of tree which grows to mature heights of 165 to 260 feet (50 - 80 m) tall, with a straight stem, and a globose, conical crown.
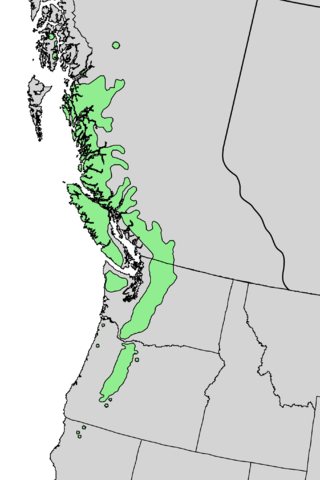
Distribution. This species is native to the US - southeastern Alaska, western Washington and Oregon, and northwestern California. It is also native to Canada - western British Columbia. It grows at altitudes of sea level to 5,000 feet (1,500 m) of elevation in the north of the range, and 3,300 - 7,500 feet (1,000 - 2,300 m) elevation in the south of the range, always in temperate rain forests with relatively high precipitation and cool, humid summers. Common associate trees are Douglas fir.
Hardy to Zone 5 - cold hardiness limit between -20° and -10°F (-28.8°C and -23.3°C).













